jackhuang5919@gmail.com
How to Rebuild an Excavator Hydraulic Pump: Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Rebuild an Excavator Hydraulic Pump: Step-by-Step Guide
- Introduction: Why you might rebuild an excavator hydraulic pump
- Understand common pump types before you rebuild
- Pump type comparison: characteristics and typical use
- Diagnose the hydraulic pump problem before rebuilding
- Required tools and parts for a successful pump rebuild
- Safety and preparation before you start the rebuild
- Removal: How to remove the pump from the excavator safely
- Teardown: Systematic disassembly and contamination control
- Inspect components and identify replaceable wear items
- Cleaning and parts replacement: best practices for durability
- Reassembly: alignment, torque and critical clearances
- Bench testing: how to test rebuilt pumps before reinstallation
- Reinstallation and field testing to confirm success
- Cost and time estimates for a typical pump rebuild
- When to rebuild versus when to replace the pump
- Why source parts from Weihuparts for your hydraulic pump rebuild
- Conclusion: Rebuilds save cost when done right
- Common symptoms that indicate immediate attention
How to Rebuild an Excavator Hydraulic Pump: Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction: Why you might rebuild an excavator hydraulic pump
Rebuilding a hydraulic pump is a cost-effective option when symptoms include reduced flow, intermittent operation, cavitation noise or internal leakage. For owners and workshops looking to buy replacement parts or save on downtime, knowing how to rebuild an excavator hydraulic pump correctly reduces repair costs and returns machine performance faster than waiting for a full exchange unit.
Understand common pump types before you rebuild
Excavator hydraulic pumps are typically axial piston pumps (swashplate), gear pumps, or vane pumps. Each type has distinct wear patterns and rebuild requirements, so identifying the pump type is the first step before you buy a hydraulic pump rebuild kit or specific Weihuparts components.
Pump type comparison: characteristics and typical use
Below is a concise comparison to help decide how to approach rebuilds and parts selection.
| Pump Type | Typical Operating Pressure | Strengths | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Axial piston (swashplate) | Up to ~3,000–4,500 psi (≈200–310 bar) | High efficiency, variable displacement, high pressure | Medium/large excavators, main pumps |
| Gear | Up to ~1,500–3,000 psi (≈100–200 bar) | Simple, low-cost, robust for lower pressure | Auxiliary circuits, older/smaller machines |
| Vane | Up to ~2,000–3,500 psi (≈140–240 bar) | Smoother flow, mid-range pressures, compact | Some mid-size excavators and auxiliary pumps |
Diagnose the hydraulic pump problem before rebuilding
Accurate diagnosis prevents unnecessary rebuilds. Check system pressure with a calibrated gauge, listen for cavitation (metallic sucking sounds), inspect fluid for metal particles, and observe pump flow and temperature. Low pressure with intact drive components often indicates internal wear—an ideal candidate for rebuild rather than replacement.
Required tools and parts for a successful pump rebuild
Typical tools include torque wrenches, micrometers/feeler gauges, pullers, soft-faced hammers, bench vise, ultrasonic cleaner or solvent, and a test bench for flow/pressure checks. Parts generally required are seal kits, thrust plates, piston/roller kits, springs, bearings and O-rings. Commercially available hydraulic pump rebuild kits from suppliers like Weihuparts include matched seals and wear parts to ensure reliability.
Safety and preparation before you start the rebuild
Work in a clean, well-lit area and depressurize the hydraulic system completely. Wear gloves and eye protection, and keep a clean parts tray to avoid contamination. Mark pump orientation and connections before removal to preserve system settings and avoid leaks after reassembly.
Removal: How to remove the pump from the excavator safely
Isolate the pump by shutting off the engine and relieving hydraulic pressure. Drain hydraulic oil into a clean container for inspection. Disconnect hoses with caps to prevent contamination, unbolt the pump from the drive flange, and support the weight to avoid damage. Note orientation and any shims for correct reinstallation.
Teardown: Systematic disassembly and contamination control
Work on a clean bench and photograph each step. Remove covers, drive shafts, and housing components in sequence. Use soft tools for delicate parts. Keep components separated and labeled to simplify reassembly. Clean parts in solvent or an ultrasonic cleaner—never introduce debris into the hydraulic circuit.
Inspect components and identify replaceable wear items
Inspect pistons, cylinders, swash plates, bushings and bearings for scoring, pitting or out-of-round conditions. Measure clearances against manufacturer tolerances; replace any part that exceeds wear limits. Seals and O-rings should be replaced in all rebuilds to prevent future leakage.
Cleaning and parts replacement: best practices for durability
Thorough cleaning removes abrasive particles that cause premature wear. Replace all soft parts (seals, O-rings) and any hard parts beyond tolerance. Use Weihuparts OEM-quality rebuild kits to ensure material compatibility and dimensional accuracy. Lubricate moving parts with clean hydraulic oil during assembly to prevent dry starts.
Reassembly: alignment, torque and critical clearances
Reassemble in the reverse order, keeping components clean and dry. Apply specified torque values to bolts and set correct shim or plate clearances. Incorrect torque or misalignment can produce noise, high internal leakage, or early failure—use manufacturer torque charts where available and record values for quality control.
Bench testing: how to test rebuilt pumps before reinstallation
Using a hydraulic test bench, check flow capacity at no-load and load conditions, verify pressure capability up to the system maximum, and inspect for internal leakage. Bench testing prevents machine downtime due to pump-related failures after reinstallation. Acceptable leakage and flow thresholds depend on pump model—refer to the pump specification sheet.
Reinstallation and field testing to confirm success
Reinstall the pump observing original orientation and torque specs. Refill the hydraulic reservoir with the correct oil grade and a clean filter. Start the machine at low idle to purge air and monitor for leaks, temperature rise, and correct function under light loads before full operational testing.
Cost and time estimates for a typical pump rebuild
Costs and labor vary by pump type and damage level. Typical rebuild kit parts cost can range from about $100 to $800 for common models; full component replacement or precision machining increases cost. Workshop labor is often 2–8 hours depending on complexity. Compare rebuild costs to exchange pump prices—replacement assemblies can run from several hundred to several thousand dollars for main pumps.
When to rebuild versus when to replace the pump
Rebuild when wear is localized and the pump housing and critical machined surfaces are within tolerance. Replace when the housing is cracked, shaft journals are severely scored, or when repair costs approach the price of a reman/exchange unit. Remanufactured or new pumps can be preferable for very high-hour excavators or critical uptime needs.
Why source parts from Weihuparts for your hydraulic pump rebuild
Weihuparts supplies a wide range of excavator spare parts, including hydraulic pump rebuild kits and components, focused on quality, timely delivery and cost-effectiveness. Their engineering team emphasizes durable, industry-standard components to help workshops complete reliable rebuilds and keep machinery running smoothly.
Conclusion: Rebuilds save cost when done right
How to rebuild an excavator hydraulic pump comes down to correct diagnosis, clean workmanship, proper parts and thorough testing. With the right tools, OEM-quality rebuild kits from suppliers like Weihuparts, and disciplined bench testing, a rebuild can restore pump performance and extend service life without excessive cost. Always follow safety procedures and manufacturer's specifications for best results.
Common symptoms that indicate immediate attention
Look for reduced digging power, slow or jerky actuator movement, excessive reservoir foaming, overheating or visible oil contamination. Addressing these signs early reduces the likelihood of catastrophic pump failure and more expensive repairs.

Fuel Efficiency Insights for ZAX870-5G 6WG1 Diesel Engine
Excavator Engine Replacement: When and How
Signs of Hydraulic Pump Failure Under Load: Detection, Diagnosis & Fixes
Top mini excavator parts Manufacturers and Suppliers in China
FAQ
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.
How can I place an order?
You can place an order through our user-friendly online platform or by contacting our sales team directly. Simply browse our catalog, select the parts you need, and follow the checkout process to complete your order.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
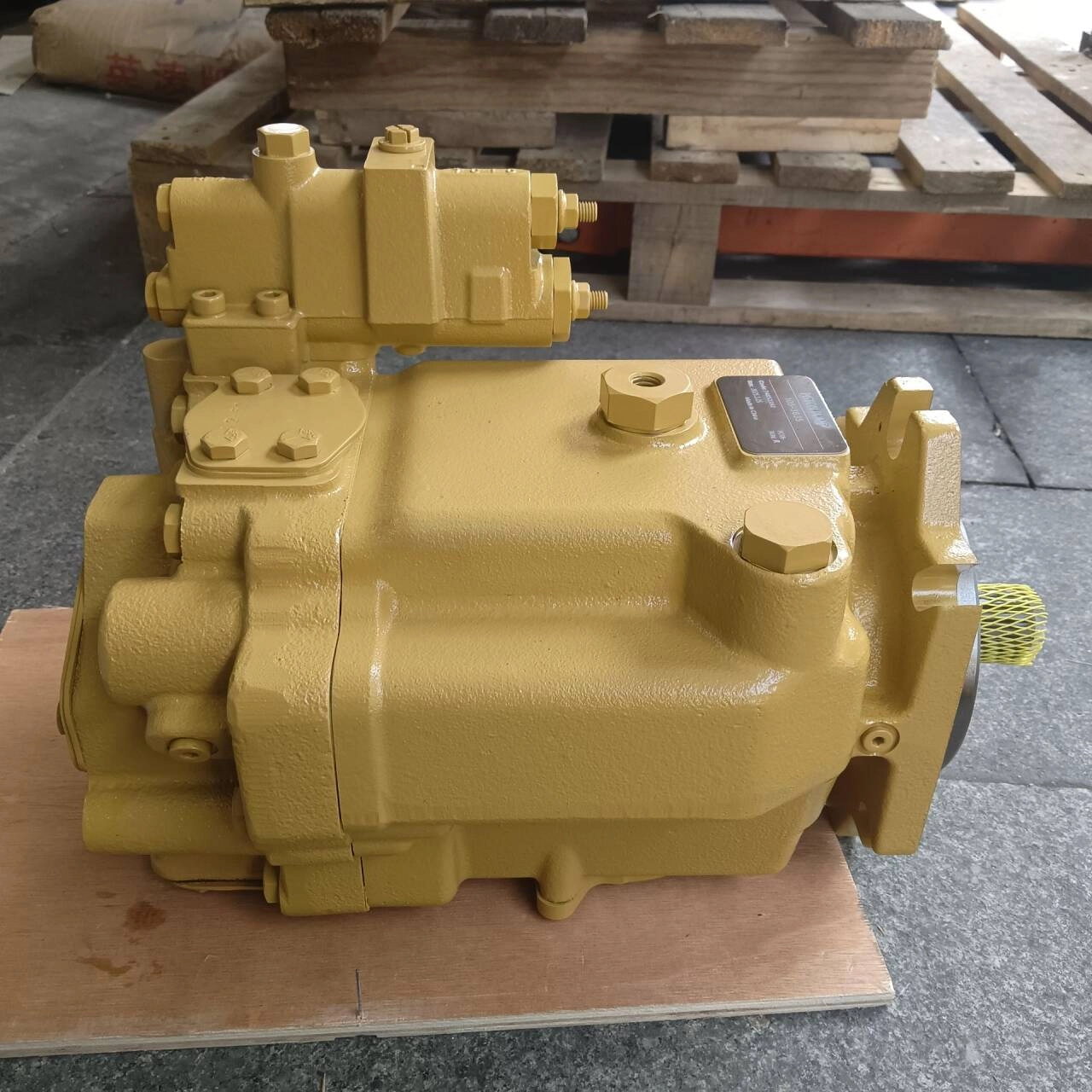

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
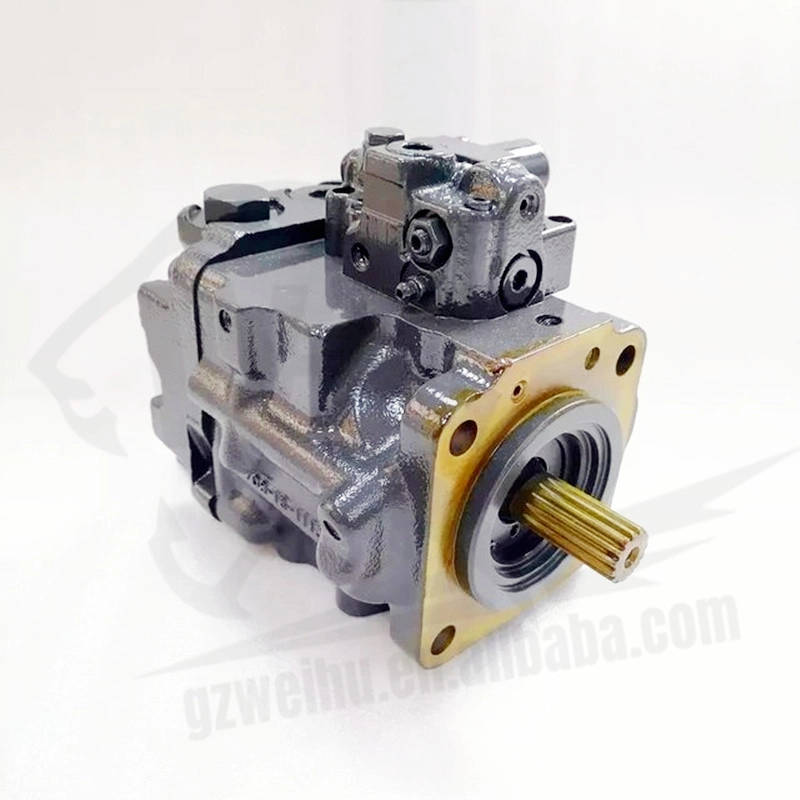

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
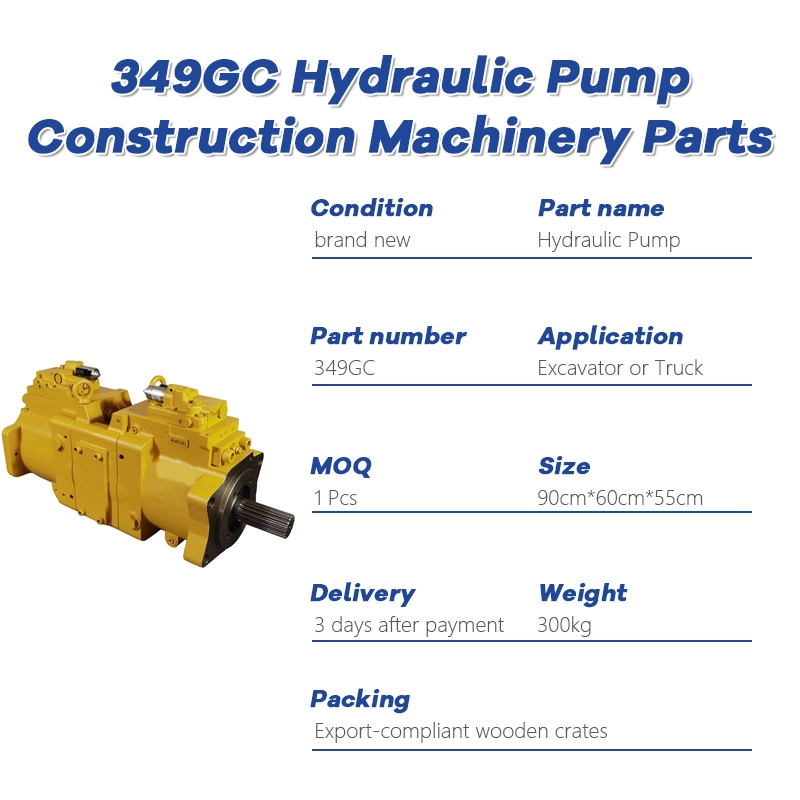
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

