jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Signs Your Excavator Hydraulic Pump Needs Replacement
- Signs Your Excavator Hydraulic Pump Needs Replacement
- Why Excavator Hydraulic Pumps Fail
- Top Signs Your Excavator Hydraulic Pump Needs Replacement
- 1. Loss of Hydraulic Pressure or Weak Performance
- 2. Intermittent or Erratic Movements
- 3. Unusual Noise: Whine, Squeal, or Rattling
- 4. Rising System Temperature
- 5. Visible Fluid Leaks or External Damage
- 6. Metal Particles or Contaminants in Hydraulic Oil
- 7. Increased Fuel Consumption or Engine Overloading
- Diagnosing Pump Problems: Practical Steps
- 1. Check Hydraulic Fluid and Filters
- 2. Pressure and Flow Tests
- 3. Temperature and Noise Monitoring
- 4. Oil Analysis and Particle Inspection
- 5. Visual and Mechanical Inspection
- Symptoms, Likely Causes, and Immediate Actions
- Repair vs Replace: How to Decide
- When to Repair/Overhaul
- When to Replace
- Cost and Replacement Options
- Maintenance Tips to Extend Pump Life
- How Weihuparts Can Help
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Signs Your Excavator Hydraulic Pump Needs Replacement
Hydraulic pumps are the heart of any excavator. When a pump starts to fail, productivity drops and repair costs rise quickly. This guide explains the most reliable signs your excavator hydraulic pump needs replacement, how to diagnose issues, estimated costs, and preventive measures to extend pump life. It also explains how Weihuparts can support your parts and replacement needs.
Why Excavator Hydraulic Pumps Fail
Understanding the common failure modes helps interpret symptoms. Pumps typically fail from contamination (dirt, water, metal particles), cavitation (air entering the system), overheating, excessive wear from high hours, and improper maintenance. Under heavy use, service life varies widely—many pumps last several thousand hours (commonly 3,000–6,000 hours in heavy applications), but life depends on operating conditions and maintenance.
Top Signs Your Excavator Hydraulic Pump Needs Replacement
1. Loss of Hydraulic Pressure or Weak Performance
If boom, arm, or bucket movements become slower, weaker, or lose holding power despite proper engine RPM, the pump may be losing internal volumetric efficiency. Persistent low pressure readings on the system gauge under expected load indicate pump wear or internal leakage in the pump.
2. Intermittent or Erratic Movements
Jerky, unpredictable motion or components moving at uneven speeds can indicate internal slipping in the pump or contaminated control valves due to deteriorating pump internal parts.
3. Unusual Noise: Whine, Squeal, or Rattling
New or abnormal whining, singing, or rasping noises from the hydraulic pump often point to cavitation or worn bearings/gears inside the pump. Cavitation occurs when air enters the suction side or oil vaporizes due to high temperatures or restrictions, producing a distinct ‘marbles in a can’ sound.
4. Rising System Temperature
If hydraulic oil temperature is running above normal operating range despite adequate cooling (typical excavator systems often operate between 60–85°C), the pump could be inefficient or causing excessive internal friction. Overheating accelerates wear and degrades hydraulic fluid.
5. Visible Fluid Leaks or External Damage
Leaks at pump seals, ports, or flange connections, or damaged pump housing indicate mechanical failure or seal breakdown. While some leaks can be patched, significant leaks or housing cracks usually require pump overhaul or replacement.
6. Metal Particles or Contaminants in Hydraulic Oil
Finding metal shavings in hydraulic oil or filters means internal component wear — a strong indicator that pump replacement should be considered. Regular oil analysis will detect this early and help decide repair vs replacement.
7. Increased Fuel Consumption or Engine Overloading
A failing pump can force the engine to run harder to maintain hydraulic output, causing higher fuel use. If fuel consumption rises without other causes, inspect hydraulic system performance and pump condition.
Diagnosing Pump Problems: Practical Steps
Follow a structured diagnosis to confirm the pump is the root cause before replacing it. This reduces unnecessary parts and downtime.
1. Check Hydraulic Fluid and Filters
Inspect oil level, color, smell, and perform a particle count. Replace filters and correct fluid issues before concluding pump failure; contamination often masks or causes pump symptoms.
2. Pressure and Flow Tests
Use a calibrated pressure gauge to measure system pressures at the pump outlet and test flow rate with a flow meter. Compare readings to OEM specifications—significant deviations point to pump wear.
3. Temperature and Noise Monitoring
Measure operating temperatures across cycles. Use listening tools (stethoscope or sonic probe) to locate noise sources—noise from the pump versus control valves helps isolate the issue.
4. Oil Analysis and Particle Inspection
Send a sample for lab analysis (spectrometric analysis and particle count). High iron or bronze particles indicate internal wear; water or glycols indicate contamination that can damage a pump.
5. Visual and Mechanical Inspection
Inspect pump mounts, couplings, drive connections, and suction lines. Restricted suction hoses, collapsed lines, or loose couplings can mimic pump failure.
Symptoms, Likely Causes, and Immediate Actions
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Immediate Diagnostic Action |
|---|---|---|
| Low pressure under load | Internal pump wear or relief valve problem | Pressure test at pump outlet; inspect relief valve setting |
| Whining/cavitation noise | Suction restriction or cavitation | Check suction lines, strainer, tank return; inspect fluid level |
| Overheating | High internal friction, poor cooling, contaminated oil | Measure temps, check cooler, change oil and filters |
| Metal particles in oil | Internal component wear | Oil analysis; consider pump teardown or replacement |
Repair vs Replace: How to Decide
Decisions should be guided by severity, cost, downtime, and availability of remanufactured options.
When to Repair/Overhaul
Minor issues (rebuildable damage, seal failures, bearing replacement) with diagnosed internal parts intact may be cost-effective to overhaul. Rebuilds are sensible if the pump body and critical components are in good condition and OEM reman parts are available.
When to Replace
Replace the pump if there is extensive internal wear (metal particles, scoring), cracked housing, repeated failures, or if downtime needs to be minimized and a tested reman/new unit can be installed quickly. Modern remanufactured pumps often carry warranties and can provide near-new performance.
Cost and Replacement Options
Costs vary by model, excavator size, and whether you choose new, remanufactured, or repair services. Typical ranges (approximate):
- New OEM pump: $2,000–$6,000+
- Remanufactured pump: $800–$3,000
- Overhaul service (parts + labor): $500–$2,500
- Labor and diagnostic fees: $200–$1,500 depending on access and hours
Choose remanufactured or new units based on warranty, lead time, and budget. Weihuparts supplies high-quality replacement parts and can advise on appropriate options for your model.
| Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| New OEM pump | Highest reliability, full warranty | Highest cost, longer lead time |
| Remanufactured pump | Lower cost, faster availability, warranty possible | Variable quality—choose reputable supplier |
| Overhaul/repair | Lowest immediate cost if limited damage | May not restore full performance; recurrence risk |
Maintenance Tips to Extend Pump Life
Routine maintenance is the most cost-effective way to avoid premature pump replacement.
- Follow OEM fluid change intervals—many manufacturers recommend 1,000–2,000 hours or annual checks, depending on use.
- Use correct hydraulic fluid grade and high-quality filters; replace filters regularly.
- Maintain proper fluid level and ensure suction lines are clean and unrestricted.
- Keep the cooling system and oil cooler clean to prevent overheating.
- Perform periodic oil analysis for early detection of wear particles.
- Address small leaks and abnormal noises quickly to prevent cascading damage.
How Weihuparts Can Help
Weihuparts serves as a reliable partner for global clients in the excavator spare parts sector. We supply a broad range of excavator hydraulic pumps, remanufactured units, and compatible components designed to meet operational needs. Weihuparts emphasizes quality, cost-effectiveness, timely delivery, and R&D-driven improvements to ensure parts meet modern performance and durability expectations. If diagnostics point to replacement, our team can recommend the best option—new, remanufactured, or compatible replacement—based on your model and budget.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs your excavator hydraulic pump needs replacement—loss of pressure, unusual noise, overheating, contamination, or erratic motion—allows you to act before a small problem becomes a major failure. Use structured diagnostic steps (fluid checks, pressure and flow testing, oil analysis) to confirm pump condition. Weigh repair vs replacement based on severity, cost, and downtime. Regular maintenance (correct fluid, filter changes, cooling care) is the best defense. For quality replacement parts and expert guidance, Weihuparts offers solutions to keep your excavator running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long should an excavator hydraulic pump typically last?A: Pump lifespan varies by model and operating conditions. Under normal service, many pumps last several thousand hours—commonly 3,000–6,000 hours in heavy applications—but proper maintenance can extend that significantly.
Q: Can a noisy hydraulic pump be fixed without replacing it?A: Sometimes. If noise is caused by suction restriction, cavitation, or loose fittings, correcting those issues can stop the noise. If noise results from internal wear or damaged components, a rebuild or replacement is usually necessary.
Q: What is the quickest way to diagnose a failing pump on site?A: Start with visual fluid inspection and filter check, then perform a pressure test at the pump outlet and listen for unusual sounds. If you find metal particles in the oil or persistent low pressure, more in-depth testing and oil analysis are needed.
Q: Are remanufactured pumps a good alternative to new OEM pumps?A: Yes—remanufactured pumps often offer a cost-effective balance of performance and warranty. Choose a reputable supplier (like Weihuparts) to ensure quality reman parts and tested units.
Q: How much does it cost to replace a hydraulic pump on an excavator?A: Costs vary by machine and option. Typical ranges: new OEM $2,000–$6,000+, reman $800–$3,000, and overhaul labor $500–$2,000. Always get quotes tailored to your model and region.
The excavator engine parts Cost Guide

ROI Calculations: When Power Meets Precision with SY550 6WG1

Hydraulic Pump Part Numbers and Identification Tips

Fuel Efficiency Metrics: Selecting the Best Diesel Engine
FAQ
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
Do you provide warranties on your products?
Yes, we stand by the quality of our products. Most parts come with a warranty that covers manufacturing defects. Please refer to the specific warranty information provided with your purchase or contact our customer service team for details.
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
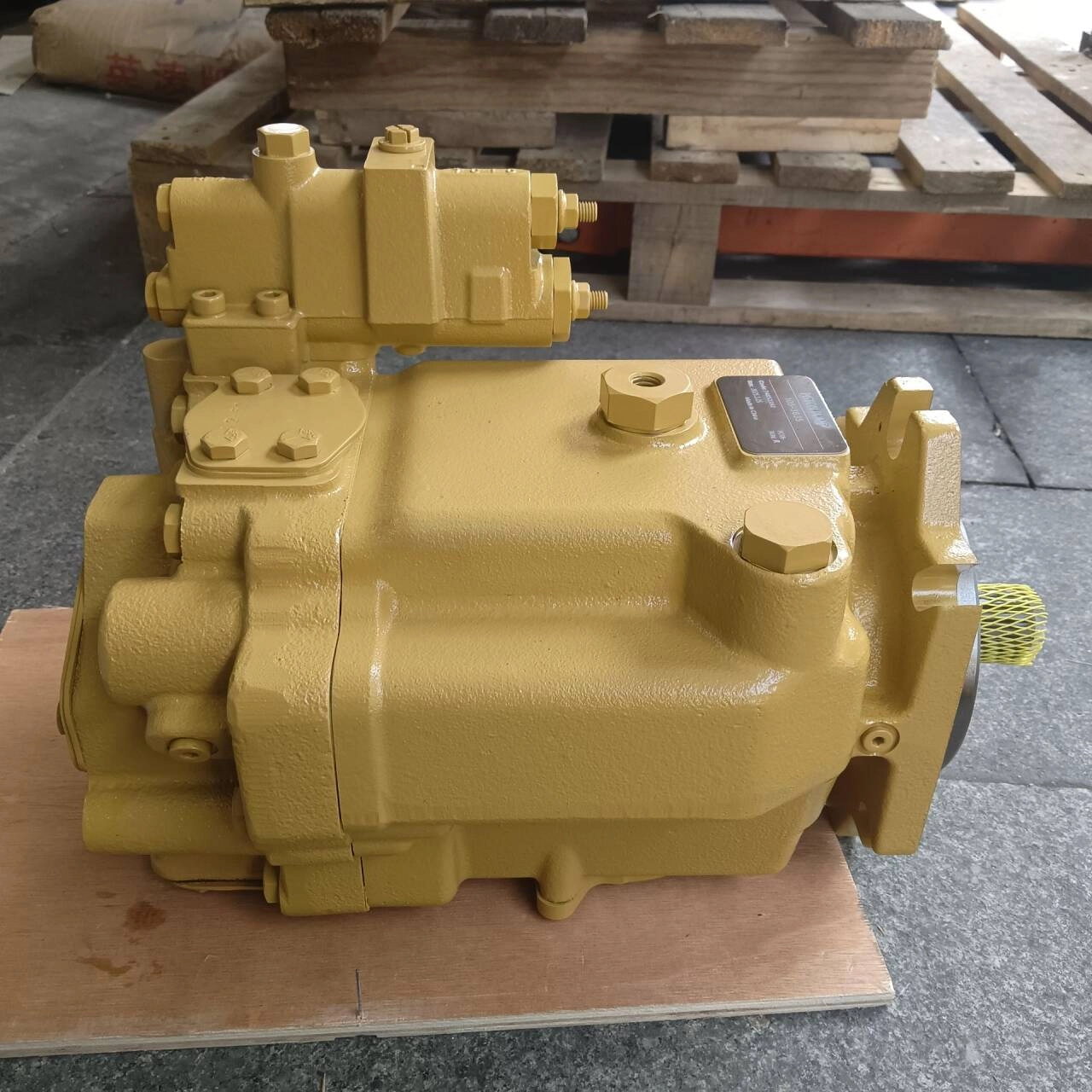

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
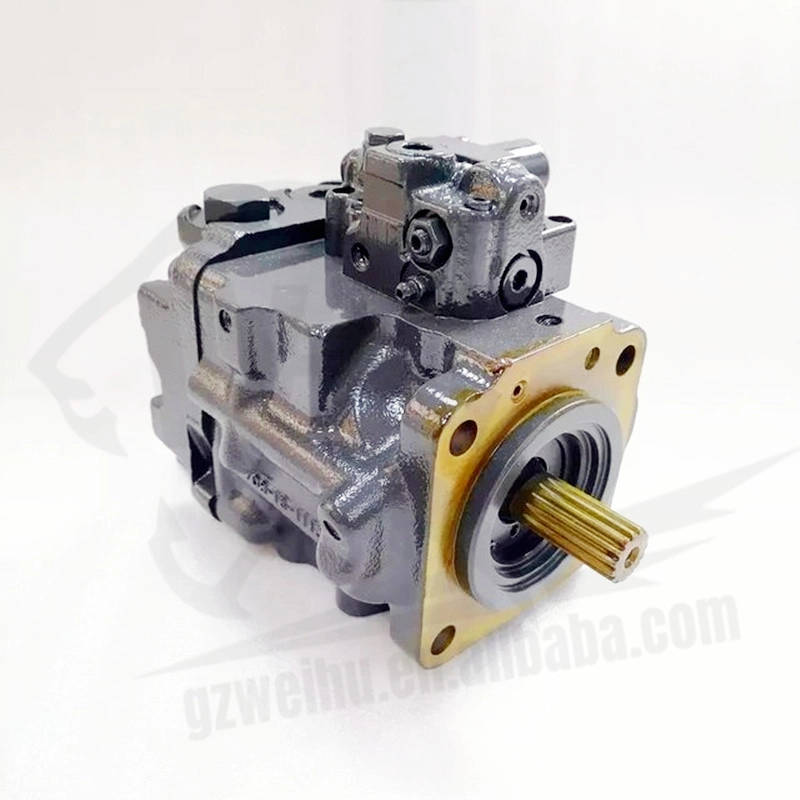

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
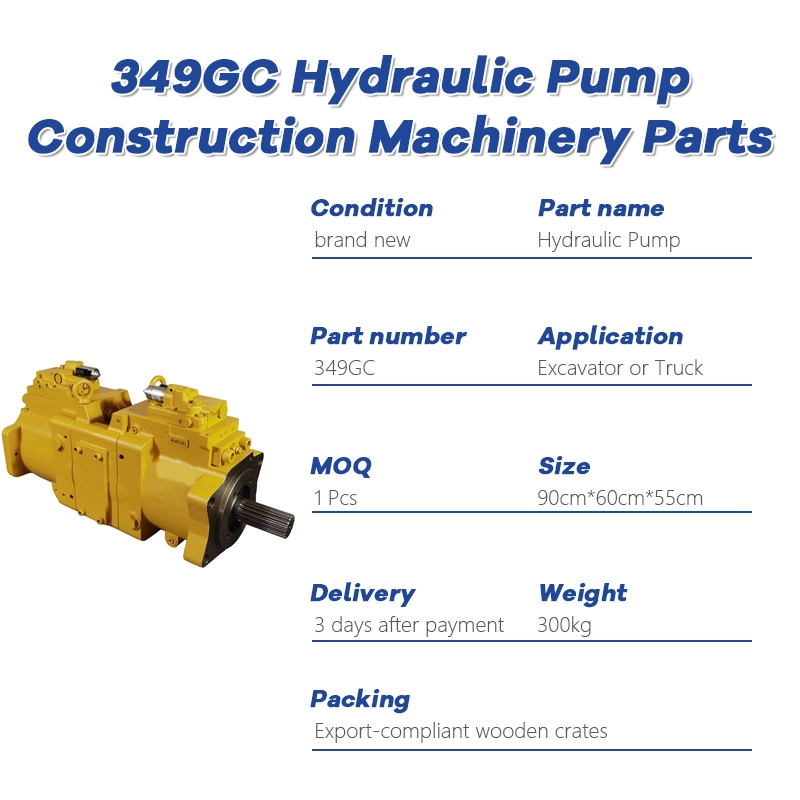
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

