jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Common Causes of Excavator Hydraulic Pump Failure — Prevent, Diagnose, Replace
- Introduction: Why understanding excavator hydraulic pump failure matters
- Context and business impact
- Contamination: The leading cause of hydraulic pump failure
- What contamination looks like and why it kills pumps
- Cavitation: Invisible shock damage inside the pump
- How cavitation forms and its telltale signs
- Overheating: Thermal breakdown of fluid and seals
- Why heat shortens pump life
- Incorrect or degraded hydraulic fluid
- How wrong fluid or old fluid damages pumps
- Air ingress and aeration
- Why entrained air is harmful
- Mechanical wear and component fatigue
- Normal wear and how operating conditions accelerate it
- Improper installation and alignment
- Installation mistakes that cause early failures
- Seal failure and its cascading effects
- Why seals are a common weak point
- Diagnosing pump failure: Practical steps for technicians
- Step-by-step diagnostic workflow
- Preventive maintenance best practices to avoid hydraulic pump failure
- Maintenance routines that protect your investment
- Repair vs Replace: making the right commercial decision
- Choosing the cost-effective path
- Comparative table: Repair vs Replace
- How Weihuparts supports pump reliability and quick recovery
- Products and service advantages for buyers with
- Practical checklist for field teams to reduce pump failures
- Daily and weekly actions that pay off
- Conclusion: Prioritize contamination control, diagnostics, and quality parts
- Final recommendations
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References and sources
Introduction: Why understanding excavator hydraulic pump failure matters
Context and business impact
Hydraulic pumps are the heart of any excavator hydraulic system; pump failure leads to lost production, expensive emergency repairs, and increased ownership costs. For fleet managers and contractors searching for Common Causes of Excavator Hydraulic Pump Failure, this guide explains root causes, symptoms, diagnostic steps, and cost-effective preventive measures. It also outlines when to repair versus replace a pump and how Weihuparts can supply quality excavator spare parts to minimize downtime.
Contamination: The leading cause of hydraulic pump failure
What contamination looks like and why it kills pumps
Solid particle contamination (dirt, metal wear particles) and water in hydraulic fluid aggressively abrade pump components, clog clearances, and chemically degrade lubricity. Industry studies estimate contamination contributes to roughly 60–80% of hydraulic component failures in fielded systems. Symptoms include increased noise, reduced flow, erratic operation, and scuffed rotors or gears on inspection.
Cavitation: Invisible shock damage inside the pump
How cavitation forms and its telltale signs
Cavitation occurs when local pressure drops below fluid vapor pressure and vapor bubbles collapse on pump surfaces, causing pitting and noise. Common causes are restricted inlet lines, clogged suction filters, high fluid temperatures, or excessive lift from suction to pump. Symptoms: loud knocking or gravel-like noise, diminished performance, and rapid surface pitting on pump components.
Overheating: Thermal breakdown of fluid and seals
Why heat shortens pump life
High operating temperatures reduce hydraulic fluid viscosity, accelerate oxidation and varnish formation, and degrade seals and elastomers. Overheating often arises from excessive system pressure, poor cooling, or dirty coolers. Symptoms include dark, burnt-smelling fluid, varnish deposits, and sticky valve behavior.
Incorrect or degraded hydraulic fluid
How wrong fluid or old fluid damages pumps
Using the wrong fluid type, incorrect viscosity, or running fluid past its service life impairs film strength and pump lubrication. Additives that prevent wear and corrosion can be depleted over time. Symptoms: increased wear rates, higher operating temperatures, and reduced pump efficiency.
Air ingress and aeration
Why entrained air is harmful
Air drawn into the hydraulic fluid causes compressibility, making pump flow erratic and causing cavitation-like damage. Common entry points include loose fittings, cracked hoses, and low reservoir fluid levels. Symptoms include spongy controls, noise, visible bubbles in the reservoir, and sudden loss of power.
Mechanical wear and component fatigue
Normal wear and how operating conditions accelerate it
Pumps experience mechanical wear from long service hours, abrasive particles, and improper maintenance intervals. Wear manifests as reduced displacement, internal leakage, higher operating temperatures, and lower system efficiency. Heavy-duty applications or frequent pressure spikes accelerate fatigue and bearing failure.
Improper installation and alignment
Installation mistakes that cause early failures
Misaligned shafts, incorrect couplings, improper torque on bolts, and incorrect piping layouts cause vibration, shaft bending, and premature seal and bearing failure. Always follow manufacturer installation procedures and torque specs to avoid avoidable damage.
Seal failure and its cascading effects
Why seals are a common weak point
Worn or damaged seals allow leakage and permit contamination and air ingress. Seal failure is often a symptom of prior problems (contamination, overheating, chemical attack), and if not addressed promptly will accelerate pump wear and system inefficiency.
Diagnosing pump failure: Practical steps for technicians
Step-by-step diagnostic workflow
1) Visual inspection: Check for external leaks, loose fittings, damaged hoses, and reservoir fluid level/clarity.2) Listen and feel: Note unusual noises, vibration, or temperature rises during operation.3) Fluid analysis: Send oil for particle count (ISO 4406), water content, viscosity, and TAN/TBN where applicable.4) Pressure and flow checks: Measure inlet/outlet pressures and flow rate to compare with pump spec.5) Remove and inspect: If needed, open the pump to inspect wear patterns, cavitation pitting, and contamination evidence.
Preventive maintenance best practices to avoid hydraulic pump failure
Maintenance routines that protect your investment
- Filtration: Use correct-rated suction and pressure filters; replace elements on schedule. Industry guidance often suggests particle counts maintained at ISO 4406 levels appropriate for the pump (e.g., 18/16/13 or cleaner for sensitive systems).
- Fluid management: Use manufacturer-specified fluids, monitor contamination and replace fluid per oil analysis.
- Cooling: Keep coolers and heat exchangers clean and sized correctly for duty cycles.
- Scheduled inspections: Check for alignment, mounting torque, and wear at regular intervals aligned with machine operating hours.
- Training: Ensure operators recognize early symptoms and stop operation before catastrophic failure.
Repair vs Replace: making the right commercial decision
Choosing the cost-effective path
Deciding whether to rebuild or replace depends on damage extent, pump age, downtime costs, and warranty considerations. For high-mileage units with extensive cavitation pitting or bearing races damaged, replacement is often more reliable and faster. For newer pumps with limited wear, a professional rebuild with genuine parts can be cost-effective.
Comparative table: Repair vs Replace
| Factor | Repair (Rebuild) | Replace (New or Remanufactured) |
|---|---|---|
| Typical cost | Lower upfront | Higher upfront |
| Downtime | Medium | Low (if stocked) |
| Longevity | Depends on wear | Longer with new components |
| Warranty | Shorter or limited | Longer, often better |
| Reliability | Good if done by OEM/qualified shop | Highest, especially with new or fully reman |
How Weihuparts supports pump reliability and quick recovery
Products and service advantages for buyers with
Weihuparts supplies a comprehensive selection of excavator hydraulic pumps, reman units, and genuine-quality spare parts to global clients. Our emphasis on quality control, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery ensures replacement pumps and components are available when you need them. Weihuparts' R&D and engineering teams validate parts for durability and compatibility across common excavator models, reducing fitment issues and warranty exposures.
Practical checklist for field teams to reduce pump failures
Daily and weekly actions that pay off
- Check reservoir fluid level and clarity daily.
- Verify inlet strainers and breathers are intact and clean.
- Monitor operating temperatures and control for overheating.
- Log noise and vibration anomalies and escalate for inspection.
- Maintain spare pump or reman unit in inventory for critical machines.
Conclusion: Prioritize contamination control, diagnostics, and quality parts
Final recommendations
Most excavator hydraulic pump failures trace back to contamination, cavitation, overheating, or maintenance lapses. Prioritizing filtration, proper fluid selection, correct installation, and prompt diagnostics will greatly reduce failures and downtime. When replacement is required, sourcing pumps and parts from a reliable supplier like Weihuparts—who combines quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery—helps get machines back to work faster and with lower lifecycle costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What immediate checks should I do if my excavator pump is noisy?Listen for cavitation (knocking) and check suction line restrictions, fluid level, and presence of air bubbles. Also inspect filters and reservoir for contamination.
How often should hydraulic fluid be analyzed on excavators?Send oil samples for analysis every 500–1000 operating hours or sooner when symptoms appear. Frequency increases in dirty or high-hour environments.
Can a worn pump be reliably rebuilt or should I always replace it?Rebuilding is viable when wear is limited and internal components are restorable. Severe cavitation, bearing damage, or pitting often favors replacement, especially for critical machines.
What ISO cleanliness level should I aim for to protect pumps?Target cleanliness depends on the pump and system; a common target for many excavator systems is ISO 4406 18/16/13 or cleaner. Check the pump manufacturer’s recommendation.
How fast can Weihuparts deliver a replacement pump?Delivery time varies by model and region; Weihuparts focuses on maintaining inventory for common models and provides expedited shipping options for critical needs.
References and sources
- Caterpillar Maintenance and Repair Guidelines (manufacturer service manuals)
- ISO 4406:2017 — Hydraulic fluid cleanliness code (International Organization for Standardization)
- ISO 11171 — Hydraulic fluid particle characterization
- International Fluid Power Society (IFPS) technical materials on contamination and maintenance
- Hydraulics & Pneumatics industry articles on cavitation and pump reliability
- Practical field service guides from OEMs (e.g., Komatsu, Hitachi, Volvo) and Weihuparts internal testing and R&D reports (2023–2024)
How to Test Excavator Hydraulic Pumps: Tools & Methods

Troubleshooting Hydraulic Pump Performance Issues on 336D

Supply Chain Risks and Lead Time Strategies for Pump Procurement

Inspection and Pre-Purchase Checklist for ZAX870-5G Engines
FAQ
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
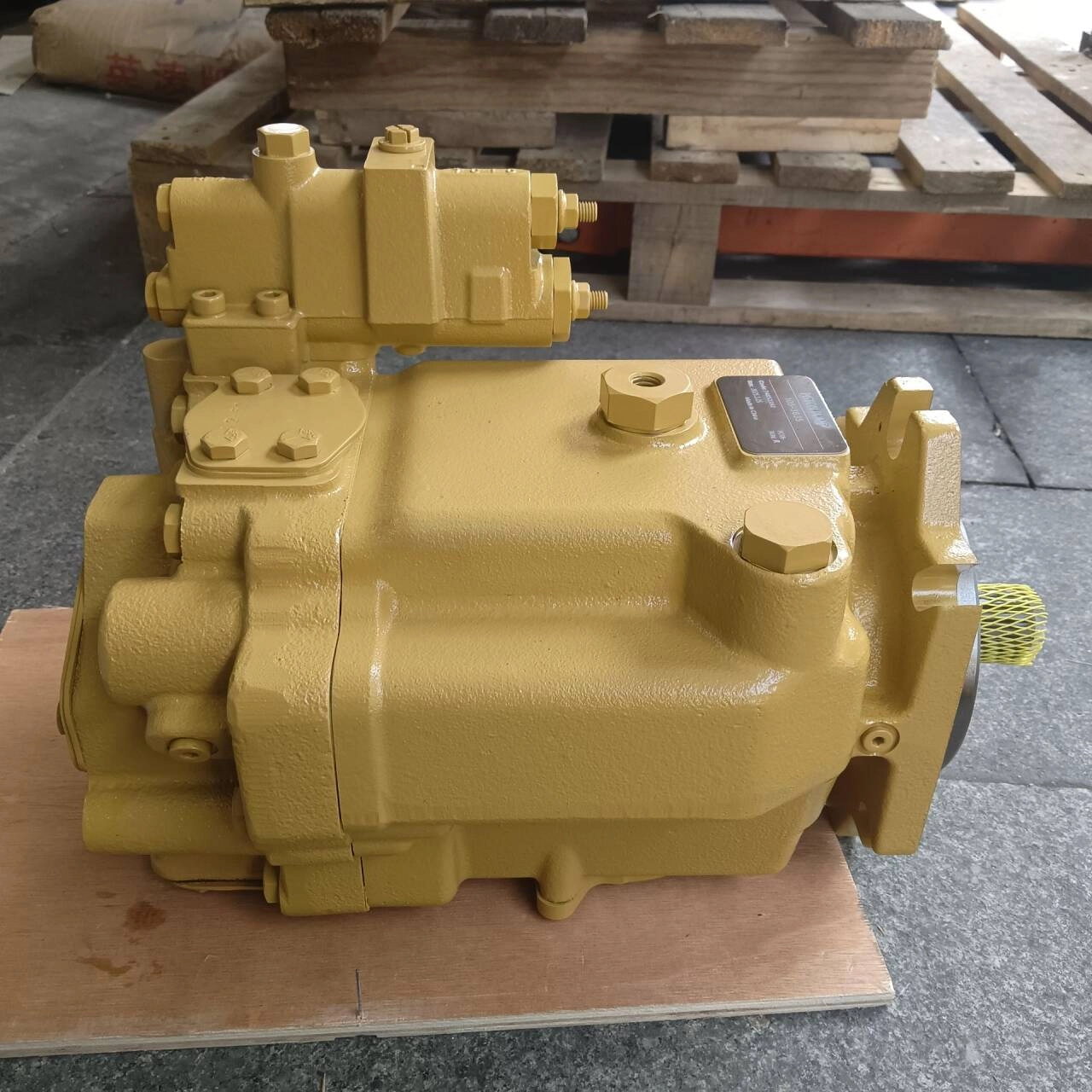

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
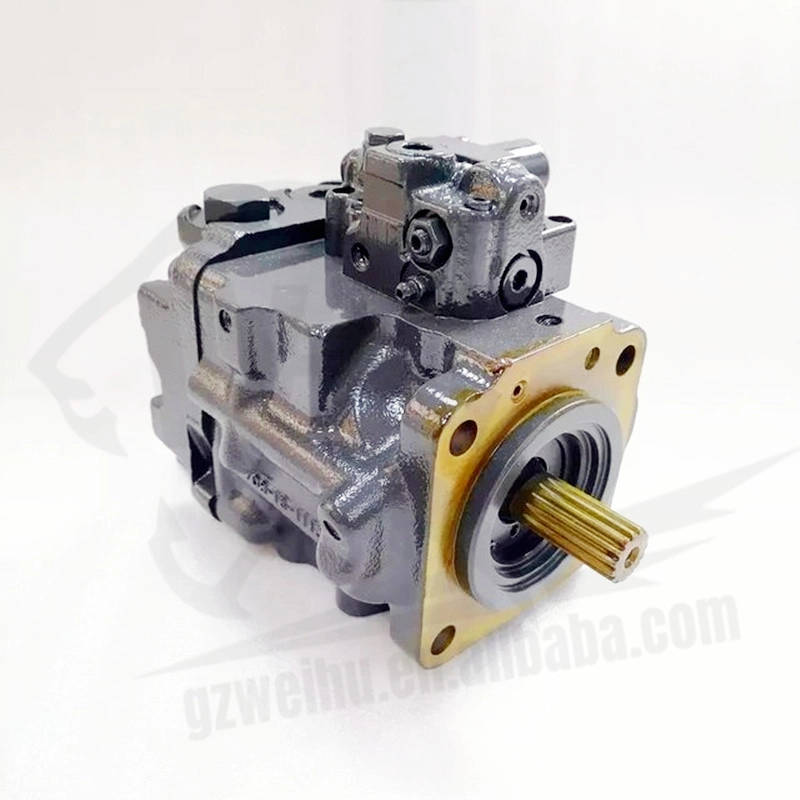

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
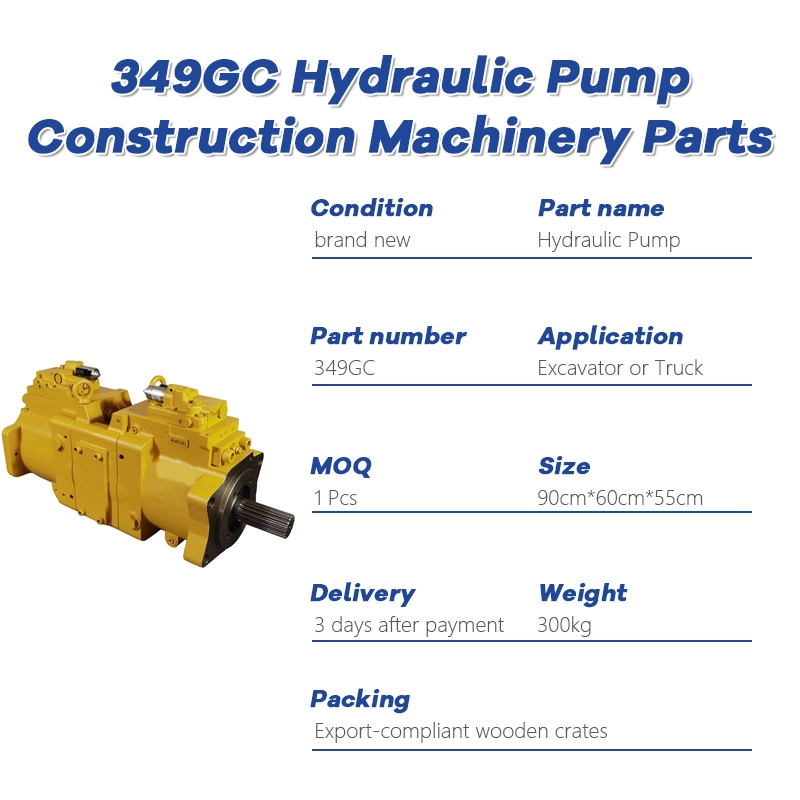
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-

