jackhuang5919@gmail.com
How to Rebuild an Excavator Engine: Step-by-Step
- How to Rebuild an Excavator Engine: Step-by-Step
- Introduction — Why rebuild an excavator engine?
- Safety first — Create a safe workspace for engine overhaul
- Tools and equipment — What you need to rebuild an excavator engine
- Parts and sourcing — Choosing quality excavator engine parts
- Documentation and preparation — Gather manuals and records
- Engine removal — Tips for safe and efficient extraction
- Disassembly — Systematic teardown of the engine
- Cleaning and inspection — What to check on each part
- Measuring and machining — When to send parts to a machine shop
- Parts replacement strategy — What must be replaced
- Reassembly — Step-by-step reassembly of the excavator engine
- Torque and seals — Critical reassembly details
- Pre-start checks — Fluids, priming, and leak inspection
- Initial start and break-in — Testing the rebuilt excavator engine
- Testing and diagnostics — Confirm performance and emissions
- Cost vs. replacement — Rebuild or replace? (Comparison)
- Maintenance after rebuild — Keep the excavator engine healthy
- Choosing a partner for parts and technical support — Why Weihuparts can help
- Common mistakes to avoid — Lessons from the field
- When to hire a professional — Complex repairs and warranty work
- Conclusion — Practical next steps for your excavator engine rebuild
- FAQ — Common questions about rebuilding an excavator engine
- Q: How long does an excavator engine rebuild take?
- Q: Is rebuilding cheaper than replacing the engine?
- Q: How much does a rebuild cost?
- Q: Can I reuse pistons, bearings, or injectors?
- Q: What is the most important step to ensure a successful rebuild?
- Q: Where can I source quality excavator engine parts?
- Q: When should I consider replacing rather than rebuilding?
How to Rebuild an Excavator Engine: Step-by-Step
Introduction — Why rebuild an excavator engine?
Rebuilding an excavator engine is a cost-effective way to restore power, reduce fuel consumption, and extend the service life of heavy equipment. Whether you’re a workshop technician or a fleet manager, a planned rebuild addresses wear items, prevents unexpected downtime, and can offer a better return than a simple repair. In this guide we use the keyword excavator engine throughout to keep the information focused on practical, real-world steps.
Safety first — Create a safe workspace for engine overhaul
Safety is the first priority when working on any excavator engine. Work in a well-ventilated, clean area with adequate lighting, a heavy-duty hoist/crane, engine stand, and a fire extinguisher. Use personal protective equipment (PPE): safety glasses, gloves, steel-toed boots, and hearing protection where required. Disconnect batteries and isolate fuel and hydraulic systems before beginning removal.
Tools and equipment — What you need to rebuild an excavator engine
A successful rebuild requires the right tools. Basic items include an engine crane, torque wrenches, micrometers, plastigage, feeler gauges, dial indicator, ring compressor, piston ring filer (if needed), valve spring compressor, bearing pullers, ultrasonic cleaner or parts washer, and a calibrated hydraulic press. Also prepare consumables: gasket sets, main and rod bearings, piston rings, seals, oil, coolant, and assembly lube. Using proper tools improves accuracy and reduces rework.
Parts and sourcing — Choosing quality excavator engine parts
Sourcing reliable parts is key. For excavator engine rebuilds, choose OEM or high-quality aftermarket components: complete gasket kits, pistons, liners (if applicable), bearings, timing components, injectors, and oil pumps. Weihuparts serves as a reliable partner for global clients in the excavator spare parts sector and provides a comprehensive selection tailored to many engine families. Buying proven parts reduces failures after reassembly.
Documentation and preparation — Gather manuals and records
Before teardown, obtain the specific service manual and torque specifications for the excavator engine model. Record engine serial numbers, operating hours, and failure symptoms. Photograph connection points, wiring harness routing, and mounting orientations to speed reassembly. Label parts and fasteners in containers or bags to maintain order.
Engine removal — Tips for safe and efficient extraction
Removing the excavator engine requires planning. Drain fluids (oil, coolant, fuel) into approved containers. Remove ancillary components: alternator, starter, intake and exhaust manifolds, radiators, and controls. Use slings and an engine hoist rated above the engine weight. Lift steadily and place the engine onto a stable engine stand for teardown. A clean, flat surface prevents damage to mating faces and components.
Disassembly — Systematic teardown of the engine
Disassemble in an organized sequence: timing gear/chain, valve train, cylinder head(s), oil pan, oil pump, front and rear covers, and finally the crankcase internals. Inspect and tag each component. Keep fasteners from each subassembly together. Clean as you go to make inspection easier and to prevent cross-contamination between parts.
Cleaning and inspection — What to check on each part
Thorough cleaning helps reveal cracks, wear, and corrosion. Use a parts washer or ultrasonic cleaner for non-electrical components. Inspect the cylinder bores for scoring and taper, pistons for ring land damage, connecting rods for bend/twist, crank journals for wear, and the crankshaft for cracks using magnaflux if available. Check cylinder head valves, seats, and guides. Replace or machine components that are beyond service limits in the engine manual.
Measuring and machining — When to send parts to a machine shop
Measure tolerances with micrometers, bore gauges, and dial indicators. Common decisions include: hone or sleeve cylinder bores, grind or polish crankshaft journals, align-bore or align-hone the block, and pressure-test the cylinder head. If journals or bores exceed service limits, machining or replacement is necessary. Typical machining tasks extend component life but add time and cost; plan lead times accordingly.
Parts replacement strategy — What must be replaced
Replace wear items during every rebuild: piston rings, main and rod bearings, all seals and gaskets, timing components, oil pump (recommended), fuel injectors (test or replace), and filters. Consider replacing turbochargers and injectors if they show loss of performance. Investing in quality parts reduces repeat work and post-rebuild warranty claims.
Reassembly — Step-by-step reassembly of the excavator engine
Reassembly must be clean and methodical. Use assembly lube on bearings and cam lobes. Install pistons with the correct ring orientation and gap position. Torque main caps and rod bolts in the correct sequence and to the specified torque. Reinstall the cylinder head with a new gasket, following the prescribed torque and angle steps. Refit timing gear/chain with correct timing marks. Reconnect oil pump, covers, manifolds, and accessories. Keep documentation and photos handy to verify routing and connections.
Torque and seals — Critical reassembly details
Always use a calibrated torque wrench and the engine manual’s torque values. Replace torque-to-yield bolts as recommended. Use proper sealants only where specified; overuse can clog oil passages. Apply correct lubricants and use thread lockers per manufacturer specs. Correct torque and sealing prevent leaks and catastrophic failures.
Pre-start checks — Fluids, priming, and leak inspection
Before starting, fill with new oil and coolant and prime the oil system if possible. Crank the engine without starting (using starter) to build oil pressure and verify circulation. Inspect for leaks, unusual noises, or abnormal fluid conditions. Verify fuel system priming and bleed air from injectors if required. Double-check wiring and sensor connections before initial firing.
Initial start and break-in — Testing the rebuilt excavator engine
On first start, monitor oil pressure, coolant temperature, and exhaust. Keep RPMs low and avoid heavy loads during the break-in period (typically the first 50–100 operating hours). Change oil and filter after the initial break-in short interval (commonly 10–25 hours) to remove machining debris. Follow the manufacturer-recommended break-in procedure for ring and bearing seating to ensure longevity.
Testing and diagnostics — Confirm performance and emissions
Run a road or function test under controlled conditions. Measure oil pressure, fuel consumption, and exhaust smoke. Use diagnostic tools to verify engine control module readings, injection timing, and boost levels. Compare performance metrics to factory specifications. Address any imbalance, misfire, or leak promptly to avoid larger issues.
Cost vs. replacement — Rebuild or replace? (Comparison)
Deciding whether to rebuild or replace hinges on cost, downtime, and long-term needs. The table below shows typical ranges; actual costs vary by engine model, size, and region.
| Option | Typical Cost Range (USD) | Downtime | Expected Life After Work |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rebuild (overhaul) | $5,000 – $25,000 | 1–4 weeks | 3,000 – 10,000+ hours (with quality parts) |
| Remanufactured replacement | $15,000 – $60,000 | 1–3 weeks | 5,000 – 15,000+ hours |
| New engine | $30,000 – $120,000+ | 2–6 weeks | 10,000+ hours (manufacturer warranty) |
Maintenance after rebuild — Keep the excavator engine healthy
After a rebuild, establish a strict maintenance schedule: oil and filter changes based on hours and operating conditions, scheduled fuel and air filter replacements, coolant system checks, and periodic valve and injection timing inspections. Record maintenance activities and monitor fluids for contamination. Preventative maintenance preserves the investment from the rebuild.
Choosing a partner for parts and technical support — Why Weihuparts can help
For reliable parts and technical support during a rebuild, partner with a supplier that understands excavator engine needs. Weihuparts focuses on quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery for excavator spare parts. Their R&D and engineering teams develop durable components that meet industry standards, helping workshops complete rebuilds with confidence and minimize post-rebuild failures.
Common mistakes to avoid — Lessons from the field
Common rebuild mistakes include skipping proper measurements, reusing critical wear parts, improper torquing, inadequate cleaning, and rushing the break-in process. Avoid these by following the service manual, using quality parts, and performing careful inspections. When in doubt, consult experienced technicians or the parts supplier for guidance.
When to hire a professional — Complex repairs and warranty work
Large engines, cracked blocks, and head resurfacing or complex fuel-system calibrations often require professional machine-shop work or OEM-level support. If the rebuild affects warranty coverage for a machine or involves specialized calibration (e.g., electronic high-pressure common-rail systems), use certified professionals to protect your investment and ensure compliance with emissions rules.
Conclusion — Practical next steps for your excavator engine rebuild
Rebuilding an excavator engine is a structured process: prepare, document, disassemble, inspect, measure, machine where needed, replace wear parts, and reassemble with correct torque and seals. With the right parts partner and disciplined procedures, a rebuild can restore performance and extend engine life while controlling costs. Contact parts specialists like Weihuparts to source reliable components that fit your rebuild plan.
FAQ — Common questions about rebuilding an excavator engine
Q: How long does an excavator engine rebuild take?
A: Typical turnaround is 1–4 weeks for a standard overhaul, depending on machine size, parts availability, and machining needs. Complex or large engines may take longer.
Q: Is rebuilding cheaper than replacing the engine?
A: Generally yes — rebuilding is usually less expensive than buying a new engine. However, if the block or crankshaft is irreparably damaged, replacement may be more economical long-term.
Q: How much does a rebuild cost?
A: Costs vary by engine size and condition; typical ranges are $5,000–$25,000 for an overhaul. Always get a detailed estimate including parts, labor, and machining.
Q: Can I reuse pistons, bearings, or injectors?
A: Bearings, piston rings, and seals should be replaced. Pistons and injectors may be reused if within service limits and tested, but replacement is often recommended to ensure reliability.
Q: What is the most important step to ensure a successful rebuild?
A: Accurate measurement and inspection combined with quality parts and correct torque procedures. Follow the engine service manual closely and use calibrated tools.
Q: Where can I source quality excavator engine parts?
A: Trusted suppliers like Weihuparts supply a broad selection of excavator spare parts, backed by engineering support. Choose suppliers with proven quality control and parts traceability.
Q: When should I consider replacing rather than rebuilding?
A: Consider replacement if repair costs approach the price of a remanufactured or new engine, or when structural components (block/crank) are damaged beyond service limits.
Common Hydraulic Pump Problems and How to Fix Them
Where to Buy excavator engine parts
Hydraulic Pump Noise: Causes and How to Fix It
The B2B Buyer’s Guide to electric hydraulic pump
FAQ
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
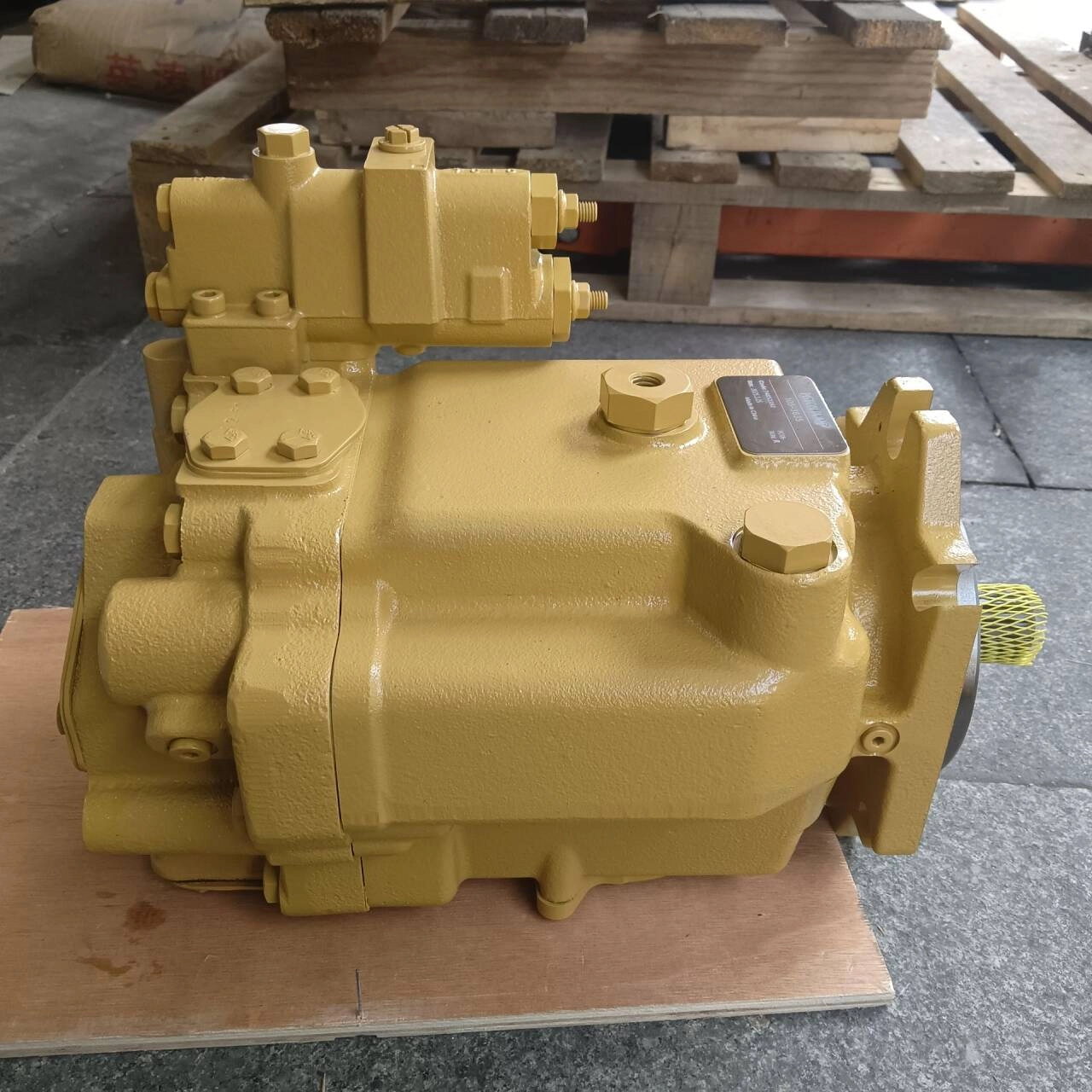

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
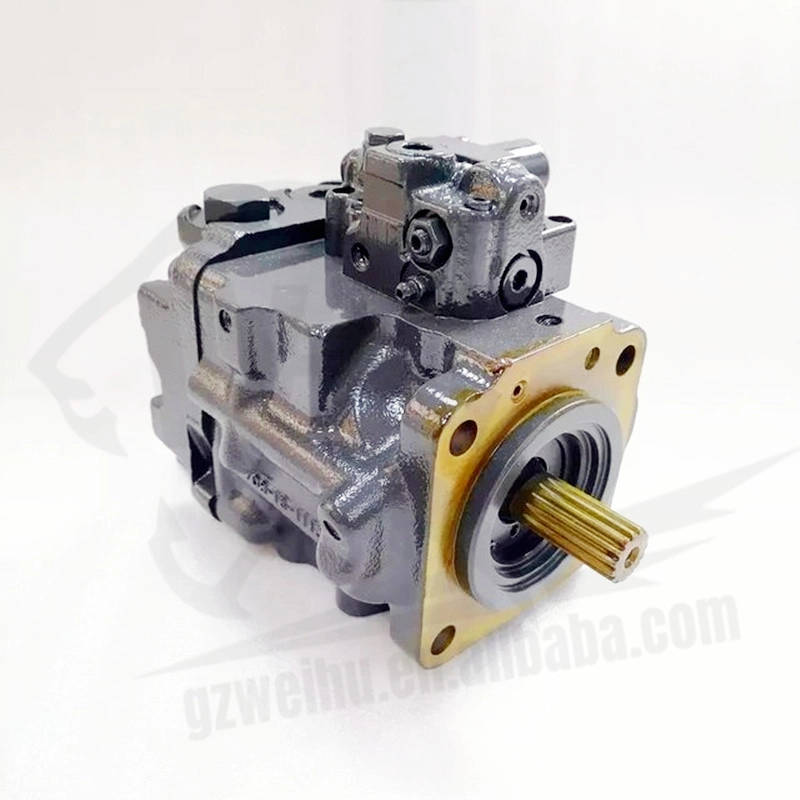

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
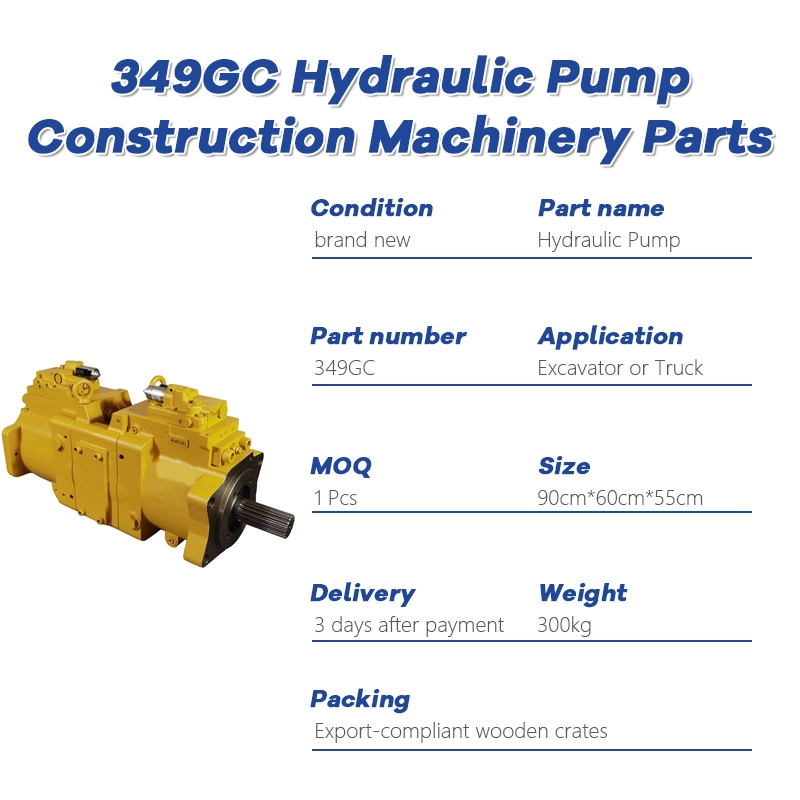
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

