jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Top Causes of Hydraulic Pump Overheating in Excavators 2026
- Why Excavator Hydraulic Systems Fail: A Practical Guide
- Introduction — hydraulic pump overheating as an operational risk
- Common mechanical causes of hydraulic pump overheating — hydraulic pump diagnostics
- Contamination and filtration issues — excavator spare parts and filter selection
- Thermal and fluid-related causes — hydraulic oil temperature management
- Cavitation and air ingestion — practical checks for inlet conditions
- System pressure and operational causes — how duty cycles affect hydraulic pump lifespan
- Installation and compatibility issues — choosing the right replacement hydraulic pump
- Comparing pump types — failure modes and overheating tendencies
- Preventive maintenance checklist — keep hydraulic pump temperatures under control
- When to repair vs replace — economic and technical criteria for hydraulic pump decisions
- Weihuparts — a reliable partner for excavator spare parts and hydraulic pump needs
- Cost comparison — repair vs replacement (indicative)
- Practical troubleshooting flow — a step-by-step approach
- FAQ — common questions on hydraulic pump overheating in excavators
- Contact and parts inquiry — get support or view replacement hydraulic pump options
- References
- Disclaimer
Why Excavator Hydraulic Systems Fail: A Practical Guide
Introduction — hydraulic pump overheating as an operational risk
Hydraulic pump overheating is one of the most common contributors to excavator downtime and premature component failure. For fleet owners, operators, and maintenance teams, recognizing the root causes and applying proven diagnostics and corrective actions is essential to controlling lifecycle cost and ensuring safety on the jobsite. This article explains the top causes of hydraulic pump overheating in excavators for 2026, with practical checks, data-backed temperature thresholds, and recommended parts and services including replacement hydraulic pump options and excavator spare parts guidance.
Common mechanical causes of hydraulic pump overheating — hydraulic pump diagnostics
Mechanical wear and misalignment are leading mechanical causes of pump overheating. Over time, axial piston pumps, vane pumps and gear pumps accumulate internal wear (clearance increase, worn bearings, damaged vanes) that reduces volumetric efficiency and increases internal leakage. That leakage converts hydraulic energy to heat inside the pump housing.
- Symptoms: rising oil temperature with moderate load, abnormal pump noise (whine/grind), pressure fluctuation under constant loads.
- Diagnostic checks: measure delta pressure across pump, observe pump inlet/outlet lines for pulsation, inspect suction strainer and inlet plumbing for deformation that causes cavitation.
- Corrective actions: measure pump volumetric efficiency (flow vs displacement tests), replace worn pump elements or complete replacement hydraulic pump if wear exceeds service limits, align shaft couplings, and replace damaged bearings.
Contamination and filtration issues — excavator spare parts and filter selection
Contamination (solid particles, water, varnish) raises fluid friction, blocks cooler passages and filter elements, and abrades close-clearance pump parts. A clogged filter increases pressure drop causing the pump to work harder and generate heat.
- Symptoms: rapid temperature rise after filter change intervals, increasing particle counts on fluid analysis, presence of metallic wear debris in strainer.
- Diagnostic checks: conduct particle count (ISO 4406), fluid analysis for viscosity and water content, inspect breather and return-line filters for clogging.
- Corrective actions: replace filters with correct beta rating, perform system flush if contaminated, correct breather and seal leaks to prevent ingress.
Thermal and fluid-related causes — hydraulic oil temperature management
Hydraulic fluid selection and thermal management are central to controlling pump temperature. Wrong viscosity, degraded fluid, or insufficient cooling capacity will cause overheating.
- Wrong oil viscosity: too high viscosity increases shear heating; too low viscosity reduces film strength and increases metal-to-metal contact. Use OEM-recommended viscosity grades and verify viscosity index.
- Degraded oil: oxidation increases acidity and sludge formation which impairs heat transfer and clogs coolers.
- Cooling system failure: blocked cooler cores, failing hydraulic fans, damaged thermostats and contaminated cooler fins reduce heat rejection.
Recommended operating fluid temperature ranges (industry guidance):
| Oil Temperature (°C) | Expected Effect |
|---|---|
| Ambient to 40°C | Good viscosity, normal operation |
| 40–60°C | Typical operating range for many excavators; efficient heat transfer |
| 60–80°C | Marginal — monitor for viscosity loss and oxidation |
| >80°C | High risk of accelerated oil degradation, seal damage, and pump wear |
Data sources: industry maintenance guidance and fluid manufacturers advise keeping hydraulic oil typically below ~80°C; see references.
Cavitation and air ingestion — practical checks for inlet conditions
Cavitation occurs when local vapor pressure drops below vapor pressure of the fluid, leading to collapsing vapor bubbles at pump inlet or within the pump. The collapse causes microscale impacts that damage pump surfaces and cause heating.
- Symptoms: loud gravelly noise, pitting on pump components, intermittent pressure loss, elevated temperature under high load.
- Diagnostic checks: inspect suction piping for restrictions, check tank level and suction lift, verify suction strainer clean and correctly sized, and measure NPSH available vs NPSH required for the pump.
- Corrective actions: reduce suction lift, increase tank fluid level, shorten and enlarge suction lines, replace damaged suction strainers, and if needed select pump with lower NPSHr.
System pressure and operational causes — how duty cycles affect hydraulic pump lifespan
Over-pressurization (valve setting errors, relief valve failure, or repeated shock loads) forces the pump to exceed design limits and generate excess heat. Heavy-duty cycles and incorrect machine use (e.g., continuous high-load digging) will accelerate heating.
- Symptoms: relief valve chatter, short cycling, rapid oil temperature increases during peak work, and reduced pump output at elevated temps.
- Diagnostic checks: inspect pressure gauges, test relief valve settings, log pressure spikes with a data logger.
- Corrective actions: re-tune relief circuits, install accumulators to smooth shocks, educate operators on duty-cycle limits, and consider higher-rated pumps for heavy applications.
Installation and compatibility issues — choosing the right replacement hydraulic pump
Incorrect installation, mismatched pump displacement or incorrect shaft coupling can induce abnormal loads and thermal stress. When sourcing a replacement hydraulic pump, ensure the pump matches pressure rating, displacement, mounting flange, shaft type, and seal compatibility for the excavator model.
- : procurement teams should compare OEM vs reputable aftermarket options for warranty, material quality, and delivery time when ordering excavator parts or replacement hydraulic pump.
- Checklist: confirm pump model number, maximum working pressure, displacement per revolution, shaft dimensions, and port orientation before purchase.
Comparing pump types — failure modes and overheating tendencies
Different pump technologies present distinct overheating risks. The table below summarizes typical characteristics relevant to excavator applications.
| Pump Type | Typical Pressure Capability | Common Overheat Cause | Suitability for Excavators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Axial piston (variable) | High (up to 350 bar+) | High internal leakage when worn; control spooling errors | Preferred for high-performance excavators |
| Vane pump | Medium (up to ~210 bar) | Vane wear and cavitation on suction side | Good for medium-duty machines |
| Gear pump | Lower (up to ~140 bar) | High shear heating under high viscosity; inefficient at high pressure | Used in auxiliary circuits |
Preventive maintenance checklist — keep hydraulic pump temperatures under control
Routine maintenance reduces the probability of overheating. Key items to include in a PM program:
- Daily: monitor oil temperature, check for leaks and unusual noises.
- Weekly: inspect and clean cooler fins, check fan operation, inspect belts and couplings.
- Monthly: sample oil for particle count and water content; inspect suction strainer.
- Semi-annual/annual: full fluid analysis, system flush if contamination detected, inspect and test relief valves, check pump performance (flow/pressure tests).
When to repair vs replace — economic and technical criteria for hydraulic pump decisions
Deciding whether to repair a hydraulic pump or replace it depends on wear level, cost, downtime, and expected remaining life. Practical thresholds:
- Repair: when wear is localized (bearing, seals, vane replacement) and pump core is within OEM tolerances; repair cost typically <40% of new unit and leads time acceptable.
- Replace: when internal clearances exceed service limits, displacement loss >15–20%, or when performance upgrades (higher pressure rating or improved efficiency) are required. Replacement also recommended when warranty, compatibility, or lifecycle cost favors a new pump.
Weihuparts — a reliable partner for excavator spare parts and hydraulic pump needs
Weihuparts serves as a reliable partner for global clients in the excavator spare parts sector. We provide a comprehensive selection of excavator parts designed to support a variety of operational needs, whether for routine tasks or high-performance excavator systems.
With a focus on quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery, Weihuparts is dedicated to supporting businesses by ensuring the availability of essential parts to keep machinery running smoothly. Weihuparts places a strong emphasis on innovative R&D, continually advancing the design and performance of excavator parts. With a dedicated team of engineers and technicians, the company focuses on developing high-quality, durable, and efficient components that meet the latest industry standards.
Our vision is to be a leading excavator parts manufacturer and a pioneer in transforming the excavator industry through quality, sustainability, and innovation. We aspire to set a global standard for service and reliability in the excavator parts market, creating lasting partnerships and ensuring that our solutions contribute to the success of every project we serve.
Why choose Weihuparts for hydraulic pump and related needs?
- Competitive advantage: comprehensive inventory of hydraulic pump models and critical spare parts with quality testing and traceability.
- Technical strength: R&D team for material selection and improved pump design to resist wear and thermal stress.
- Service reliability: global delivery options and experienced technical support for installation guidance and troubleshooting.
- Main product focus: hydraulic pump, engine assembly, excavator engine — delivering reliable components engineered for durability and performance.
Cost comparison — repair vs replacement (indicative)
| Action | Typical Cost Range (USD) | Downtime Impact | Warranty/Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minor repair (seals, bearings) | 200–1,200 | Low (hours to 1 day) | Short-term |
| Full rebuild | 1,000–4,000 | Medium (1–3 days) | Limited (depends on remanufacturer) |
| New replacement hydraulic pump | 2,000–8,000+ | Medium (1–3 days) | Full OEM/aftermarket warranty |
Note: costs are indicative and vary by model, region, and supplier. Procurement should factor parts availability and expected life.
Practical troubleshooting flow — a step-by-step approach
- Confirm overheating: log oil temperature and correlate with ambient temperature and load.
- Check cooling components: fan, radiator, cooler fins, thermostats.
- Inspect fluid condition: particle count, water content, viscosity, and oxidation indicators.
- Evaluate suction/inlet conditions: suction strainer, piping, tank level, NPSH.
- Check system pressure: record spikes, inspect relief valves and control valves.
- Assess pump mechanical condition: sound, vibration, flow/pressure testing for volumetric efficiency.
- Decide repair vs replace based on measured wear, cost, and expected uptime requirements.
FAQ — common questions on hydraulic pump overheating in excavators
Q1: What is a safe operating temperature for an excavator hydraulic pump?
A: Most excavator hydraulic systems operate efficiently between 40–60°C. Temperatures above 80°C increase risk of accelerated oil degradation, seal and pump damage. Monitor trends rather than single readings.
Q2: How quickly does contaminated oil cause pump overheating?
A: It depends on contamination level. Fine particles and water can promote overheating within weeks if filters are bypassing or system is heavily contaminated. Regular particle counting and fluid analysis catch problems early.
Q3: Can a failing cooler be the only cause of overheating?
A: Yes — blocked fins, collapsed cooler cores, or fan failure can alone reduce heat rejection sufficiently to cause overheating. Always inspect the cooler as part of the diagnosis.
Q4: When should I replace the hydraulic pump instead of repairing it?
A: Replace when volumetric efficiency loss exceeds service limits, internal clearances are beyond rebuild tolerance, or when replacement significantly lowers lifecycle cost and downtime compared with repair.
Q5: Does switching to a synthetic hydraulic oil reduce overheating risk?
A: High-quality synthetic fluids typically have better viscosity index and thermal stability, improving heat control and oxidation resistance. Ensure fluid compatibility with seals and follow OEM specifications.
Q6: How do I reduce overheating caused by heavy-duty cycles?
A: Mitigate with duty-cycle planning, installing accumulators to smooth peaks, using higher-capacity coolers, or selecting pumps rated for continuous high load.
Contact and parts inquiry — get support or view replacement hydraulic pump options
If your fleet is experiencing hydraulic pump overheating or you need a reliable source of excavator spare parts, contact Weihuparts for technical support, expedited parts delivery, and guidance on replacement hydraulic pump selection. Visit Weihuparts to view hydraulic pump, engine assembly, and excavator engine product offerings or request a parts quote and technical consultation.
References
- Noria Corporation — Heat in Hydraulic Systems: causes and countermeasures. https://www.noria.com/library/articles/heat-in-hydraulic-systems/ (Accessed 2025-11-30)
- Machinery Lubrication — Hydraulic Oil Overheating: causes and solutions. https://www.machinerylubrication.com/Read/287/hydraulic-oil-overheating (Accessed 2025-11-30)
- Caterpillar — Operation & Maintenance resources for hydraulic systems. https://www.cat.com/en_US/support/operations/operations-maintenance. (Accessed 2025-11-28)
- Engineering Toolbox — Viscosity vs Temperature. https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/viscosity-temperature-d_413. (Accessed 2025-11-29)
- Hydraulics & Pneumatics — industry articles on pump selection and thermal management. https://www.hydraulicspneumatics.com/ (Accessed 2025-11-25)
Disclaimer
The information provided is for guidance based on industry practice and publicly available sources. For machine-specific service, always consult OEM manuals and accredited service technicians.

Compatibility checklist for ZAX870-5G 6WG1 engine assemblies
Choosing the Right Hydraulic Pump for Heavy-Duty Excavators

Supply Chain Risks When Sourcing Engineered Diesel Engines
Best Symptoms to Monitor for Hydraulic Pump Wear 2026
FAQ
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.
How can I place an order?
You can place an order through our user-friendly online platform or by contacting our sales team directly. Simply browse our catalog, select the parts you need, and follow the checkout process to complete your order.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
Are your parts compatible with all excavator brands?
Weihuparts strives to offer parts compatible with a wide range of excavator brands and models. However, we recommend checking the product specifications or consulting with our team to ensure compatibility with your specific excavator.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
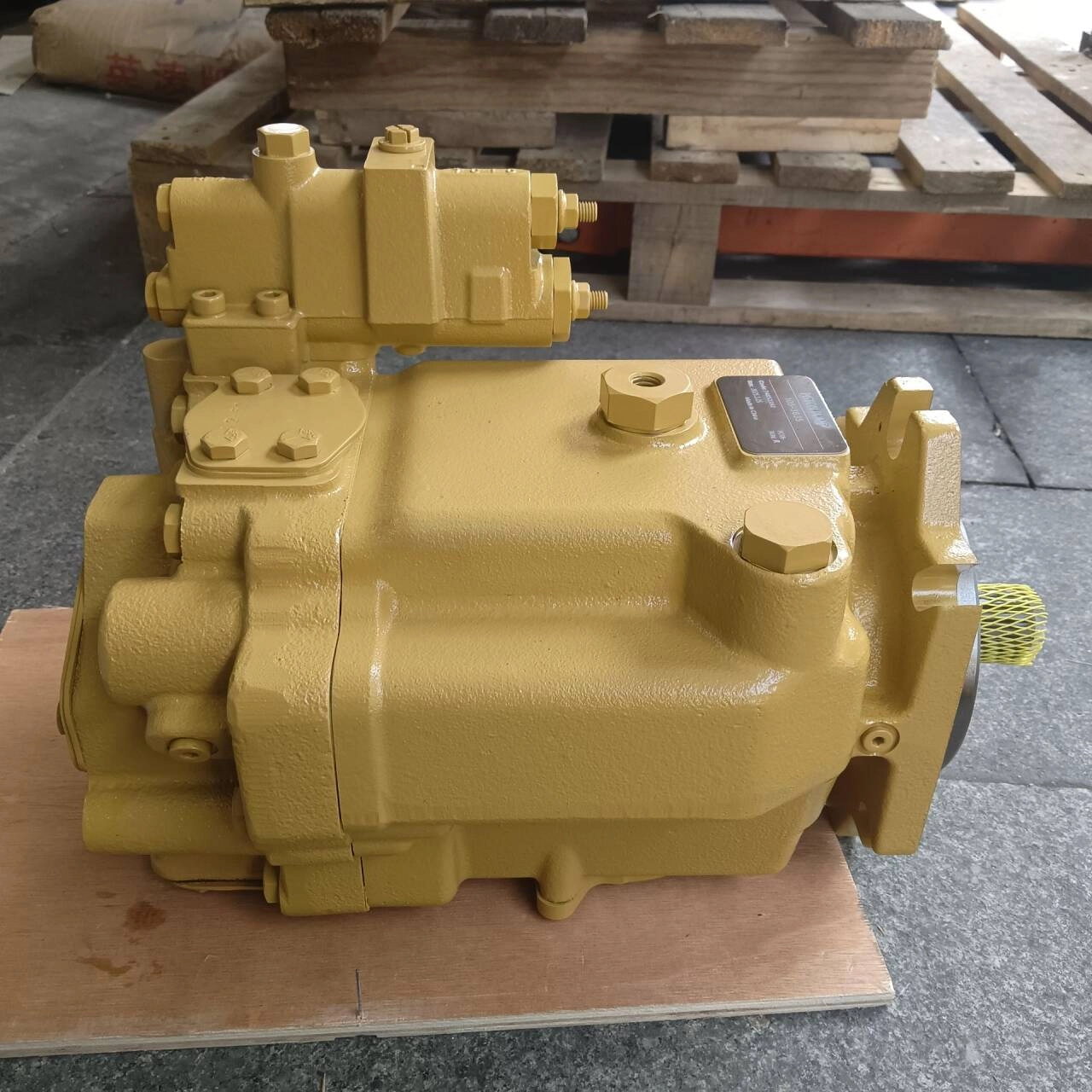

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
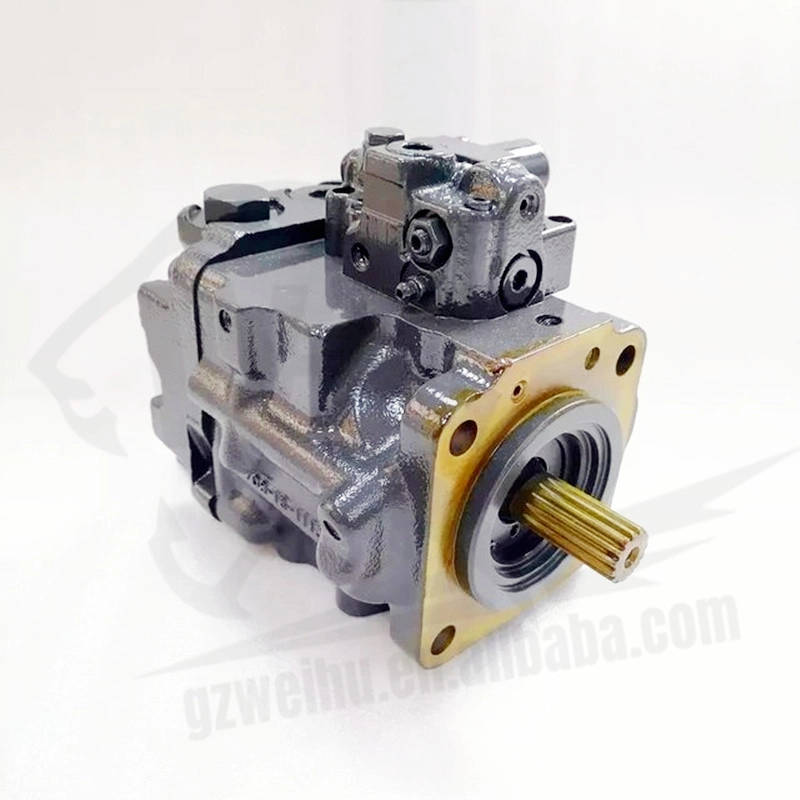

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
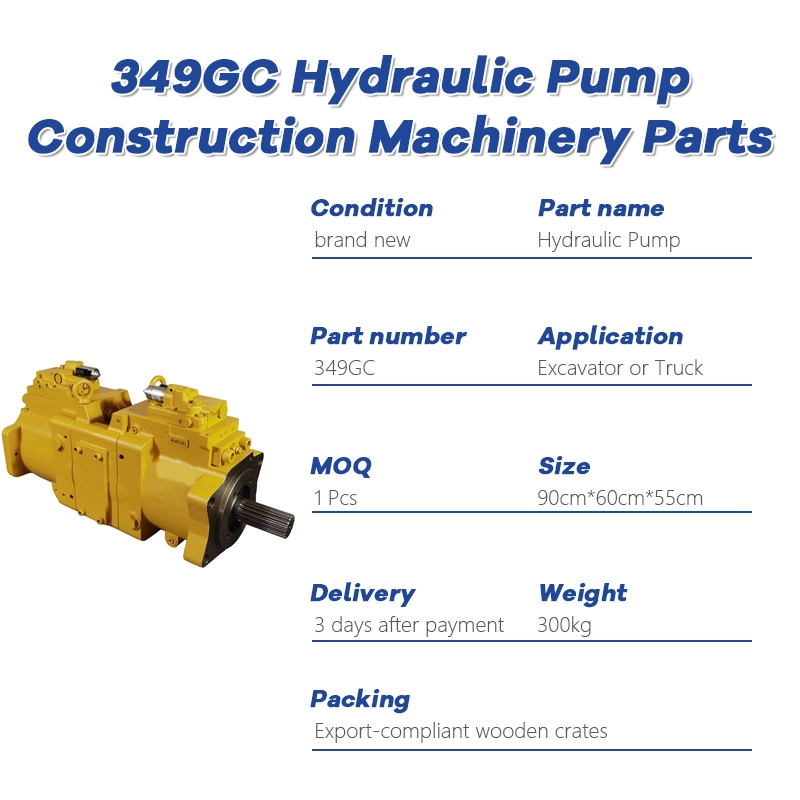
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

