jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Excavator Hydraulic Pump Maintenance Checklist: A Practical Guide
- Excavator Hydraulic Pump Maintenance Checklist: Why It Matters
- How to Use This Excavator Hydraulic Pump Maintenance Checklist
- Daily Checks: Prevent Immediate Failures
- 1. Visual Inspection for Leaks
- 2. Hydraulic Fluid Level and Appearance
- 3. Operating Noise and Vibration
- Weekly Checks: Basic Performance Monitoring
- 4. Temperature and Pressure Checks
- 5. Filter Indicators and Breath Filters
- Monthly Checks: In-Depth Inspections
- 6. Hydraulic Fluid Sampling and Analysis
- 7. Inspect Hoses, Fittings, and Couplings
- 8. Check Pump Mounting and Alignment
- Quarterly or 500–1,000 Hour Checks: Replace Wear Items
- 9. Replace Filters
- 10. Inspect Relief Valve and Control Valves
- Annual or Major Service: Overhaul and Calibration
- 11. Perform a Full Pump Performance Test
- 12. Rebuild or Replace Worn Pumps
- Common Signs of Hydraulic Pump Wear and Failure
- Troubleshooting Quick Guide
- Problem: Excessive Noise
- Problem: Low Pressure or Loss of Power
- Maintenance Intervals: Typical Recommendations
- Best Practices to Extend Hydraulic Pump Life
- Use the Right Hydraulic Fluid and Keep It Clean
- Warm Up Before Heavy Use
- Train Operators and Document Maintenance
- Selecting Replacement Parts: OEM vs Aftermarket
- How Weihuparts Supports Your Hydraulic Pump Maintenance
- Conclusion: Follow the Checklist to Reduce Downtime and Cost
- Frequently Asked Questions
Excavator Hydraulic Pump Maintenance Checklist: Why It Matters
Hydraulic pumps are the heart of an excavator’s powertrain. Proper maintenance of the excavator hydraulic pump prevents unexpected failures, reduces repair costs, and keeps projects on schedule. This Excavator Hydraulic Pump Maintenance Checklist is designed for operators, maintenance technicians, and fleet managers who want a practical, reliable routine to maintain hydraulic pump health.
How to Use This Excavator Hydraulic Pump Maintenance Checklist
Follow this checklist as a tiered program: daily, weekly, monthly, and annual tasks. Adjust intervals based on operating hours, environment (dusty, wet, or high-temperature conditions), and OEM recommendations. Document each check in your equipment log for informed decision-making and trend analysis.
Daily Checks: Prevent Immediate Failures
1. Visual Inspection for Leaks
Check the pump housing, seals, fittings, hoses, and nearby hydraulic lines for oil leaks. Even small wet spots can indicate seal wear or loose fittings. Address leaks immediately to avoid contamination and loss of hydraulic fluid.
2. Hydraulic Fluid Level and Appearance
Verify reservoir level using the sight glass or dipstick. Look at fluid color and clarity; milky, foamy, or heavily darkened fluid can signal contamination or breakdown. Maintaining correct fluid level reduces cavitation risk and helps maintain pump pressure.
3. Operating Noise and Vibration
Listen for unusual noises—grinding, whining, or knocking—during warm-up and under load. Excessive vibration or noise often precedes mechanical failure such as worn bearings, internal wear, or cavitation.
Weekly Checks: Basic Performance Monitoring
4. Temperature and Pressure Checks
Record operating temperature and hydraulic system pressure. Normal operating temperature typically ranges within manufacturer guidelines; persistent overheating reduces fluid life and accelerates component wear. Monitor pressure consistency to spot leaking valves or internal pump wear.
5. Filter Indicators and Breath Filters
Check filter change indicators and breathers for clogging. Replace indicators or primary filters as needed. A clogged breather can create vacuum conditions and draw contaminants into the reservoir.
Monthly Checks: In-Depth Inspections
6. Hydraulic Fluid Sampling and Analysis
Take a fluid sample for analysis to detect contamination (water, metal particles, and glycol) and to evaluate fluid condition. Fluid analysis helps predict failures before visible symptoms appear.
7. Inspect Hoses, Fittings, and Couplings
Look for abrasion, swelling, cracks, and loose fittings. Replace hoses showing wear. Tighten loose fittings to the recommended torque—but avoid over-tightening, which can strip threads or damage seals.
8. Check Pump Mounting and Alignment
Ensure the pump is securely mounted and aligned. Misalignment can cause shaft wear, bearing failure, and leaks at mechanical seals.
Quarterly or 500–1,000 Hour Checks: Replace Wear Items
9. Replace Filters
Change hydraulic filters based on your equipment’s duty cycle. A common practice is replacing filters every 500–1,000 operating hours, or sooner in harsh environments. Clean filters maximize fluid cleanliness and protect pump internals.
10. Inspect Relief Valve and Control Valves
Ensure relief valves are set to manufacturer specifications and check for sticking or wear. Malfunctioning relief valves can lead to overpressure and pump damage.
Annual or Major Service: Overhaul and Calibration
11. Perform a Full Pump Performance Test
Run a hydraulic pump performance test to evaluate volumetric and mechanical efficiency. Testing can quantify internal leakage, wear, and reduced output so you can plan repairs or rebuilds.
12. Rebuild or Replace Worn Pumps
If test results or physical inspection show significant internal wear, rebuild or replace the pump. Rebuild kits are available for many popular pump models but choose OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts to ensure reliability.
Common Signs of Hydraulic Pump Wear and Failure
Watch for these warning signs: decreased flow or power, increased system noise (whine or knock), overheating, foaming fluid, and visible contamination in samples. Address the root cause quickly—often contamination, cavitation, or improper maintenance.
Troubleshooting Quick Guide
Problem: Excessive Noise
Possible causes: cavitation, air ingress, worn bearings, or misalignment. Check fluid level and breathers, inspect suction lines for restrictions, and verify pump mounting.
Problem: Low Pressure or Loss of Power
Possible causes: internal wear, clogged filters, leaking valves, or pump displacement loss. Check filters, measure pressure at pump and implement controlled load tests.
Maintenance Intervals: Typical Recommendations
Intervals vary by OEM, operating conditions, and fluid type. Below is a general comparison of common maintenance tasks and typical intervals. Use this table as a baseline—always follow your machine’s service manual for exact intervals.
| Task | Typical Interval | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Visual daily check (leaks, level, noise) | Daily | Critical for early detection |
| Filter inspection / indicator | Weekly to monthly | Change as indicated or every 500–1,000 hours |
| Hydraulic oil level & temperature | Daily | Maintain correct level and monitor trends |
| Hydraulic fluid analysis | Every 500–1,000 hours | Detect contamination early |
| Filter change | 500–1,000 hours | Shorten interval in harsh conditions |
| Full pump test & overhaul | Annually or at performance decline | Plan rebuild/replacement when efficiency drops |
Best Practices to Extend Hydraulic Pump Life
Use the Right Hydraulic Fluid and Keep It Clean
Use fluids that meet OEM viscosity and additive specifications. Contaminants (water, dirt, glycol) shorten component life—use quality filtration and breathers and store fluids in clean containers.
Warm Up Before Heavy Use
Allow the system to reach operating temperature before applying heavy loads. Cold fluid is more viscous and increases stress on the pump and components.
Train Operators and Document Maintenance
Operator behavior affects pump life. Train operators to avoid abrupt loads and to report anomalies. Maintain inspection logs and fluid analysis records to identify trends and make informed maintenance decisions.
Selecting Replacement Parts: OEM vs Aftermarket
Choosing replacement pumps, seals, and filters influences reliability and cost. OEM parts generally guarantee fit and performance; reputable aftermarket parts can offer cost savings but insist on vendor traceability, material quality, and warranty—especially for high-wear items like pump pistons, bearings, and seals.
How Weihuparts Supports Your Hydraulic Pump Maintenance
Weihuparts serves as a reliable partner for global clients in the excavator spare parts sector. We provide a comprehensive selection of excavator parts designed to support routine maintenance and high-performance requirements. With a focus on quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery, Weihuparts offers replacement pump components, filters, seals, and rebuild kits that help you follow this Excavator Hydraulic Pump Maintenance Checklist precisely.
Conclusion: Follow the Checklist to Reduce Downtime and Cost
Implementing this Excavator Hydraulic Pump Maintenance Checklist reduces the risk of costly failures and extends pump life. A disciplined program—daily visual checks, scheduled filter changes, fluid analysis, and annual performance testing—keeps pumps operating efficiently and saves money over the machine lifecycle. Combine these practices with genuine, high-quality parts and responsive support from a trusted supplier like Weihuparts to maximize uptime and productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How often should I change hydraulic oil in an excavator?A: Typical OEM guidance varies, but many operators change hydraulic oil between 2,000–4,000 hours based on fluid condition and fluid analysis. More frequent changes may be necessary under severe conditions.
Q: What are the top causes of hydraulic pump failure?A: The most common causes are contamination, cavitation (air in the system), overheating, improper fluid viscosity, and mechanical wear from poor alignment or inadequate maintenance.
Q: Can I rebuild my hydraulic pump instead of replacing it?A: Yes. Rebuilding with high-quality kits can restore pump performance and reduce cost compared to full replacement. Evaluate rebuild vs replacement based on performance tests, cost, and downtime requirements.
Q: What level of filtration should I use for excavator hydraulics?A: Use filtration rating and types recommended by your OEM. Common practices include multi-stage filtration with micron ratings appropriate for the pump and control valves—fluid analysis will help determine if upgrades are needed.
Q: How can I detect early cavitation symptoms?A: Early signs include a distinct high-pitched whining noise, decreased system performance, and small air bubbles in returned fluid. Check suction line restrictions, pump inlet height, fluid level, and breather condition.
If you need parts, technical specifications, or help building a tailored maintenance schedule for your fleet, contact Weihuparts for expert support and reliable excavator parts.
Top Causes of Hydraulic Pump Overheating in Excavators 2026
Best Hydraulic Pump Brands for Excavators to Watch 2026
Where to Buy engine assembly
How to Rebuild an Excavator Hydraulic Pump: Step-by-Step Guide
FAQ
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.
How can I place an order?
You can place an order through our user-friendly online platform or by contacting our sales team directly. Simply browse our catalog, select the parts you need, and follow the checkout process to complete your order.
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
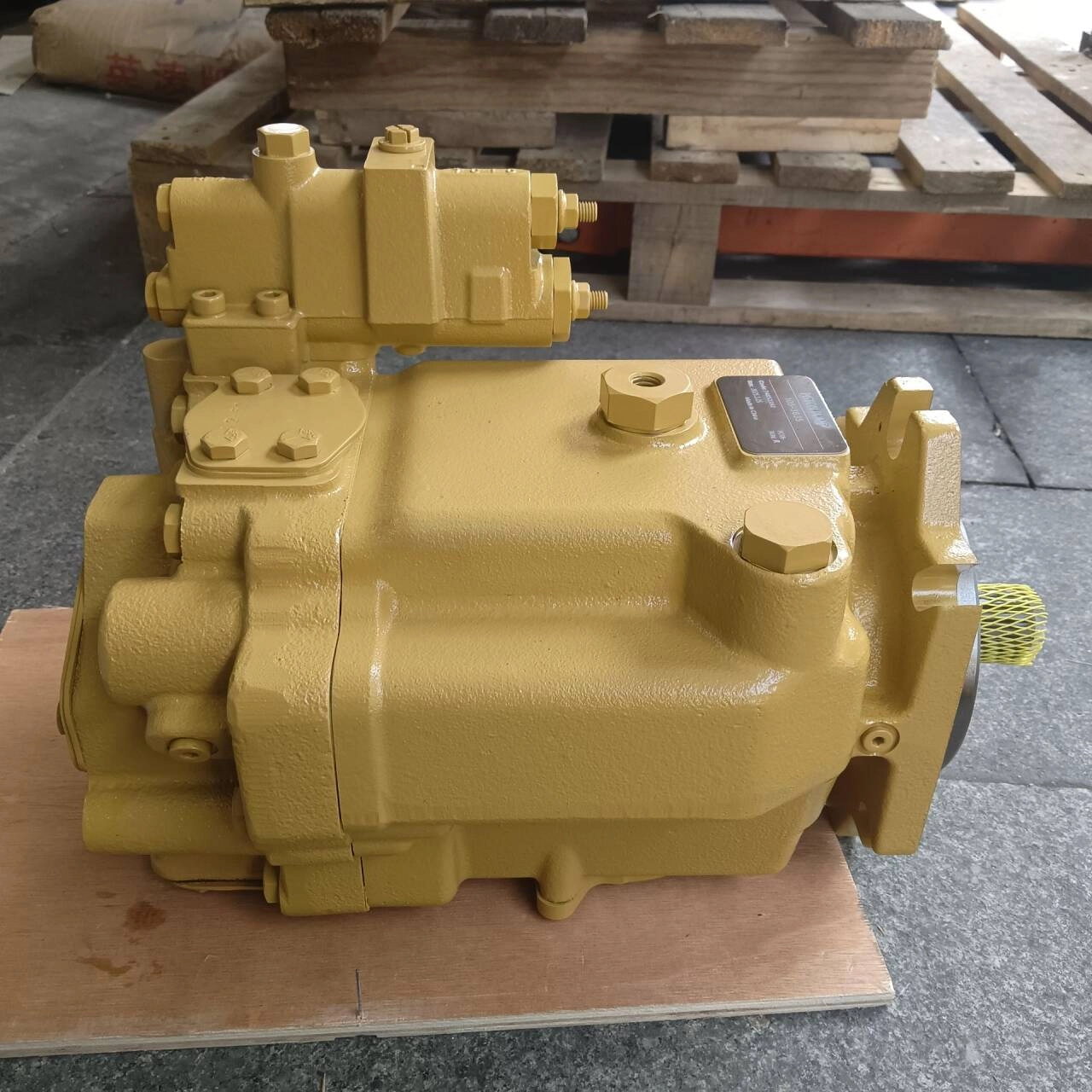

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
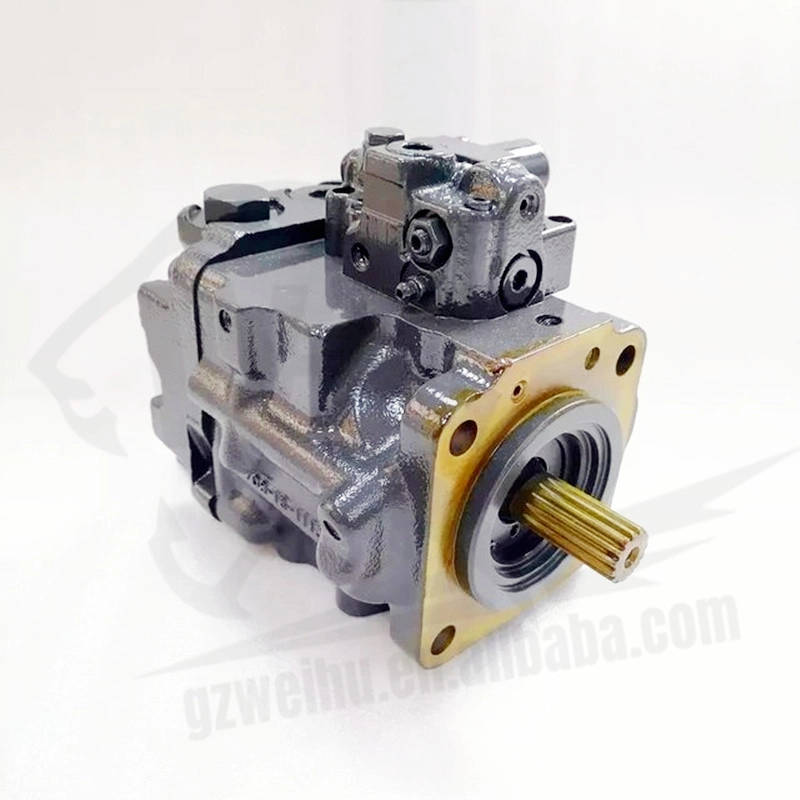

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
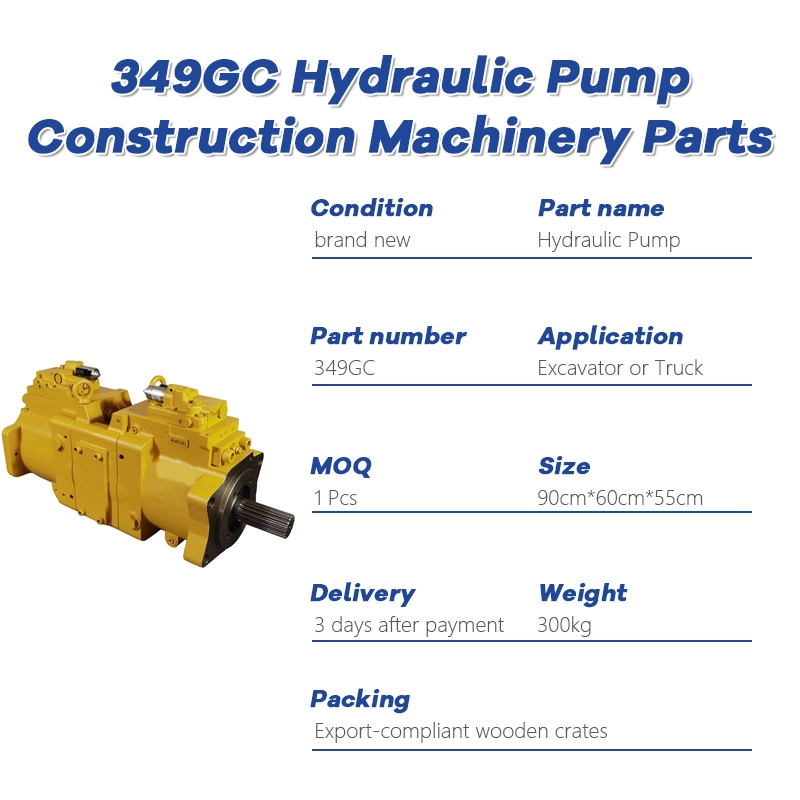
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

