jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Excavator Engine Troubleshooting: Common Problems and Solutions
- Introduction: Why Excavator Engine Troubleshooting Matters
- Protect uptime and reduce repair costs
- Common Symptoms and What They Usually Indicate
- No-start or slow cranking
- Hard starting and rough idle
- Loss of power or sluggish acceleration
- Excessive smoke (black, white, or blue)
- Overheating and coolant loss
- High fuel consumption
- Abnormal noises
- Oil, coolant, or fuel leaks and contamination
- Electrical and sensor-related faults
- Step-by-step Troubleshooting Workflow
- Safety first—protect people and equipment
- Initial visual and basic checks
- Read fault codes with proper diagnostics
- Fuel system checks
- Air intake, turbocharger, and exhaust checks
- Cooling system checks
- Lubrication system and oil checks
- Electrical and sensor verification
- When to inspect injection and mechanical components
- Knowing when to escalate
- Maintenance Best Practices and Parts to Keep On Hand
- Routine service intervals to prevent failures
- Key spare parts for rapid repairs
- Why choose Weihuparts for excavator parts
- Quick Fixes That Often Work On Site
- Simple checks that restore function fast
- Conclusion: Systematic Troubleshooting Saves Time and Money
- Follow a methodical approach and use quality parts
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction: Why Excavator Engine Troubleshooting Matters
Protect uptime and reduce repair costs
Excavator Engine Troubleshooting: Common Problems and Solutions is essential for fleet managers, operators, and service techs who must keep machines productive. Unexpected engine failures cause downtime, increase repair costs, and can create safety hazards on site. Knowing how to quickly diagnose symptoms and follow a clear troubleshooting workflow helps you get machines back to work faster while avoiding unnecessary parts replacement.
Common Symptoms and What They Usually Indicate
No-start or slow cranking
A machine that won't start is among the most urgent excavator engine problems. Typical causes include weak batteries, poor battery connections, defective starter motor, clogged fuel lines, air in the fuel system, water or microbial contamination in diesel, or locked-up fuel injectors. Start by checking battery voltage (a healthy battery typically shows ~12.6 V at rest and 24 V for dual banks) and cable condition, then confirm fuel delivery and proper compression.
Hard starting and rough idle
Hard starting and rough idle often point to fuel quality issues, clogged fuel filters, faulty injectors, air leaks in the intake, or faulty sensors (such as coolant or air temperature sensors). Dirty air filters, low fuel pressure, or incorrect engine timing can also cause uneven idling and misfires.
Loss of power or sluggish acceleration
Loss of power is frequently traced to clogged fuel filters, turbocharger problems, air intake restrictions, clogged EGR or DPF systems (on newer machines), or poor fuel quality. Mechanical issues such as low compression, worn piston rings, or valve problems are less common but more serious causes.
Excessive smoke (black, white, or blue)
Smoke color gives diagnostic clues: black smoke usually indicates excess fuel/air imbalance (dirty injectors, clogged air filter, turbo fault); white smoke often indicates unburned fuel from poor compression or fuel system leaks, or coolant entering combustion chambers; blue smoke usually points to oil burning due to worn piston rings, turbo seal failure, or valve guide wear. Correct diagnosis requires inspection of fuel, air, lubrication, and turbo systems.
Overheating and coolant loss
Overheating may be caused by clogged radiators, failed thermostats, malfunctioning water pumps, collapsed hoses, low coolant level, or heavy loads in hot environments. External causes such as blocked airflow (debris in radiator fins) are common on construction sites. Modern engines may also overheat if DPF regeneration repeatedly fails and increases exhaust temperatures.
High fuel consumption
High fuel consumption often links to inefficient combustion (bad injectors, incorrect fuel maps, turbo inefficiency), poor operator habits, or heavy idling. Emission control issues like a malfunctioning EGR or DPF that causes frequent regeneration can raise fuel burn as well.
Abnormal noises
Knocking, tapping, or loud metallic sounds can indicate injector problems, piston slap, bearing failure, or valve train wear. A whining or grinding sound near the turbo or accessory drive may signal bearing failure or accessory misalignment. Early detection through listening routines prevents catastrophic engine damage.
Oil, coolant, or fuel leaks and contamination
Leaks reduce system pressure and can lead to overheating, loss of lubrication, or fuel starvation. Fuel contamination—water, particulate matter, or microbial growth—causes injector and pump damage. Regular checks and filtration prevent many of these excavator engine problems.
Electrical and sensor-related faults
Modern excavator engines depend on electronic controls and sensors. Faulty sensors, poor CAN bus communication (J1939), damaged wiring, or a malfunctioning ECU can trigger engine derate, start problems, or incorrect behavior. Use of proper diagnostic tools and OEM wiring diagrams is important for correct troubleshooting.
Step-by-step Troubleshooting Workflow
Safety first—protect people and equipment
Before any troubleshooting, isolate power, apply wheel chocks, allow hot engines to cool, and wear PPE. Safety prevents accidental injuries when working with fuel systems, batteries, or pressurized cooling systems.
Initial visual and basic checks
Start with a visual inspection: check fluid levels (engine oil, coolant, fuel), look for leaks, inspect belts, hoses, air filter condition, and radiator fins. Confirm battery terminals are clean and tight. Small problems seen early often fix major symptoms quickly.
Read fault codes with proper diagnostics
Connect an OEM or J1939-capable diagnostic tool to read engine fault codes. Recorded codes provide direction—do not rely solely on code clearing. Use service manuals to interpret codes and freeze-frame data. Many manufacturers log limp-mode events and associated engine hours.
Fuel system checks
Inspect fuel filters and water separators—replace if uncertain. Check fuel pressure at the rail (manufacturer specs vary) and look for air in the fuel lines. If contamination is suspected, drain and inspect fuel samples. Clean or replace contaminated tanks and lines; microbial growth in diesel can be treated and a fuel polish performed.
Air intake, turbocharger, and exhaust checks
Inspect and clean air filters and housings; compression tests may reveal intake leaks. Check turbocharger for shaft play, oil leaks at seals, and damaged compressor/turbine blades. Confirm intake hoses and clamps are secure; even small leaks reduce engine efficiency severely.
Cooling system checks
Inspect radiator, cooling fan, thermostats, water pump, and coolant quality. Clean radiator fins and confirm fan operation (hydraulic or electric). Typical causes of overheating include blocked airflow, failed thermostats, or low coolant due to external leaks.
Lubrication system and oil checks
Check oil level and condition—contaminated or low oil affects bearing lubrication and turbo bearings. Oil analysis helps detect metal wear and contamination early. Replace oil and filters per recommended service intervals and use OEM-spec oils and filter media for best protection.
Electrical and sensor verification
Verify battery charge and alternator output, inspect harness connectors for corrosion, and test sensors that commonly affect performance (coolant temp, MAP, crank/cam sensors). Clean or replace corroded connectors and ensure proper grounding.
When to inspect injection and mechanical components
If basic checks don't resolve symptoms, test injectors (flow and spray pattern), fuel pump health, and perform a compression test. Low compression or injector failure typically requires workshop repair. Keep data logs and compare readings to OEM tolerance ranges.
Knowing when to escalate
If diagnostics indicate major mechanical damage (low compression, bearing failure, cracked head), contact a qualified engine rebuild specialist or the OEM dealer. For emission-system failures (DPF, EGR, SCR), consult emission control specialists to avoid noncompliant repairs.
Maintenance Best Practices and Parts to Keep On Hand
Routine service intervals to prevent failures
Recommended service intervals vary by manufacturer and operating conditions. Typical guidance: engine oil and filter changes every 250–500 operating hours in normal conditions; fuel filters inspections/replacements every 250–500 hours; air filter inspections daily on dusty sites and replacements 500–1,000 hours depending on environment; coolant and major inspections every 1,000–2,000 hours. Adjust intervals for severe service, hot climates, or heavy duty cycles.
Key spare parts for rapid repairs
Maintain a small inventory of high-failure or quick-replace items: engine oil and filters, fuel filters and water separators, air filter elements, belts, thermostats, radiator hoses, injector seals, gaskets, starter motor or solenoid, batteries, and turbo rebuild kits. Having these on hand drastically reduces downtime.
Why choose Weihuparts for excavator parts
Weihuparts serves global clients in the excavator spare parts sector with a broad selection designed for routine and high-performance engines. Weihuparts focuses on quality, cost-effectiveness, timely delivery, and continuous R&D to improve part durability and performance. Using proven spare parts from a trusted supplier avoids fitment issues and supports longer engine life, reducing the frequency of excavator engine troubleshooting tasks.
Quick Fixes That Often Work On Site
Simple checks that restore function fast
Before heavy troubleshooting, these quick fixes often solve common excavator engine problems: clean or replace air filters, tighten battery terminals, drain water separators, replace clogged fuel filters, clean radiator fins, and clear debris around the turbo and exhaust. Always record what you change so you can backtrack if needed.
Conclusion: Systematic Troubleshooting Saves Time and Money
Follow a methodical approach and use quality parts
Excavator Engine Troubleshooting: Common Problems and Solutions becomes manageable with a step-by-step workflow: start with safety, perform visual checks, read fault codes, and systematically inspect fuel, air, cooling, lubrication, and electrical systems. Preventive maintenance and quality spare parts from suppliers like Weihuparts reduce the frequency of failures. When in doubt, use OEM diagnostic tools and escalate to trained technicians for major mechanical issues. A thoughtful combination of operator care, scheduled maintenance, and the right replacement parts keeps excavators productive and reduces costly downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I check first if my excavator won't start?Check battery voltage and connections first (clean, tight terminals), then fuel supply (check water separator, fuel filters, and fuel tank), and listen for starter engagement. If batteries and fuel supply are good, read engine fault codes and test the starter and ignition circuits.
How can I tell whether smoke is caused by fuel or oil?Black smoke usually means too much fuel or poor air supply; blue smoke signals oil burning (piston rings or turbo seals); white smoke often indicates unburned fuel or coolant entering combustion. Visual inspection, injector tests, and oil analysis help confirm the cause.
How often should I replace fuel and air filters on an excavator?Typical recommendations are to inspect filters daily in dusty environments and replace fuel/air filters every 250–500 engine hours under normal use. Adjust intervals for heavy or severe operating conditions and follow OEM guidance.
Can a clogged DPF cause engine overheating or power loss?Yes. A heavily restricted diesel particulate filter (DPF) can increase exhaust backpressure, reduce engine performance, raise operating temperatures, and trigger derate. Proper DPF maintenance and correct regeneration procedures are necessary to avoid related engine problems.
When should I call a professional instead of attempting repairs myself?Call a professional if diagnostics point to low compression, internal mechanical damage, major turbo failure, or when you lack the tools to read and interpret engine control fault codes. Also consult specialists for emission-system repairs to remain compliant with regulations.
Are aftermarket parts reliable for excavator engines?Quality aftermarket parts can be reliable if sourced from reputable suppliers who use tested materials and meet OEM specifications. Weihuparts emphasizes R&D and quality control to provide durable components and timely delivery, helping maintain engine reliability while managing costs.
How can I reduce fuel contamination risks on site?Use clean storage, fill from clean dispensing systems, install water separators and coalescing filters, periodically sample and test fuel, and consider fuel polishing if contamination is detected. Keep tanks sealed and use biocides if microbial growth is identified.
What diagnostic tools are recommended for excavator engines?Use OEM service tools for brand-specific codes and parameters. For general diagnostics, J1939-capable CAN bus readers and handheld scanners are useful. Always pair tools with manufacturer service manuals and wiring diagrams for accurate troubleshooting.
How Hydraulic Pump Efficiency Impacts Excavator Performance 2026
Diesel vs Gas Excavator Engines: Pros and Cons

Troubleshooting Common Doosan DX65 Pump Issues

Benefits of OEM vs Aftermarket Hydraulic Pumps for DX65
FAQ
How can I place an order?
You can place an order through our user-friendly online platform or by contacting our sales team directly. Simply browse our catalog, select the parts you need, and follow the checkout process to complete your order.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.
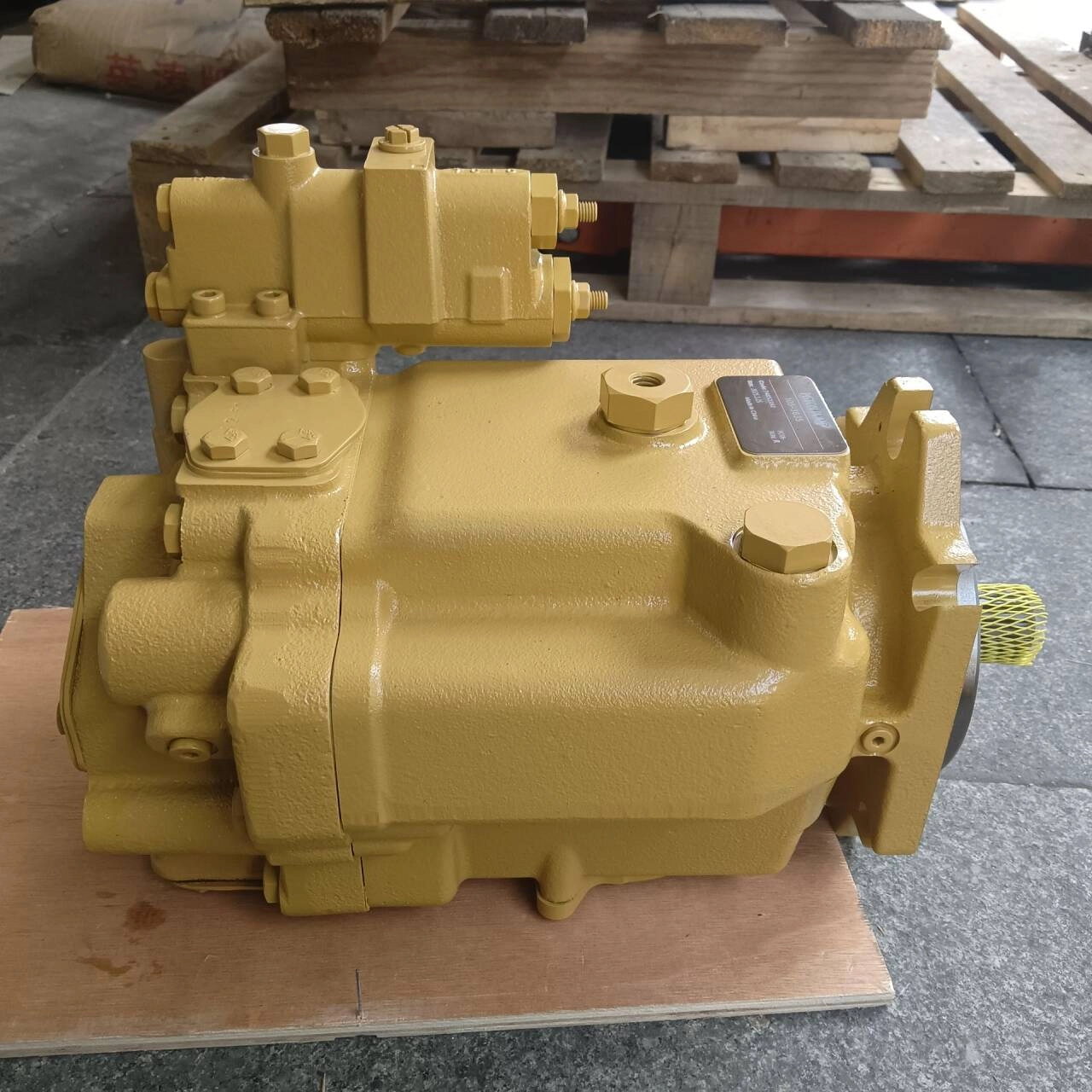

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
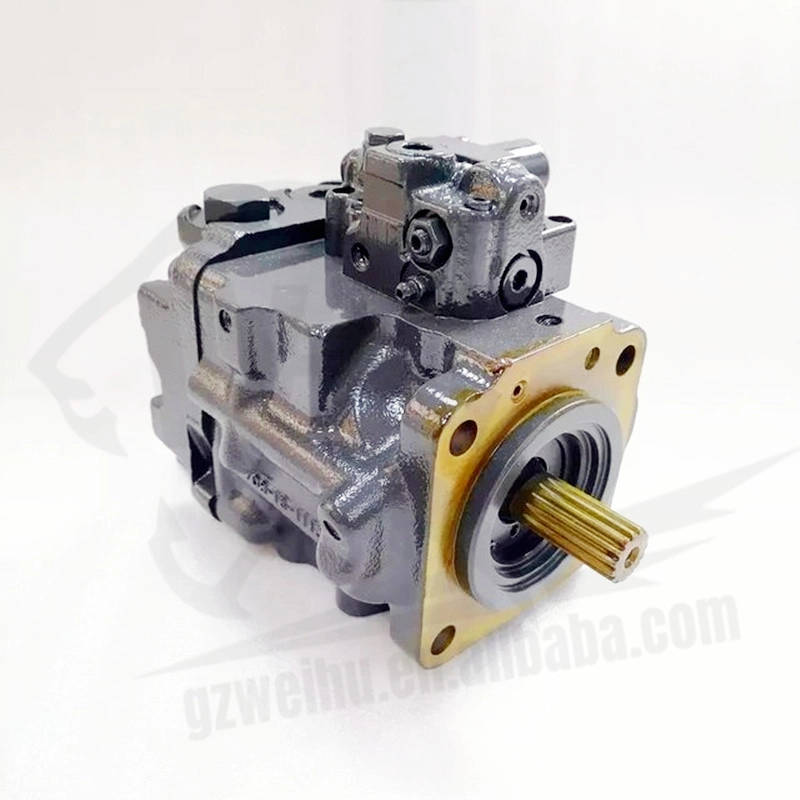

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
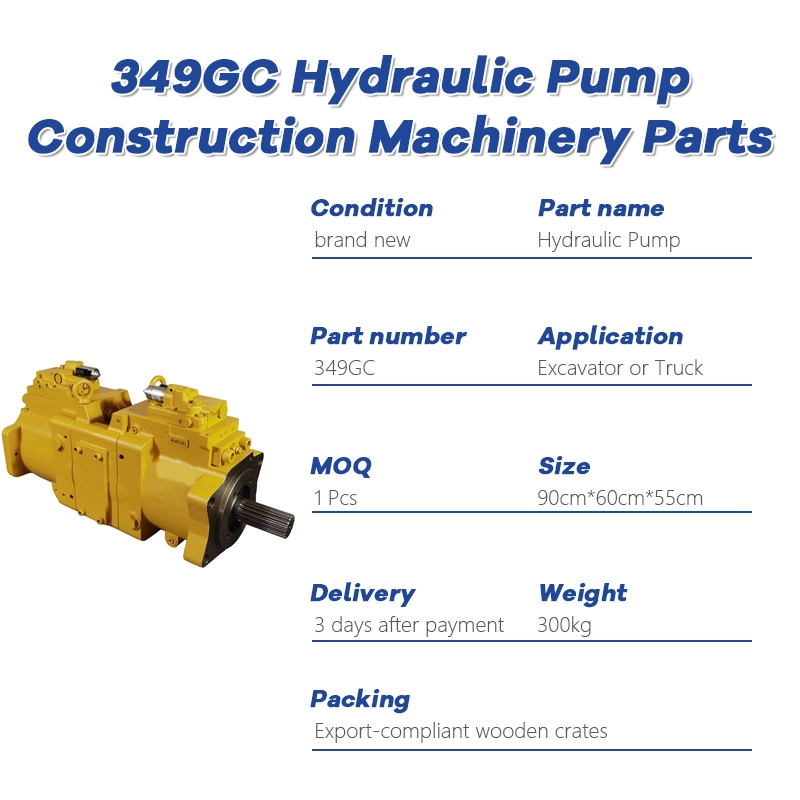
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-

