jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Ultimate Guide to Hydraulic Pumps for 2026: Types & Trends
A comprehensive guide for 2026 covering hydraulic pump fundamentals, Pascal's Law, types (gear, vane, piston), maintenance, and emerging trends like electrification and IoT.
- What is a Hydraulic Pump? The Heart of Fluid Power Systems
- The Fundamental Working Principle: How Hydraulic Pumps Generate Power
- The Cycle of Flow Generation
- Decoding Hydraulic Pump Classifications: Positive vs. Non-Positive Displacement
- Positive Displacement Pump
- Non-Positive Displacement Pump
- Essential Types of Hydraulic Pumps: A Detailed Overview
- 1. Gear Pumps (External & Internal)
- 2. Vane Pumps
- 3. Piston Pumps (Axial & Radial)
- Specialized Pump Types
- Fixed vs. Variable Displacement Hydraulic Pumps
- Comparing Hydraulic Pump Types
- Hydraulic Pump Applications Across Key Industries
- How to Select the Right Hydraulic Pump for Your System
- Common Hydraulic Pump Problems & Troubleshooting Guide
- Maximizing Lifespan: Best Practices for Hydraulic Pump Maintenance
- The Future of Hydraulic Pumps: Innovations and Emerging Trends
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the primary function of a hydraulic pump?
- What are the three most common types of hydraulic pumps?
- Do hydraulic pumps create pressure?
- What is the difference between fixed and variable displacement pumps?
- What kind of maintenance do hydraulic pumps require?
- What are common signs of a failing hydraulic pump?
- How important is hydraulic fluid cleanliness for pump life?
- Can hydraulic pumps be integrated with smart technology?
- References
What is a Hydraulic Pump? The Heart of Fluid Power Systems
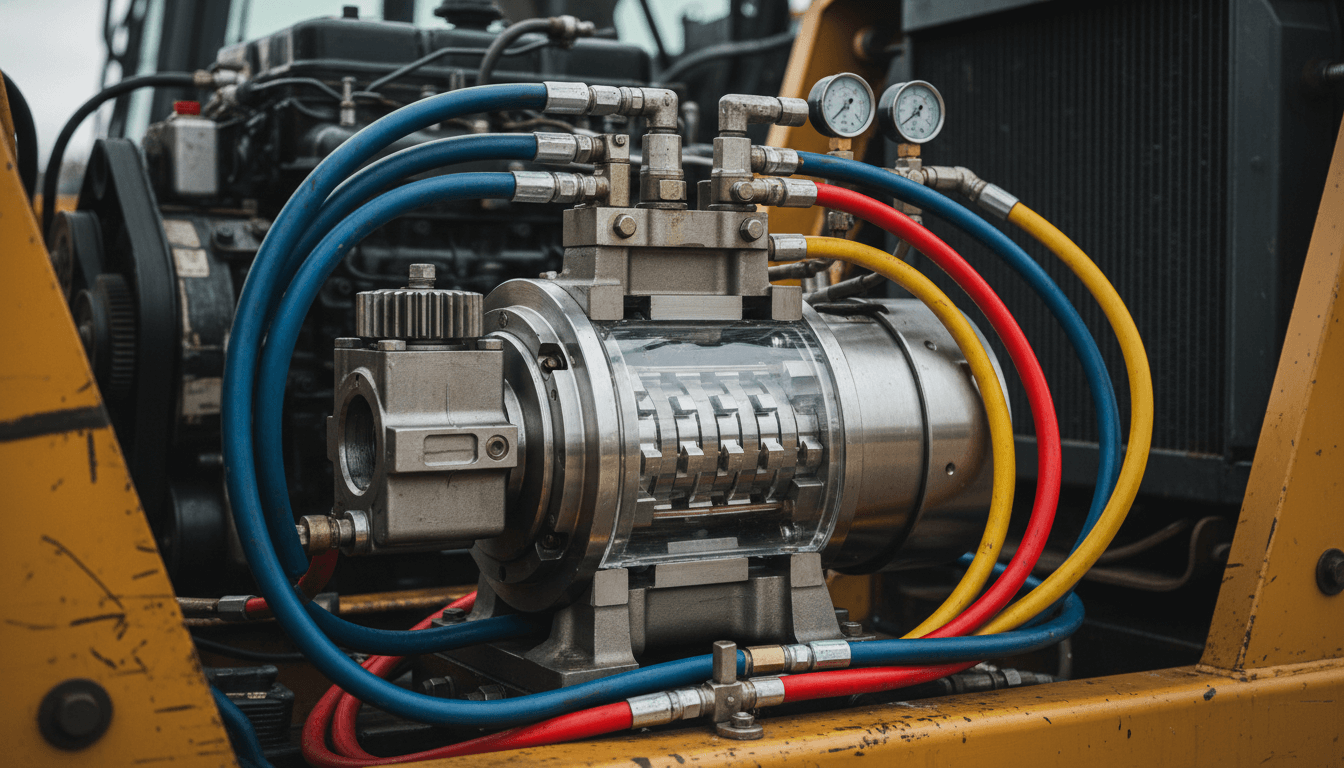
A hydraulic pump is the powerhouse of any hydraulic system, responsible for converting mechanical energy from a prime mover (such as an electric motor or internal combustion engine) into hydraulic energy. This energy manifests as fluid flow, which is then used to generate pressure when it meets resistance. As one of the most critical hydraulic system components, the pump essentially dictates the performance and efficiency of the entire machine.
Contrary to common belief, a pump does not create pressure directly; it creates flow. Pressure is only developed when the fluid flow meets resistance from the load or system components. For those seeking a fundamental understanding of these mechanisms, our guide on What Is a Hydraulic Pump offers an excellent starting point. Whether you are engineering complex industrial machinery or sourcing parts of excavator systems, understanding the pump's role is paramount.
The Fundamental Working Principle: How Hydraulic Pumps Generate Power
The operation of all hydraulic pumps relies on the creation of a vacuum at the pump inlet. This vacuum allows atmospheric pressure to force liquid from the reservoir into the inlet line. Once the fluid enters the pump, it is mechanically pushed into the hydraulic system. This process is deeply rooted in Pascal's Law, which states that a change in pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to all portions of the fluid and to the walls of its container, as explained by NASA's educational resources on fluid dynamics.
The Cycle of Flow Generation
1. Vacuum Creation: Mechanical action creates a low-pressure area at the inlet.
2. Fluid Ingress: Atmospheric pressure pushes fluid into the pump.
3. Displacement: The internal mechanism (gears, vanes, or pistons) traps the fluid.
4. Flow Generation: The fluid is forced out into the discharge port.
Decoding Hydraulic Pump Classifications: Positive vs. Non-Positive Displacement
When categorizing hydraulics pumps, the most significant distinction lies between positive and non-positive displacement designs.
Positive Displacement Pump
A positive displacement pump delivers a fixed volume of fluid for every cycle of operation, regardless of the system pressure (within design limits). According to Global Pumps, this characteristic makes them the standard for high-pressure hydraulic applications. They create a seal between the inlet and outlet, preventing fluid slippage. This category includes the vast majority of pumps used in heavy machinery, such as the main pump in an excavator or a hydraulic pump motor in industrial presses.
Non-Positive Displacement Pump
These pumps, such as centrifugal pumps, produce a continuous flow where the output volume changes significantly with pressure. They are generally unsuitable for high-pressure fluid power applications but are excellent for low-pressure fluid transfer.
Essential Types of Hydraulic Pumps: A Detailed Overview
1. Gear Pumps (External & Internal)
Gear pumps are the workhorses of the industry—simple, economical, and robust. They operate by trapping fluid between the teeth of rotating gears.
· Best for: Medium pressure applications (up to 250 bar) and systems where cost is a primary driver.
· Common Use: Mobile hydraulics and lubrication pumps.
2. Vane Pumps
Vane pumps utilize sliding vanes that extend and retract against a cam ring. Balanced vane pumps are known for their quiet operation and high efficiency in medium-pressure ranges.
· Best for: Indoor industrial applications (injection molding) where noise reduction is critical.
· Note: They are less tolerant of contamination than gear pumps.
3. Piston Pumps (Axial & Radial)
For high-pressure, high-efficiency requirements, piston pumps are the gold standard. They can be fixed or variable displacement. In variable displacement models, the flow rate can be adjusted without changing the input speed, a feature critical for energy efficiency in modern machinery.
· Best for: High-pressure mobile and industrial applications, such as the main hydraulic system in cranes and excavators.
Specialized Pump Types
· Hydraulic Ram Pump: A cyclic water pump powered by hydropower. While less common in oil hydraulics, it remains a vital technology for water management.
· Electric Hydraulic Pump: These units combine an electric motor with a pump, often used in stationary industrial tools or as compact 12v hydraulic pump power packs for mobile applications like dump trailers.
· Hand Pumps: Simple, manually operated pumps for backup or testing purposes.
Fixed vs. Variable Displacement Hydraulic Pumps
Choosing between fixed and variable displacement is a decision between cost and control.
· Fixed Displacement: The flow rate is constant per revolution. To change the speed of the actuator, you must change the pump speed or use a flow control valve (which generates heat). These are common in simpler excavator parts and auxiliary circuits.
· Variable Displacement: The internal geometry (e.g., swashplate angle) can be altered to change the flow rate. This allows for precise control and significant energy savings, as the pump only delivers the flow required by the load.
Comparing Hydraulic Pump Types
|
Feature |
Gear Pump |
Vane Pump |
Piston Pump |
|
Pressure Range |
Low to Medium (up to 250 bar) |
Medium (up to 175-200 bar) |
High (up to 400+ bar) |
|
Efficiency |
75-85% |
80-90% |
90-95% |
|
Noise Level |
Moderate to High |
Low |
Moderate |
|
Cost |
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
Sensitivity to Contamination |
Low (Rugged) |
High |
Medium |
Hydraulic Pump Applications Across Key Industries
Hydraulic pumps drive the world's heavy machinery.
· Construction: In an excavator, the main pump is the heart of the machine. Sourcing high-quality excavator parts often involves finding compatible piston pumps that can withstand extreme duty cycles. Whether it's a hydraulic hydraulic pump system (a redundancy often seen in legacy cataloging) or a modern load-sensing unit, reliability is key.
· Automotive: Electric hydraulic pressure pump units are increasingly used in power steering and braking assist systems.
· Material Handling: Forklifts and telehandlers rely on gear pumps for lifting and steering.
· Industrial: Hydraulic presses and injection molding machines utilize high-performance vane and piston pumps for precise cycle control.
How to Select the Right Hydraulic Pump for Your System
Selection goes beyond just flow (GPM) and pressure (PSI). Engineers must consider:
1. Fluid Viscosity: Ensure the pump can handle the fluid's viscosity range, especially in extreme temperatures.
2. Drive Speed: Match the pump's RPM rating with the prime mover (e.g., electric motor or diesel engine).
3. Control Type: Do you need load sensing, pressure compensation, or simple fixed flow?
4. Efficiency Targets: For continuous duty applications, the higher initial cost of a piston pump is often offset by energy savings.
Common Hydraulic Pump Problems & Troubleshooting Guide
Even the best pumps fail. Effective hydraulic pump repair starts with accurate diagnosis. According to Miller Hydraulic and other industry experts, the most common failure modes include:
· Cavitation: Occurs when the pump cannot draw in enough fluid, leading to the formation and implosion of vapor bubbles. This sounds like marbles rattling inside the pump and causes severe internal damage.
· Aeration: Air enters the inlet stream, causing a whining noise and spongy actuator movement.
· Contamination: The number one killer of hydraulic components. Particle contamination causes abrasive wear on valve plates and pistons.
· Overheating: Often caused by internal leakage (slippage) or a blocked cooler, leading to fluid degradation.
Maximizing Lifespan: Best Practices for Hydraulic Pump Maintenance
To avoid frequent replacements of parts of excavator or industrial pumps:
· Monitor Fluid Cleanliness: Adhere to ISO 4406 cleanliness codes. Use high-efficiency filtration.
· Regular Inspections: Check for external leaks and unusual noises daily.
· Start-up Procedures: Never start a pump dry. Ensure the case is filled with fluid (if required) to prevent instant failure.
The Future of Hydraulic Pumps: Innovations and Emerging Trends
As we look toward 2026, the industry is shifting toward electrification and intelligence. The integration of IoT sensors allows for predictive maintenance, where the pump itself warns the operator before failure.
For a deep dive into what lies ahead, read our forecast on hydraulic pumps 2026. We are seeing a rise in "digital hydraulics" and variable speed drives that couple electric motors directly with pumps for on-demand power. The market for electric hydraulic pump systems is expanding rapidly, moving from small auxiliary units to primary power sources in off-highway equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of a hydraulic pump?
A hydraulic pump converts mechanical power (from an engine or motor) into hydraulic energy, primarily in the form of fluid flow. It creates a vacuum at the inlet to draw fluid from a reservoir and then displaces that fluid into the hydraulic system, generating flow against resistance.
What are the three most common types of hydraulic pumps?
The three most common types are gear pumps, vane pumps, and piston pumps. Each type has distinct characteristics regarding pressure capability, efficiency, noise levels, and ideal applications.
Do hydraulic pumps create pressure?
No, hydraulic pumps primarily create flow; pressure is generated by the resistance to that flow within the hydraulic system. The pump pushes fluid, and when that fluid encounters resistance (like an actuator moving a load), pressure builds up.
What is the difference between fixed and variable displacement pumps?
A fixed displacement pump delivers a constant volume of fluid per revolution, regardless of system pressure. A variable displacement pump can adjust the volume of fluid delivered per revolution, allowing for precise control and improved energy efficiency.
What kind of maintenance do hydraulic pumps require?
Regular maintenance includes monitoring hydraulic fluid cleanliness and quality, checking for leaks, inspecting components for wear, and ensuring proper system alignment. Preventative measures like timely fluid changes and filter replacements are crucial for extending pump lifespan.
What are common signs of a failing hydraulic pump?
Common signs include unusual noises (whining, grinding), loss of system pressure or slow operation, excessive heat generation, and visible fluid leaks. Reduced efficiency and inconsistent performance can also indicate a failing pump.
How important is hydraulic fluid cleanliness for pump life?
Hydraulic fluid cleanliness is extremely important as contamination is a leading cause of pump wear and failure. Particles in the fluid can cause abrasive wear to internal pump components, seals, and bearings, significantly reducing lifespan and efficiency.
Can hydraulic pumps be integrated with smart technology?
Yes, modern hydraulic pumps are increasingly integrated with smart technologies, including sensors for pressure, temperature, and flow. This allows for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and connectivity with IoT platforms for enhanced control and operational insights.
References





FAQ
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.
Do you provide warranties on your products?
Yes, we stand by the quality of our products. Most parts come with a warranty that covers manufacturing defects. Please refer to the specific warranty information provided with your purchase or contact our customer service team for details.

The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -

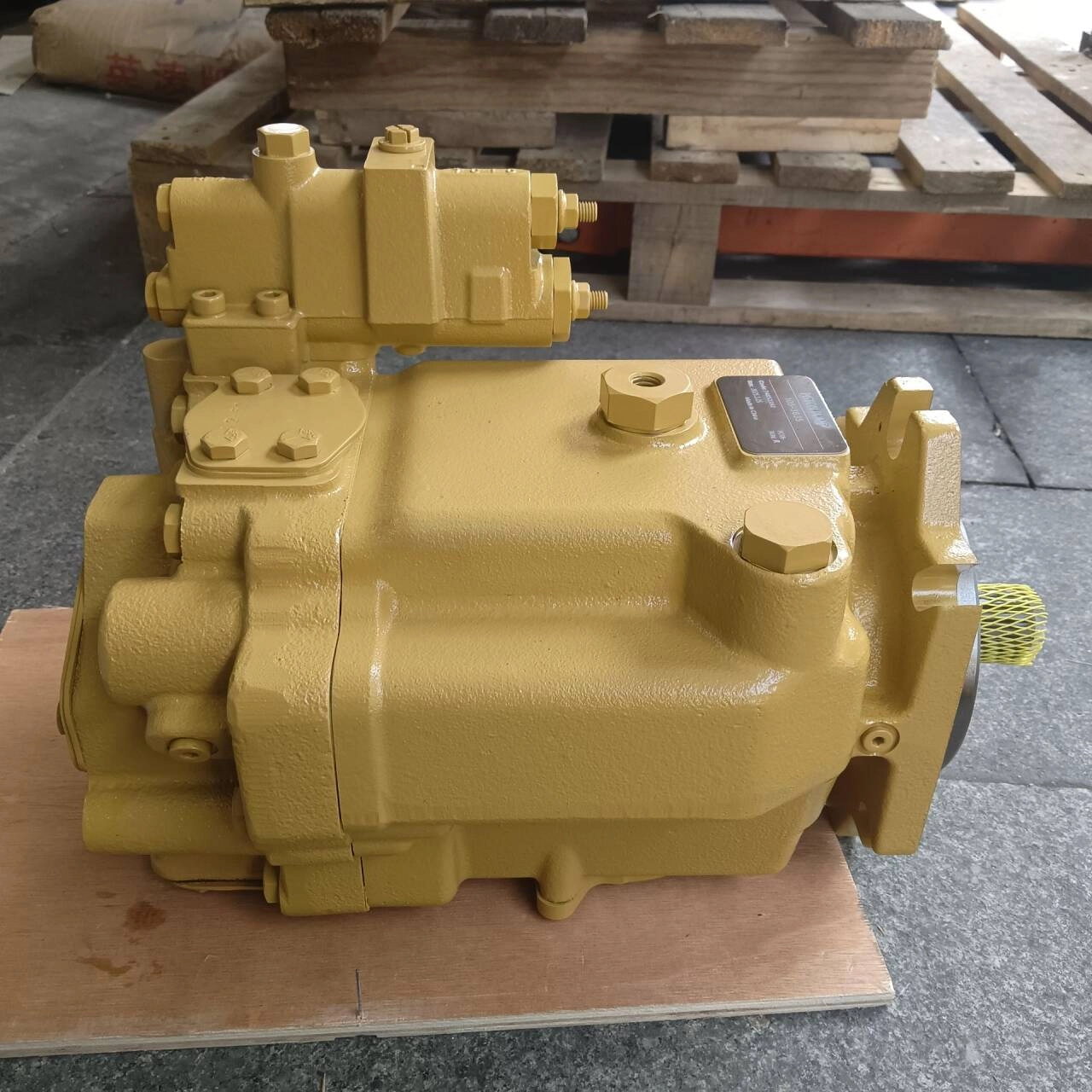
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
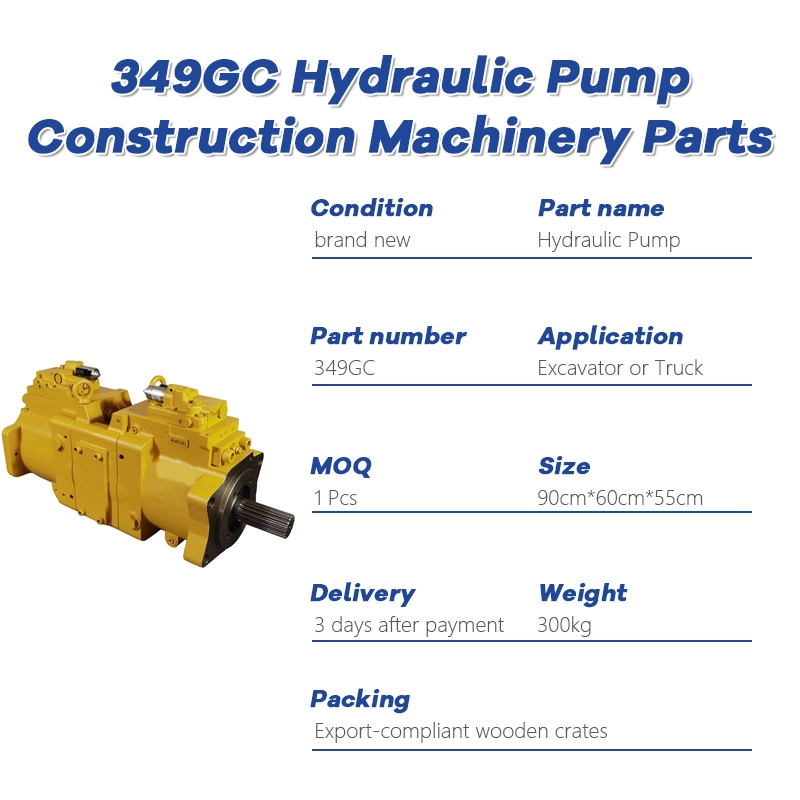
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-