jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Signs of Hydraulic Pump Failure Under Load: Detection, Diagnosis & Fixes
- Introduction: Why recognizing Signs of Hydraulic Pump Failure Under Load matters
- Quick context
- Top signs of hydraulic pump failure under load
- 1. Loss of pressure or weak hydraulic performance
- 2. Loud or unusual noises (whine, rattle, knock)
- 3. Overheating of hydraulic fluid or components
- 4. Fluid foaming, aeration, or cavitation signs
- 5. Visible contamination or metal particles in fluid
- 6. Intermittent or pulsating output under load
- 7. External leaks or steam near the pump
- Why hydraulic pumps fail under load
- Common root causes
- Environmental and operational contributors
- How to diagnose hydraulic pump failure under load
- Step-by-step on-site checks
- Tools and tests to prioritize
- Signs vs likely causes vs immediate actions (comparison)
- Repair, replacement, and parts considerations
- When to repair vs replace
- Choose quality replacement parts
- On-the-job fixes and temporary measures
- Short-term steps to keep operating safely
- Preventive maintenance to avoid pump failure under load
- Routine checks and service items
- Condition monitoring and predictive maintenance
- Conclusion: Act early to avoid costly failures
- Final recommendations
- About Weihuparts
- Who we are
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction: Why recognizing Signs of Hydraulic Pump Failure Under Load matters
Quick context
Hydraulic pumps are the heart of excavator systems. When a pump starts to fail under load, operational safety, productivity, and repair costs can all be affected. This guide explains common signs of hydraulic pump failure under load, how to diagnose the root causes, immediate actions to take, and best practices to prevent recurrence — all with practical, user-focused advice you can apply on-site.
Top signs of hydraulic pump failure under load
1. Loss of pressure or weak hydraulic performance
One of the clearest signs of hydraulic pump failure under load is a sudden or progressive drop in system pressure or slow/weak actuator movement when the machine is working. If the pump cannot maintain rated pressure under load, boom speed, lifting capacity, or digging force will be reduced.
2. Loud or unusual noises (whine, rattle, knock)
Unusual noises under load — such as whining, grinding, or knocking — often indicate internal wear, cavitation, or air ingestion. Noise that appears or becomes louder only when the system is under load commonly points to a pump struggling to deliver required flow or ingesting air.
3. Overheating of hydraulic fluid or components
Persistent high fluid temperature during heavy work can result from inefficient pump compression, internal leakage, or contaminated fluid. Overheating reduces component life and can cause seals and hoses to fail.
4. Fluid foaming, aeration, or cavitation signs
Foamy fluid, bubbles in the reservoir, or a sputtering actuator often mean cavitation or air has entered the system. Cavitation under load damages pump surfaces quickly and reduces effective flow.
5. Visible contamination or metal particles in fluid
Finding metal shavings or excessive contamination during fluid checks is a major red flag. It often indicates internal wear of gears, pistons, or bearings while the pump is loaded.
6. Intermittent or pulsating output under load
Pulsation, surging, or intermittent pressure commonly result from damaged internal components, worn valves, or broken pump elements that fail under higher load demands.
7. External leaks or steam near the pump
Leaking seals or fittings that appear under load (but not at idle) point to rising internal pressure, thermal expansion, or seal degradation. Steam or mist near the pump signals overheating and requires immediate shutdown.
Why hydraulic pumps fail under load
Common root causes
Pumps fail under load for several predictable reasons: internal wear (bearings, pistons, gears), contamination, cavitation, poor lubrication, incorrect fluid viscosity, relief valve misadjustment, or mechanical drive problems (belt, coupling, shaft misalignment). Operating outside manufacturer-specified pressure/temperature limits accelerates failure.
Environmental and operational contributors
High dust, poor filtration, incorrect fluid change intervals, repeated shock loads, and extended high-temperature operation all increase the probability of pump failure when the system is put under heavy load.
How to diagnose hydraulic pump failure under load
Step-by-step on-site checks
Follow a structured diagnostic approach to find the real issue without guessing:
- Check hydraulic fluid level and condition (color, smell, presence of foam, visible particles).
- Listen for noises while operating under load and try to localize the source (pump, motor, valves).
- Measure system pressure under load and at idle using a calibrated gauge. Note differences between no-load and loaded pressure.
- Inspect suction hoses, filters, and fittings for leaks, collapsing hoses, or loose connections that can cause air ingestion or reduced suction.
- Monitor fluid temperature, and compare against manufacturer limits (many systems operate safely up to 80–90°C, but always follow OEM specs).
- Collect a fluid sample for particle analysis if metal contamination is suspected.
Tools and tests to prioritize
Essential diagnostic tools: pressure gauges, flow meters (if available), infrared thermometer, stethoscope or ultrasonic leak detector, and a particle-counting test kit. A bench test or swap test with a known-good pump is often the most conclusive method when on-site checks are inconclusive.
Signs vs likely causes vs immediate actions (comparison)
| Observed Sign | Likely Cause | Immediate Action |
|---|---|---|
| Loss of pressure under load | Internal leakage, worn pump, relief valve set low | Check pressure gauge, test relief valve, inspect for internal wear |
| Loud whining only when loaded | Cavitation or air ingestion, bearing wear | Inspect suction line & filter, check reservoir level, reduce load |
| Overheating fluid | Poor cooling, excessive internal pump friction, wrong fluid | Stop work, let system cool, verify cooler and fluid specs |
| Metal particles in fluid | Internal component wear or fatigue | Collect sample, plan pump replacement, avoid further operation |
Repair, replacement, and parts considerations
When to repair vs replace
Minor wear, seal failures, or isolated component damage can often be repaired. However, when inspection or fluid analysis shows significant metal contamination or major internal scoring, replacement is usually the most cost-effective and reliable option — especially for high-load or safety-critical machines.
Choose quality replacement parts
Using quality OEM or high-spec aftermarket components reduces repeat failures. Weihuparts offers a wide range of excavator pump components and full pumps designed to meet operational demands with quality control, timely delivery, and technical support to help minimize downtime.
On-the-job fixes and temporary measures
Short-term steps to keep operating safely
If immediate replacement isn’t possible, take temporary steps: reduce load and cycle time, avoid extreme operating conditions, ensure fluid level is correct, change a clogged suction/return filter, and keep an eye on temperature and pressure. These measures can buy time but are not long-term solutions.
Preventive maintenance to avoid pump failure under load
Routine checks and service items
Maintain a preventive schedule: regular fluid changes with proper viscosity and cleanliness ratings, timely filter replacements, scheduled inspections for leaks and noises, vibration monitoring, and keeping the cooling system clean. Implementing a simple checklist that includes pressure and temperature logging under typical loads can detect degradation early.
Condition monitoring and predictive maintenance
Adopt fluid analysis (particle counts, ferrous wear testing), vibration analysis, and periodic pressure/flow testing. Predictive maintenance is often cheaper than unexpected downtime and extends pump life.
Conclusion: Act early to avoid costly failures
Final recommendations
Recognizing signs of hydraulic pump failure under load — like pressure loss, unusual noises, overheating, cavitation, or contamination — enables faster diagnosis and better decisions about repair or replacement. Use structured checks, proper tools, and quality replacement parts. If you rely on excavators for critical work, partner with a parts supplier like Weihuparts to ensure access to reliable components and technical support that help keep your machines productive and safe.
About Weihuparts
Who we are
Weihuparts serves as a reliable partner for global clients in the excavator spare parts sector. We provide a comprehensive selection of excavator parts designed to support a variety of operational needs, whether for routine tasks or high-performance excavator systems. With a focus on quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery, Weihuparts is dedicated to supporting businesses by ensuring the availability of essential parts to keep machinery running smoothly. Weihuparts emphasizes innovative R&D and maintains a team of engineers focused on high-quality, durable, and efficient components that meet industry standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What immediate checks should I perform when I suspect pump failure under load?A: Check fluid level and condition, listen for noises, measure pressure under load, inspect suction hoses and filters, and monitor temperature. Take the machine out of heavy duty until you confirm the cause.Q: Can cleaning the filters fix loss of pressure under load?A: If a clogged suction filter is restricting flow, cleaning or replacing it can restore performance. But if internal pump wear or cavitation is present, filters won’t solve the root problem.Q: How dangerous is operating with a failing hydraulic pump?A: It risks sudden loss of control, further component damage, and heat-related failures. Operating under these conditions can be unsafe and increase repair costs.Q: How often should hydraulic fluid be changed to prevent pump failure?A: Follow OEM recommendations; typical intervals vary by machine use and environment. Use condition monitoring (fluid analysis) to adjust intervals based on actual wear and contamination levels.Q: When should I contact Weihuparts for help?A: Contact Weihuparts when you need reliable replacement pumps, specific components, or technical guidance on diagnosis and parts selection to restore excavator performance.

Impact of Temperature on 336D Hydraulic Pump Lifespan
Tips for buy electric hydraulic pump

Partnering with Suppliers for 336D Hydraulic Pump Supply

Supplier Evaluation: Heavy Duty CAT Replacement Pumps
FAQ
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.
How can I place an order?
You can place an order through our user-friendly online platform or by contacting our sales team directly. Simply browse our catalog, select the parts you need, and follow the checkout process to complete your order.
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.
Do you provide warranties on your products?
Yes, we stand by the quality of our products. Most parts come with a warranty that covers manufacturing defects. Please refer to the specific warranty information provided with your purchase or contact our customer service team for details.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
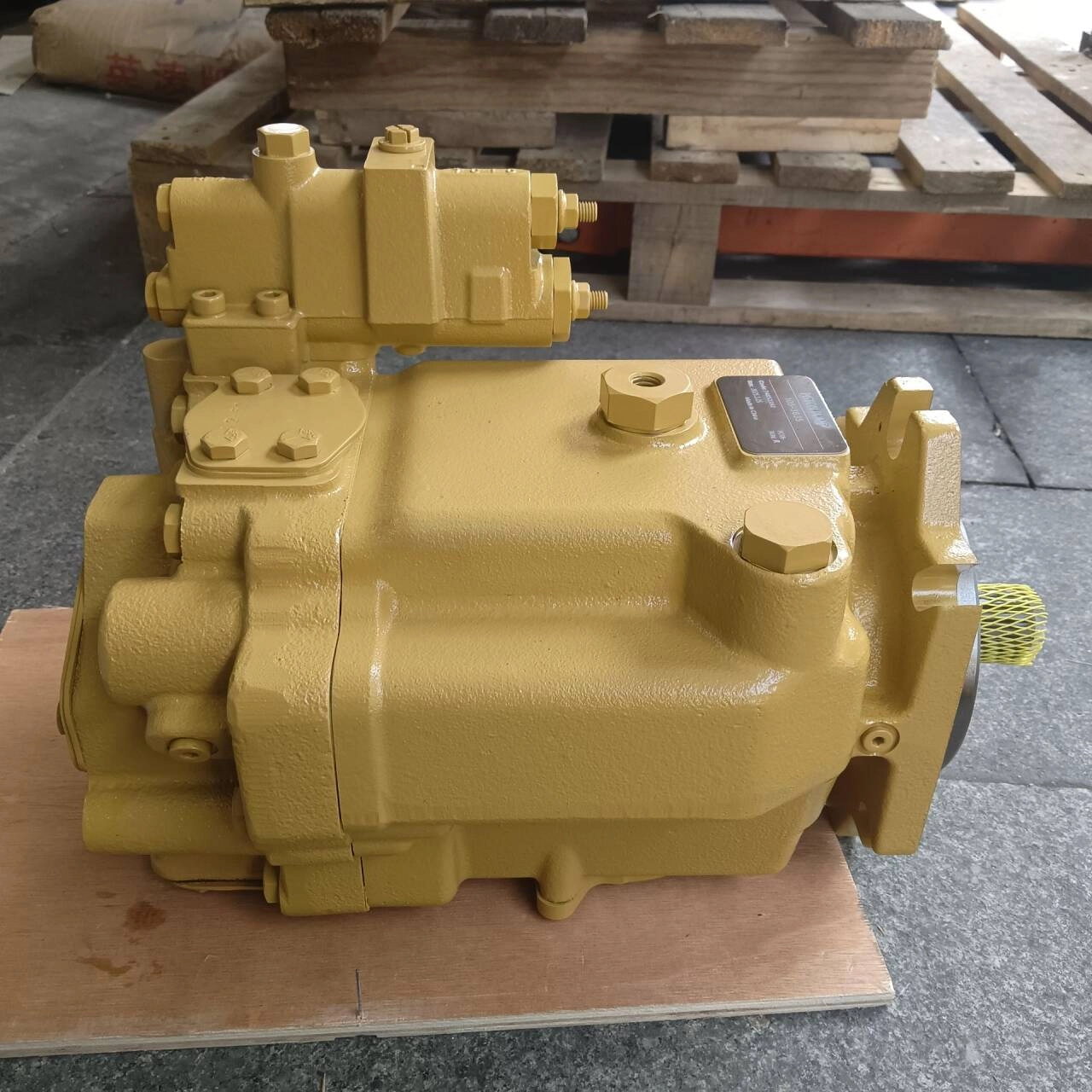

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
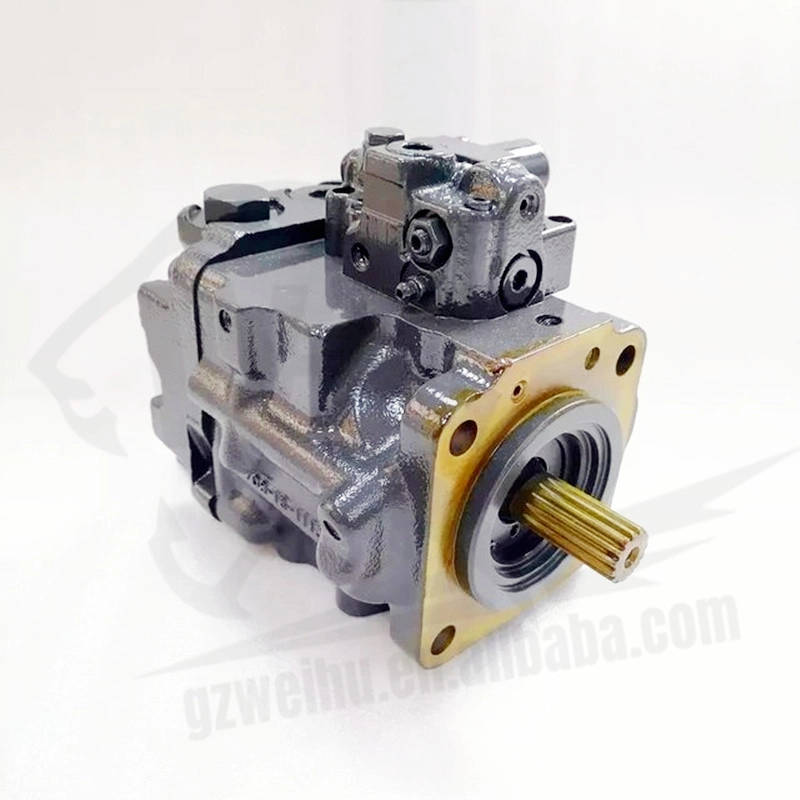

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
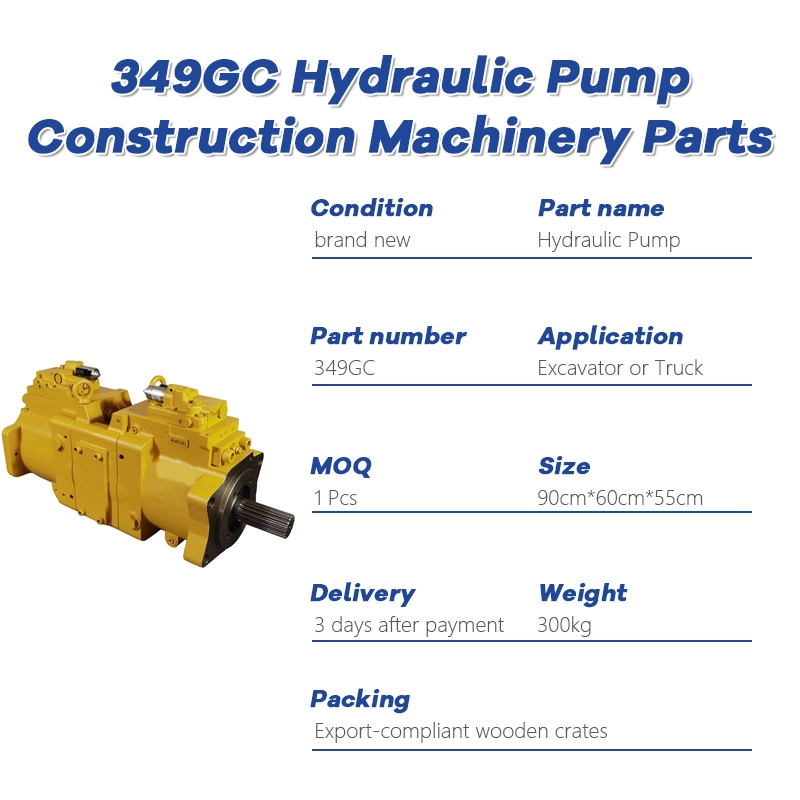
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

