jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Excavator Hydraulic Pump vs Motor: Key Differences and How to Choose
- Excavator Hydraulic Pump vs Motor: Key Differences
- What a Hydraulic Pump Does
- Function and role
- Common pump types
- What a Hydraulic Motor Does
- Function and role
- Common motor types
- Key Differences at a Glance
- How to Read Performance: Flow, Pressure, Torque, and Power
- Basic hydraulic power formula
- Example calculation
- Efficiency and Real-World Performance
- Typical efficiencies
- Practical Selection Criteria for Excavator Owners
- Match pump and motor to application
- Commercial keywords to guide purchasing
- Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Lifespan
- Common maintenance tips
- Typical longevity
- When to Repair vs Replace
- Weihuparts: Your Partner for Excavator Pumps and Motors
- About Weihuparts
- Decision Flow: How to Choose Between Pump or Motor Options
- Quick Comparison Table: Pump vs Motor (Selection Focus)
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References
Excavator Hydraulic Pump vs Motor: Key Differences
Understanding the difference between an excavator hydraulic pump and a hydraulic motor is fundamental for operators, technicians, and purchasing managers. Although they are complementary components in hydraulic systems, their roles, performance metrics, failure modes, and selection criteria differ significantly. This article explains those differences in clear, actionable terms, offers selection and maintenance guidance, and helps you choose the right components for optimal excavator performance.
What a Hydraulic Pump Does
Function and role
An excavator hydraulic pump converts mechanical energy from the engine or prime mover into hydraulic energy (flow and pressure). It supplies pressurized hydraulic fluid to valves, cylinders, and motors. In short, the pump is the source of hydraulic power.
Common pump types
Excavators typically use three main pump types:
- Axial piston pumps (variable or fixed displacement) — high pressure, high efficiency, used in modern mid-to-large excavators.
- Vane pumps — moderate pressure, quieter, used in some mid-range systems.
- Gear pumps — simple, robust, lower cost, typically used in auxiliary circuits or small machines.
What a Hydraulic Motor Does
Function and role
A hydraulic motor converts hydraulic energy (pressure and flow) back into mechanical rotational energy (torque and speed). Hydraulic motors drive travel motors, swing drives, winches, and attachments. Where the pump is the power source, the motor is the actuator that performs motion work.
Common motor types
Hydraulic motors mirror pump types: gear motors (simple, lower torque), vane motors (smoother operation), and piston motors (high torque and efficiency for heavy-duty travel and swing applications).
Key Differences at a Glance
Below is a focused comparison that highlights the commercial and technical differences important for buyers and technicians.
| Aspect | Hydraulic Pump | Hydraulic Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary function | Convert mechanical to hydraulic energy (creates flow) | Convert hydraulic to mechanical energy (produces torque) |
| Direction of energy | Engine → Hydraulic circuit | Hydraulic circuit → Mechanical output |
| Key specs | Displacement, flow (L/min), max pressure (bar), efficiency | Displacement, speed (RPM), torque (Nm), efficiency |
| Common failure modes | Cavitation, wear, leakage, overheating | Seizure, internal leakage, shaft wear, overheating |
| Typical use in excavator | Primary main pumps, pilot pumps, auxiliary pumps | Final drives (travel), swing motors, attachment motors |
How to Read Performance: Flow, Pressure, Torque, and Power
Basic hydraulic power formula
Hydraulic power (kW) can be calculated as: Power (kW) = Pressure (bar) × Flow (L/min) / 600.This simple formula helps you estimate the hydraulic power a pump must supply and the theoretical power a motor can deliver before accounting for losses.
Example calculation
If a pump provides 200 bar at 100 L/min, hydraulic power = (200 × 100) / 600 = 33.33 kW. With a motor efficiency of 90%, the motor’s mechanical output ≈ 33.33 × 0.90 = 30.0 kW. These calculations help choose compatible pump and motor sizes.
Efficiency and Real-World Performance
Typical efficiencies
Efficiencies vary with type and condition. General guidance:
- Axial piston pumps/motors: mechanical efficiencies often 85–95% when new and well-maintained.
- Vane pumps/motors: around 80–90% in good condition.
- Gear pumps/motors: typically 70–85% (lower at higher pressures).
System efficiency is the product of pump and motor efficiencies; realistic system output is lower than nominal hydraulic power due to leakage and parasitic losses.
Practical Selection Criteria for Excavator Owners
Match pump and motor to application
Consider the following checklist when purchasing or specifying components:
- Required flow and pressure based on implement demands and machine size.
- Peak vs continuous duty cycles—choose piston units for sustained heavy use.
- Efficiency needs to minimize fuel consumption and heat generation.
- Space, weight, and mounting constraints on the machine.
- Availability and cost of spare parts and service support.
Commercial keywords to guide purchasing
When searching or requesting quotes, use targeted phrases like “high-pressure axial piston pump,” “excavator travel motor replacement,” “115 kW hydraulic pump for excavators,” or “reliable swing motor for hydraulic excavators” to find suitable commercial suppliers and parts.
Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Lifespan
Common maintenance tips
- Keep hydraulic fluid clean: replace filters per manufacturer schedule and monitor fluid cleanliness (ISO 4406 codes).
- Monitor operating temperatures—overheating accelerates wear.
- Check for cavitation noise (pumps) and loss of torque or jerky movement (motors).
- Follow recommended oil types and viscosities—incorrect fluids reduce efficiency and life.
Typical longevity
With proper maintenance, modern hydraulic pumps and motors can last 5–10+ years in heavy equipment applications. Life expectancy depends on operating hours, duty cycle, fluid cleanliness, and environmental conditions.
When to Repair vs Replace
Decide based on cost, downtime, and residual life. Minor leakage or seal wear can usually be repaired. Severe internal wear, bent shafts, or repeated failures often justify replacement. For high-cycle travel motors or main pumps, consider replacement with upgraded designs (e.g., piston technology) if uptime is critical.
Weihuparts: Your Partner for Excavator Pumps and Motors
About Weihuparts
Weihuparts serves as a reliable partner for global clients in the excavator spare parts sector. We offer a comprehensive selection of excavator parts designed to support routine tasks and high-performance systems. Weihuparts emphasizes quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery to keep machines running smoothly. Our R&D team focuses on durable, efficient components that meet industry standards. Whether you need main pumps, travel motors, swing motors, or hydraulic accessories, Weihuparts provides compatible parts and technical support to help you make the right choice.
Decision Flow: How to Choose Between Pump or Motor Options
Use this step-by-step approach:
- Define machine application and duty cycle (light, intermittent, continuous heavy).
- Calculate required flow and pressure using implement specs and the hydraulic power formula.
- Choose pump type that matches pressure/flow needs and efficiency targets (piston for high pressure, gear for simple/low-cost circuits).
- Select motor type based on torque and speed needs (piston motors for travel/swing; gear motors for auxiliary drives).
- Verify compatibility (mountings, shaft, displacement) and plan for maintenance accessibility.
Quick Comparison Table: Pump vs Motor (Selection Focus)
| Selection Factor | Pump Considerations | Motor Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Primary spec to check | Maximum flow (L/min), max pressure (bar), displacement | Displacement, rated torque (Nm), rated speed (RPM) |
| Best for | Generating system power: main circuits, variable flow control | Driving wheels, tracks, swing, attachments |
| Typical cost driver | Materials and complexity (variable-displacement adds cost) | Torque capacity and sealing technology |
Conclusion
Hydraulic pumps and motors perform opposite but complementary roles in excavator hydraulic systems. Pumps generate hydraulic power; motors convert that power into useful mechanical output. Choosing the right pump and motor depends on duty cycle, required flow/pressure, efficiency goals, and maintenance capabilities. By understanding the differences and applying simple calculations, you can specify components that improve machine uptime, reduce operating cost, and match performance requirements. For reliable parts and technical support, consider suppliers like Weihuparts that focus on quality, innovation, and global service.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the main difference between a hydraulic pump and a motor?A: A pump converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy (flow and pressure); a motor converts hydraulic energy back into mechanical rotational energy (torque and speed).
Q: How do I calculate hydraulic power for matching components?A: Use Power (kW) = Pressure (bar) × Flow (L/min) / 600. Then factor in pump and motor efficiencies to estimate mechanical output.
Q: Which is more efficient, piston or gear designs?A: Piston (axial) designs are generally more efficient and better for high-pressure, continuous-duty applications; gear units are simpler and cheaper but usually less efficient.
Q: How often should hydraulic oil and filters be changed?A: Follow the equipment manufacturer's schedule; typical heavy-duty guidance is filter changes every 250–500 operating hours and oil changes every 1,000–2,000 hours depending on contamination levels and operating conditions.
Q: Can I replace a failed motor with a different displacement motor?A: You can if it meets torque and speed requirements and fits mounting and coupling constraints, but mismatched displacement may affect system balance and control. It's best to verify compatibility with a technician or supplier.
References
- Parker Hannifin technical articles and pump/motor catalogs (industry reference for hydraulic components).
- Bosch Rexroth product literature and engineering guides on hydraulic pumps and motors.
- ISO 1219 and ISO 4406 cleanliness standards summaries (industry standards for hydraulic systems and fluid cleanliness).
- Hydraulics & Pneumatics magazine technical articles and case studies.
- Manufacturer maintenance manuals (Komatsu, Caterpillar) for hydraulic excavator best practices.

Compatibility Checklist for Isuzu D1703 in Heavy Machinery

Sourcing Strategy: Reliable Suppliers for Hydraulic Hydraulic Pump Parts

Procurement Checklist: 336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump Specs

How Procurement Teams Evaluate Heavy Duty CAT Hydraulic Pumps
FAQ
Are your parts compatible with all excavator brands?
Weihuparts strives to offer parts compatible with a wide range of excavator brands and models. However, we recommend checking the product specifications or consulting with our team to ensure compatibility with your specific excavator.
Do you provide warranties on your products?
Yes, we stand by the quality of our products. Most parts come with a warranty that covers manufacturing defects. Please refer to the specific warranty information provided with your purchase or contact our customer service team for details.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
How can I place an order?
You can place an order through our user-friendly online platform or by contacting our sales team directly. Simply browse our catalog, select the parts you need, and follow the checkout process to complete your order.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
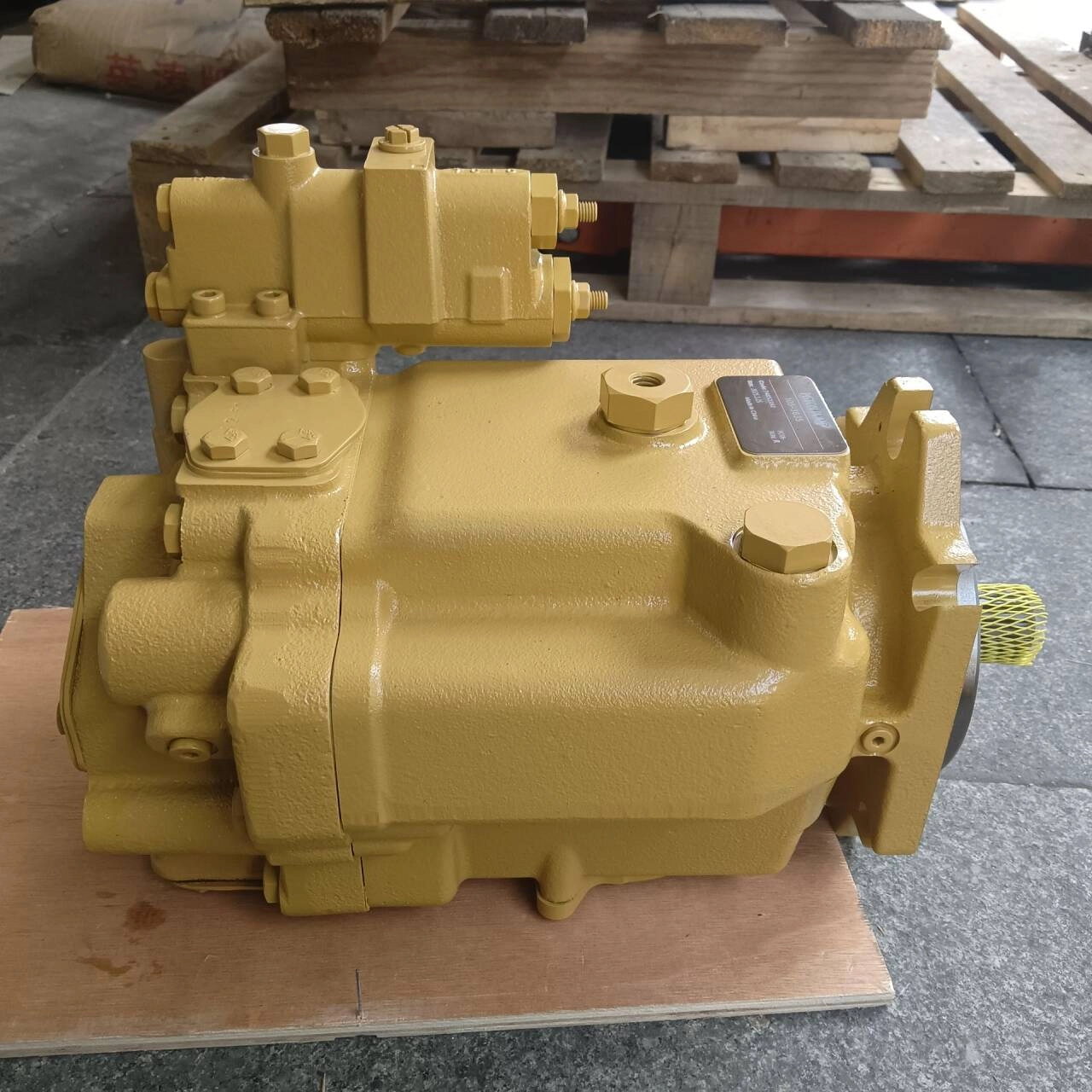

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
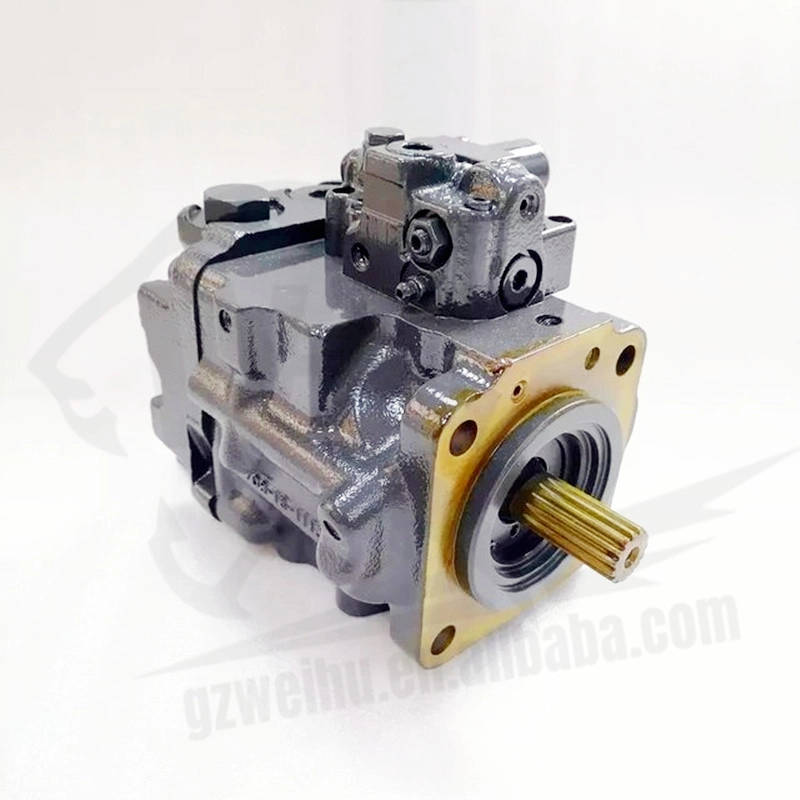

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
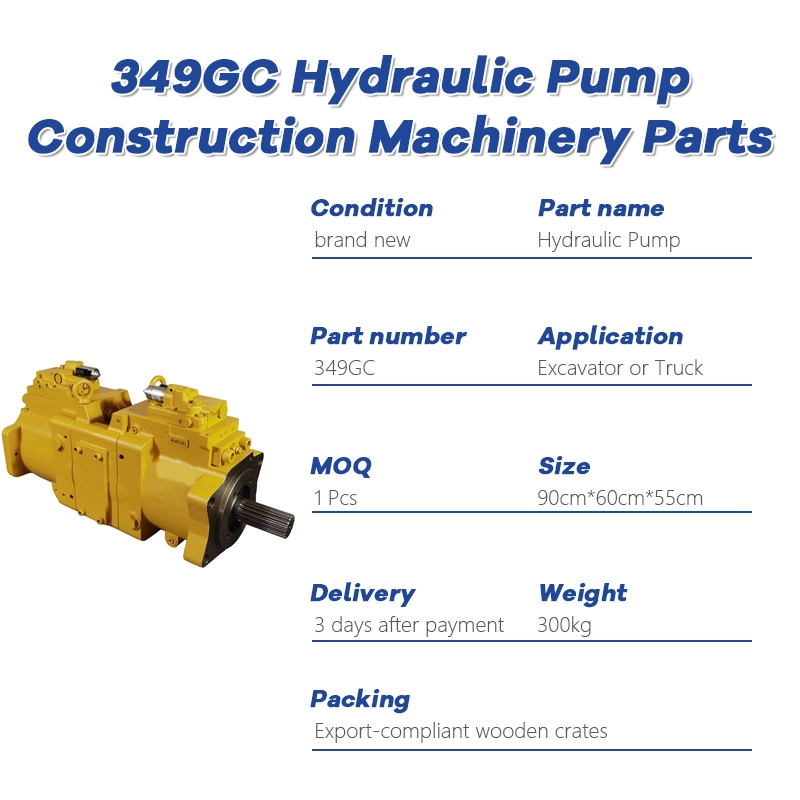
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

