jackhuang5919@gmail.com
How to Test Excavator Hydraulic Pumps: Tools & Methods
- Introduction: Why Proper Pump Testing Matters
- Purpose and user intent
- Understanding Excavator Hydraulic Pumps
- Types and operating ranges
- Essential Tools for Testing Excavator Hydraulic Pumps
- Portable and bench tools you should have
- Preparation and Safety
- Initial checks and precautions
- Step-by-Step Field Testing Methods
- 1. Visual and basic functional inspection
- 2. Pressure testing (static and dynamic)
- 3. Flow testing and volumetric efficiency
- 4. Relief valve and control valve checks
- 5. Leak-down and cavitation checks
- Bench Testing (Removed Pump Diagnostics)
- Controlled environment for definitive diagnosis
- Advanced Diagnostic Methods
- Ultrasound, vibration, thermography, and oil analysis
- Interpreting Test Results and Common Fault Patterns
- Symptoms, likely causes, and recommended actions
- Comparison of Common Test Methods
- Choose a method based on accuracy, cost, and context
- Practical Thresholds and Expected Values
- How to judge acceptable results
- Maintenance Tips to Extend Pump Life
- Simple habits that reduce failures
- Weihuparts: How We Support Your Pump Testing and Repair Needs
- Company capabilities and value
- Conclusion: A Practical Testing Roadmap
- Summary action plan
- FAQ
- Sources and References
Introduction: Why Proper Pump Testing Matters
Purpose and user intent
Operators, maintenance technicians, and fleet managers searching for How to Test Excavator Hydraulic Pumps: Tools & Methods want practical instructions to identify pump faults, confirm performance, and decide whether repair or replacement is needed. This guide gives clear, safety-focused testing workflows, the essential tools you need, and how to interpret results so you can minimize downtime and avoid unnecessary parts replacement.
Understanding Excavator Hydraulic Pumps
Types and operating ranges
Excavator hydraulic pumps are typically gear, vane, or axial-piston pumps. Most medium to large excavators run hydraulic systems within roughly 2,000–4,500 psi (14–31 MPa) depending on machine size and function. Pump health affects flow, pressure, responsiveness, and efficiency—key performance indicators for digging, swing, boom, and travel circuits.
Essential Tools for Testing Excavator Hydraulic Pumps
Portable and bench tools you should have
To test excavator hydraulic pumps reliably, gather the following tools (recommended):
- Hydraulic pressure gauge/test gauge (0–5,000 psi range) with quick-connect couplings
- Flow meter for hydraulic systems (L/min or GPM)
- Portable hydraulic test kit or manifold block to isolate circuits
- Temperature gun or thermocouple data logger
- Vibration meter and ultrasonic leak detector (for early fault detection)
- Oil analysis kit (particle count, viscosity, water content)
- Torque wrench and tachometer (for RPM verification)
- Bench test stand (for removed pumps) with speed control and load valve
Preparation and Safety
Initial checks and precautions
Before testing, follow these steps: ensure the machine is on level ground, hydraulic oil is at operating temperature (typically 40–60°C), check fluid level and reservoir breather, wear PPE, relieve system pressure, and follow manufacturer lockout/tagout. Record ambient and oil temperature because viscosity affects flow and pressure readings.
Step-by-Step Field Testing Methods
1. Visual and basic functional inspection
Start with a visual check: look for external leaks, loose fittings, damaged hoses, and abnormal noise while running. Confirm control responses and note slow or weak actuators, which can indicate low flow or low pressure.
2. Pressure testing (static and dynamic)
Connect a calibrated hydraulic pressure gauge to the pump outlet or test port. With the pump running at rated RPM, measure system pressure at idle and under commanded loads (e.g., boom lift or bucket curl). Compare readings with OEM specs. Significant pressure drop under load or inability to reach relief pressure points to internal leakage, worn pump elements, or relief valve issues.
3. Flow testing and volumetric efficiency
Use a flow meter inline at a known RPM to measure output flow (L/min). Calculate volumetric efficiency: actual flow ÷ (theoretical displacement × RPM) × 100%. Low volumetric efficiency suggests internal leakage or worn components. Bench and field data together help distinguish wear from external restrictions.
4. Relief valve and control valve checks
Isolate the pump and use a test manifold to check relief valve setpoint and stability. Fluctuating or out-of-spec relief settings can mimic pump failure—always verify valve function before condemning a pump.
5. Leak-down and cavitation checks
With actuators held in position, monitor pressure decay (leak-down) to detect internal or external leakage. Listen for cavitation (a distinct rattling or sucking sound) and check inlet pressure—low suction or clogged filters can cause cavitation, reducing pump life.
Bench Testing (Removed Pump Diagnostics)
Controlled environment for definitive diagnosis
On a bench test stand you can safely apply controlled RPM and load. Measure pressure, flow, noise, temperature rise, and vibration across the pump's speed range. Bench testing reveals internal mechanical wear (piston scoring, port plate wear) and allows precise measurement of displacement and efficiency without system variables.
Advanced Diagnostic Methods
Ultrasound, vibration, thermography, and oil analysis
Supplement mechanical tests with condition monitoring tools: ultrasound detects early cavitation and internal leakage; vibration analysis identifies bearing or imbalance issues; thermography spots hotspots from friction or relief chatter. Oil analysis (particle counts per ISO 4406, water, and viscosity) shows contamination and wear-metal trends that often precede pump failure.
Interpreting Test Results and Common Fault Patterns
Symptoms, likely causes, and recommended actions
- Low pressure but good flow: likely relief valve mis-set or pressure control valve issue.
- Low flow at rated RPM: internal wear (pistons/vanes) or swash plate damage—consider overhaul or replacement.
- Rapid temperature rise: excessive internal leakage or high load conditions—check oil viscosity, cooler, and system load.
- Cavitation noise: restricted suction, clogged strainer, or low reservoir level—inspect inlet lines and filters.
- Intermittent pressure spikes: controller malfunction or relief valve chatter—perform valve bench checks.
Comparison of Common Test Methods
Choose a method based on accuracy, cost, and context
| Method | Accuracy | Portability | Typical Cost | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual & functional checks | Low | High | Low | Daily inspection, first-line diagnosis |
| Pressure & flow testing (field) | Medium–High | Medium | Medium | Confirm performance under real load |
| Bench test stand | High | Low | High | Definitive diagnosis after removal |
| Ultrasonic & vibration | High (trend-based) | Medium | Medium–High | Predictive maintenance and early fault detection |
| Oil analysis | High for contamination/wear trends | High | Low–Medium | Ongoing health monitoring |
Practical Thresholds and Expected Values
How to judge acceptable results
Always use OEM specs when possible. General guidance: if pump volumetric efficiency drops more than 10–15% from OEM values, or if there's persistent inability to reach normal system pressure under load, prepare for repair or replacement. Oil contamination of ISO 4406 code 21/19/16 or worse indicates poor filtration and accelerated wear—address contamination control first.
Maintenance Tips to Extend Pump Life
Simple habits that reduce failures
Change filters on schedule, use correct viscosity fluid, maintain reservoir cleanliness, avoid extended operation at extremely high loads, monitor for vibration/noise changes, and keep a log of pressure and flow test results to spot trends early. Proper filtration and routine oil analysis are among the most cost-effective preventative measures.
Weihuparts: How We Support Your Pump Testing and Repair Needs
Company capabilities and value
Weihuparts serves as a reliable partner for global clients in the excavator spare parts sector. We provide a comprehensive selection of excavator parts designed to support routine maintenance and high-performance systems. Our product range, engineering support, and parts availability help you minimize downtime and ensure correct replacement parts for pumps and valves. Weihuparts emphasizes quality, timely delivery, and R&D—supporting accurate diagnostics and long-term reliability.
Conclusion: A Practical Testing Roadmap
Summary action plan
To test excavator hydraulic pumps effectively: start with visual inspection and functional checks, perform pressure and flow tests in the field, verify valves and inlet conditions, and use bench testing for definitive diagnosis. Complement mechanical checks with oil analysis, thermography, and vibration monitoring for a predictive maintenance program. Use OEM specs for pass/fail judgments and keep trend data to avoid sudden failures.
FAQ
How often should I test my excavator's hydraulic pump?For active machines, perform basic visual and functional checks daily or per-shift, pressure/flow checks monthly or after noticing performance loss, and oil analysis quarterly. Adjust frequency based on machine hours, operating conditions, and historical trends.
Can I rely on field pressure tests to decide replacement?Field pressure tests help identify issues but may not reveal internal mechanical wear precisely. If results are borderline, conduct a bench test or oil analysis for a definitive decision.
What is a normal hydraulic oil temperature?Typical operating oil temperatures are 40–60°C in many climates. Repeated operation above ~80°C can accelerate oil degradation and pump wear—investigate cooling and load conditions if high temperatures persist.
Does oil contamination really affect pump life that much?Yes. Contaminants abrade internal components, reduce tolerances, and can quickly degrade pump performance. Maintaining ISO 4406 cleanliness levels recommended by the OEM helps maximize pump life.
When should I choose overhaul versus replacement?Choose overhaul when core components (housing, shafts) are in good condition and repair costs are significantly lower than replacement. Replace when damage is extensive, parts availability is limited, or downtime cost favors a new unit. Use bench test data and cost analysis to decide.
Sources and References
- Parker Hannifin — Hydraulics service and maintenance literature
- Bosch Rexroth — Pump testing and troubleshooting guides
- Hydraulics & Pneumatics magazine — articles on pump diagnostics and predictive maintenance
- Machinery Lubrication — oil analysis and contamination control guidance
- ISO 4406 — Hydraulic fluid contamination code standard
- Industry technical bulletins from leading OEMs on pump performance and testing

Choosing the Right Hydraulic Pump for Doosan DX65
Hydraulic Pump Performance Metrics to Track in 2026

Partnering with Suppliers for 336D Hydraulic Pump Supply
How Hydraulic Pump Efficiency Impacts Excavator Performance 2026
FAQ
Are your parts compatible with all excavator brands?
Weihuparts strives to offer parts compatible with a wide range of excavator brands and models. However, we recommend checking the product specifications or consulting with our team to ensure compatibility with your specific excavator.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
Do you provide warranties on your products?
Yes, we stand by the quality of our products. Most parts come with a warranty that covers manufacturing defects. Please refer to the specific warranty information provided with your purchase or contact our customer service team for details.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
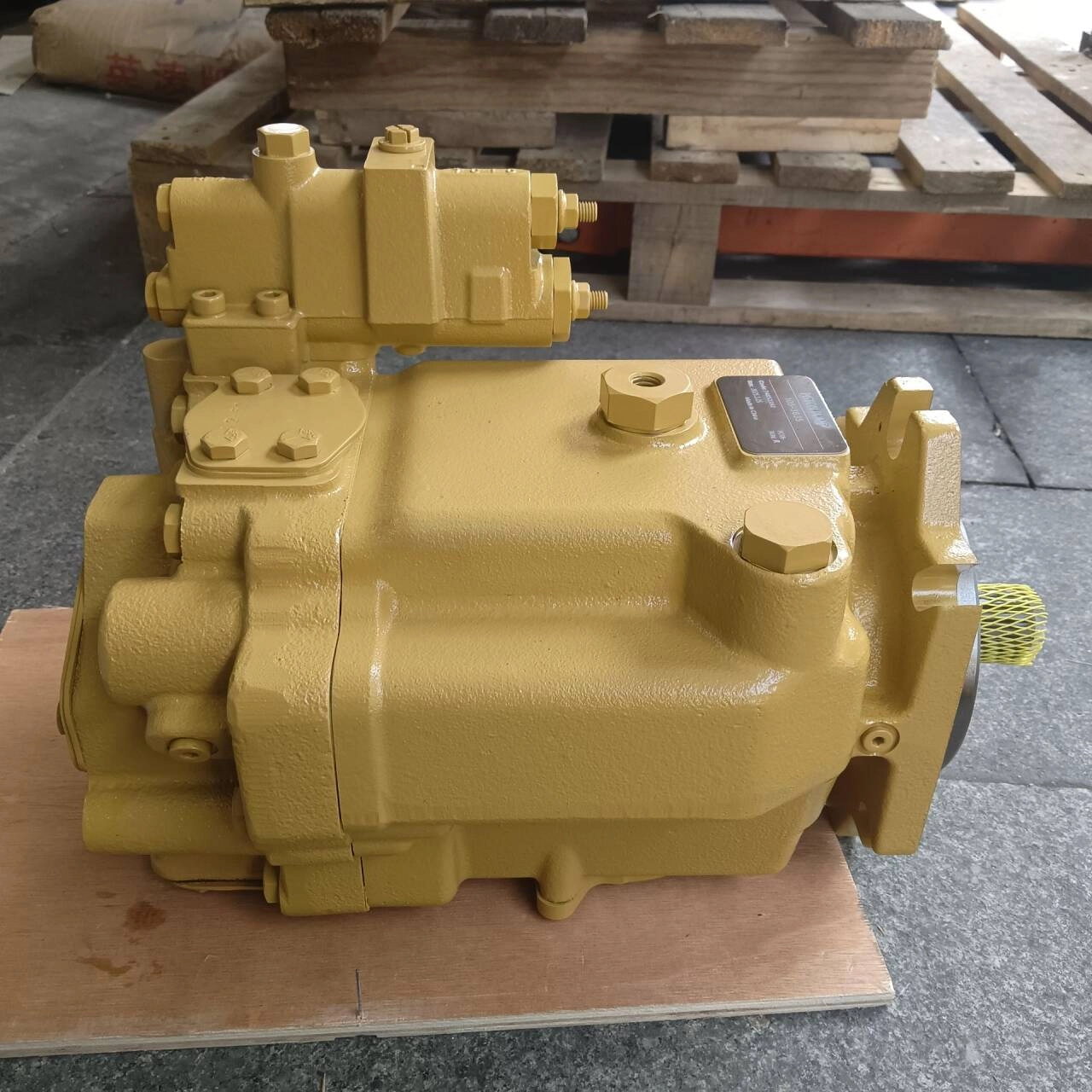

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
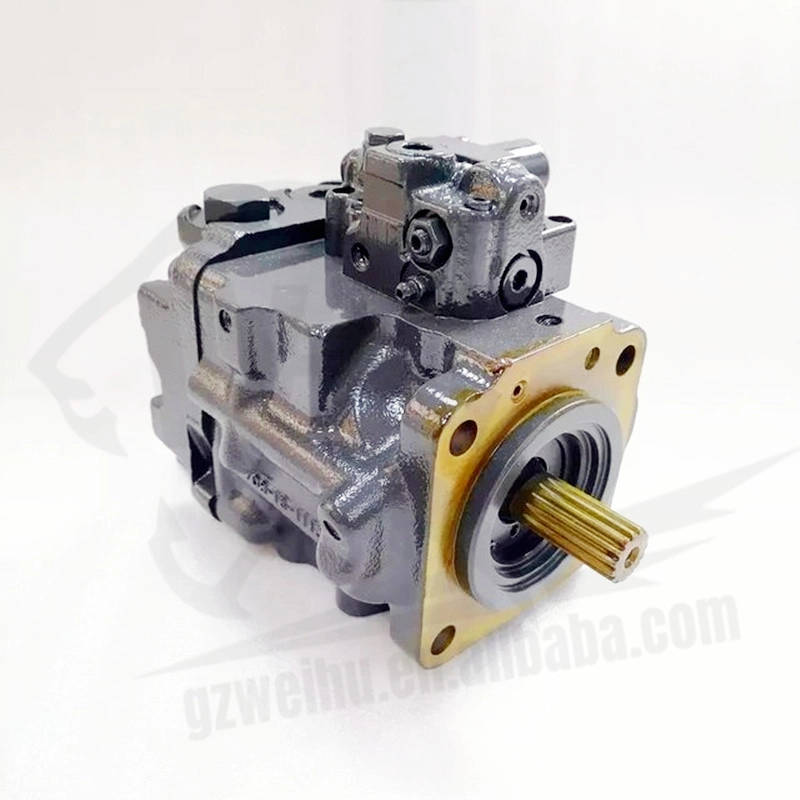

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

