jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Hydraulic Pump Troubleshooting: Low-Pressure Solutions for Excavators
- Hydraulic Pump Troubleshooting: Low-Pressure Solutions
- Why low hydraulic pressure matters for excavator performance
- Common causes of low hydraulic pump pressure
- Types of pumps and how they respond to low-pressure issues
- Safety first: tools and precautions
- Step-by-step diagnostic workflow
- 1. Confirm symptom and baseline readings
- 2. Inspect for visible leaks and condition of hydraulic fluid
- 3. Check suction side for cavitation or air entrainment
- 4. Test relief valve and pressure compensator
- 5. Measure pump flow under load
- 6. Isolate control valves and actuators
- 7. Check hydraulic temperature and fluid viscosity
- Common fixes and low-pressure solutions
- When to replace the pump vs. repair components
- Preventive maintenance to avoid low-pressure events
- How Weihuparts supports low-pressure repairs
- Conclusion: restore pressure methodically to minimize downtime
- Practical checklist for field troubleshooting
- Further reading and resources
- Frequently Asked Questions
Hydraulic Pump Troubleshooting: Low-Pressure Solutions
Low hydraulic pressure on an excavator reduces digging power, slows cycle times, and can lead to premature component wear. This guide provides practical, field-tested troubleshooting steps to identify causes and implement effective low-pressure solutions. It’s written for operators, maintenance technicians, and fleet managers who need clear, action-oriented guidance supported by industry best practices.
Why low hydraulic pressure matters for excavator performance
Hydraulic systems on excavators convert engine power into controlled motion. Typical working pressures for modern excavators range from roughly 2,500 to 3,500 psi (17 to 24 MPa) for main hydraulic circuits, depending on machine size and design. When pressure drops below expected values, output force and speed fall off, leading to lost productivity and possible safety risks.
Common causes of low hydraulic pump pressure
Understanding the likely causes lets you focus diagnostic time wisely. Frequent causes include:
- Worn or damaged pump internals (gear, vane, piston wear)
- Cavitation and air entrainment in the suction line
- Suction-side restrictions or clogged filters
- Relief valve set incorrectly or stuck/bleeding
- External or internal leaks in valves, hoses, fittings, or actuators
- Wrong fluid viscosity or fluid contamination
- Overheating causing viscosity drop and component wear
- Control valve malfunction or wrong load-sensing signals
Types of pumps and how they respond to low-pressure issues
Different pump types show different failure modes. Use the table below to match symptoms with pump characteristics when diagnosing.
| Pump Type | Typical Max Pressure | Efficiency | Common Low-Pressure Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Pump | up to ~3,000 psi (20.7 MPa) | Moderate | Low flow at all loads, noisy operation when worn |
| Vane Pump | up to ~2,000 psi (13.8 MPa) | Good at moderate pressures | Variable flow, fluttering noise, sensitive to contamination |
| Piston Pump | up to ~5,000 psi (34.5 MPa) | High | Loss of peak pressure under heavy load, internal leakage |
Safety first: tools and precautions
Before testing, ensure safety: shut off the engine when installing gauges, relieve system pressure, and wear PPE (eye protection, gloves). Use pressure gauges rated above system maximum. Common tools: quality hydraulic pressure gauge, flow meter (if available), thermometer, hand vacuum gauge for suction testing, and inspection mirror.
Step-by-step diagnostic workflow
1. Confirm symptom and baseline readings
Record system pressures at idle and full engine rpm using a pressure gauge on the pump outlet and on main circuit test ports. Compare readings to the machine’s specifications in the operator manual (typical target ranges: 2,500–3,500 psi or 17–24 MPa for many excavators).
2. Inspect for visible leaks and condition of hydraulic fluid
Check hoses, fittings, cylinders, and control valves for external leaks. Inspect fluid level, color, smell, and presence of metal particles. Contaminated or degraded fluid should be replaced and the system flushed per manufacturer guidance.
3. Check suction side for cavitation or air entrainment
Cavitation creates a knocking noise and reduces pump pressure. Inspect suction hoses for cracks, loose clamps, collapsed lines or clogged strainers. Ensure tank vent is not blocked and fluid level is adequate—low tank level can draw in air. Use a vacuum gauge to test suction; values beyond manufacturer limits indicate restriction.
4. Test relief valve and pressure compensator
Incorrect relief valve settings or a malfunctioning pressure compensator can bleed off pressure. With a calibrated gauge, verify relief valve setpoint and observe for fluctuations. If the valve is sticky or worn, service or replace it.
5. Measure pump flow under load
Low flow at nominal RPM indicates internal pump wear or slipping. A flow meter at the pump outlet or temporary return-line flow test can quantify flow loss. If flow is significantly below spec yet engine rpm is correct, pump internals or clearances may be degraded.
6. Isolate control valves and actuators
Internal leaks in directional/control valves or cylinders can mimic pump low-pressure symptoms. Use isolation procedures (block valve tests) to determine whether pressure drop occurs at the pump or downstream components.
7. Check hydraulic temperature and fluid viscosity
High temperatures lower fluid viscosity and reduce pressure. Measure operating fluid temperature—typical operating range is 40–80°C (104–176°F) for many systems. If the system runs hotter, investigate cooler efficiency, fan operation, or excessive internal leakage.
Common fixes and low-pressure solutions
Based on diagnosis, apply targeted repairs:
- Replace worn pump (or rebuild) if internal wear or excessive internal leakage is identified.
- Repair suction leaks: replace cracked hoses, clamp fittings, or clean suction strainer.
- Replace or service relief valves and pressure compensators that are out of adjustment or leaking.
- Change contaminated hydraulic fluid and filters; perform a system flush if particles or varnish are present.
- Repair or replace leaking control valves, hoses, or cylinder seals.
- Improve cooling and cooling system maintenance to keep viscosity in range.
When to replace the pump vs. repair components
Choose pump replacement when measured flow and pressure fall well below specification and component-level repairs (valves, hoses, filters) don’t correct the problem. Rebuilding a piston pump is often cost-effective for high-value units; gear pumps are commonly replaced. Weihuparts offers a range of high-quality replacement pumps, seals, and valve spools to support repairs and minimize downtime.
Preventive maintenance to avoid low-pressure events
Preventive actions reduce the chance of low-pressure failures:
- Follow scheduled fluid and filter changes (many manufacturers recommend 1,000–2,000 operating hours for hydraulic fluid checks; follow OEM intervals).
- Regularly inspect hoses, fittings, and tank breathers.
- Keep hydraulic fluid clean—target ISO cleanliness codes recommended by the OEM (often 18/16/13 or cleaner depending on system sensitivity).
- Monitor system temperatures and add cooling capacity if operating consistently at high temps.
- Train operators to avoid rapid directional changes at heavy loads that stress components.
How Weihuparts supports low-pressure repairs
Weihuparts supplies a comprehensive selection of excavator spare parts—pumps, seals, relief valves, filters, and hoses—sourced and tested to support routine and high-performance hydraulic systems. Our R&D and engineering teams validate component fit and function to help fleet managers get back to operation quickly while controlling costs.
Conclusion: restore pressure methodically to minimize downtime
Low hydraulic pump pressure is often straightforward to diagnose if you follow a methodical approach: measure, isolate, inspect, and then repair or replace. Start with the basics—fluid, filters, suction condition, and relief valves—before assuming catastrophic pump failure. When pump replacement is required, use quality parts and matched components to restore system performance reliably.
Practical checklist for field troubleshooting
- Record pressures at idle and full rpm
- Inspect fluid level, condition, and temperature
- Check suction line, tank breather, and suction strainer
- Verify relief valve setpoint and control valve behavior
- Measure flow and isolate pump vs downstream leaks
- Replace contaminated fluid, blocked filters, worn hoses, or faulty valves
- Contact parts supplier (e.g., Weihuparts) for replacement pumps or OEM-grade components
Further reading and resources
Refer to your excavator OEM service manual for exact pressure and flow specifications, recommended fluid types and viscosity, and safety procedures. For parts and application support, consult Weihuparts’ technical team to match pump models and components to your machine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What immediate checks should I do when an excavator has low hydraulic pressure?
Check hydraulic fluid level and condition; inspect for external leaks; verify suction hose condition and tank breather; measure pump outlet pressure with a gauge at idle and full engine speed.
Can air in the system cause low pressure, and how do I detect it?
Yes. Air causes cavitation and noise, reduces pressure and flow. Detect by audible knocking/air-aspirating sound, foamy fluid in the reservoir, and fluctuating gauge readings. Fix suction-side leaks, vents, and fluid level.
How much does it cost to replace a hydraulic pump on an excavator?
Costs vary by pump type and excavator size. Small gear pump replacements are less expensive than high-pressure piston pumps on large machines. Include labor, possible lines/filters, and testing in the total repair estimate. Contact suppliers for quotes specific to your model.
When is rebuilding a pump better than replacing it?
Rebuild when pump model is serviceable, parts are available, and cost of rebuild plus downtime is lower than buying new. Rebuilds are common for high-value piston pumps; simpler gear pumps are often replaced.
How can I prevent future low-pressure problems?
Implement regular fluid and filter changes, inspect suction lines and breathers, monitor temperatures, and use quality replacement parts. Maintain ISO cleanliness levels recommended by the OEM.
Top Excavator Hydraulic Pump Brands Compared: Buyer Guide

How High-Performance Main Pumps Improve DX65 Efficiency
Diesel vs Gas Excavator Engines: Pros and Cons

Choosing the Right Hydraulic Pump for Doosan DX65
FAQ
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.
Do you provide warranties on your products?
Yes, we stand by the quality of our products. Most parts come with a warranty that covers manufacturing defects. Please refer to the specific warranty information provided with your purchase or contact our customer service team for details.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
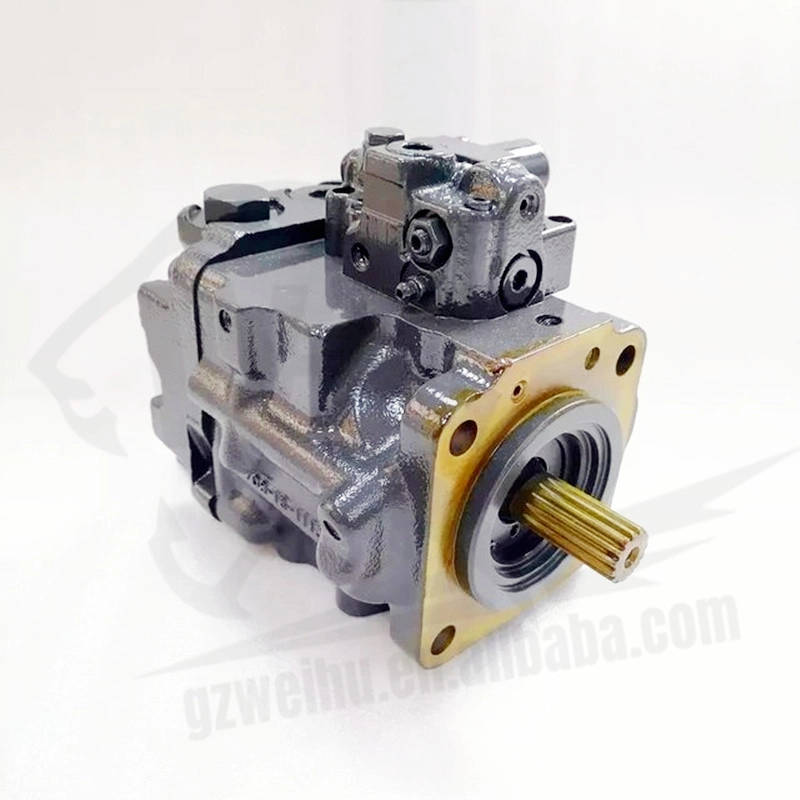

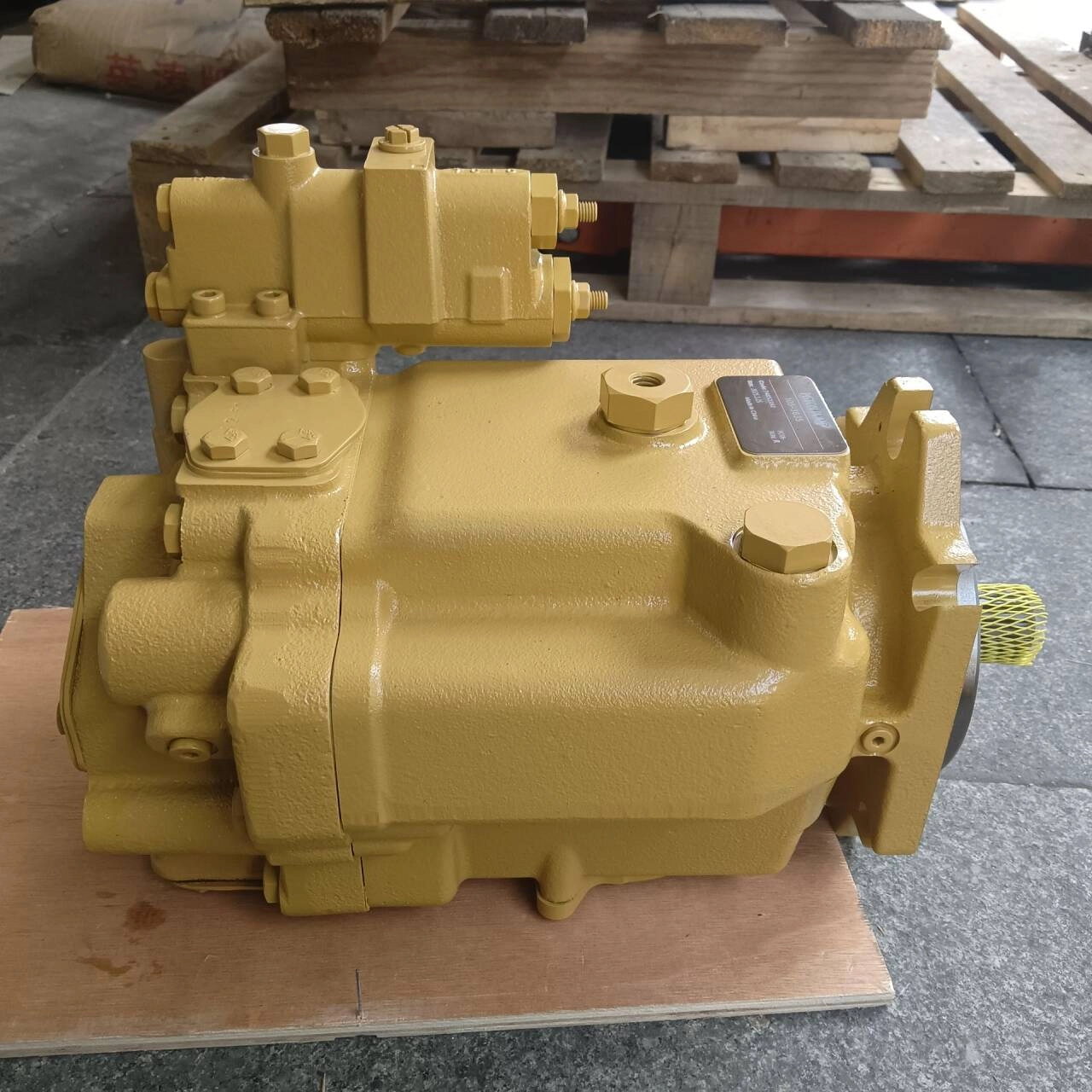
Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
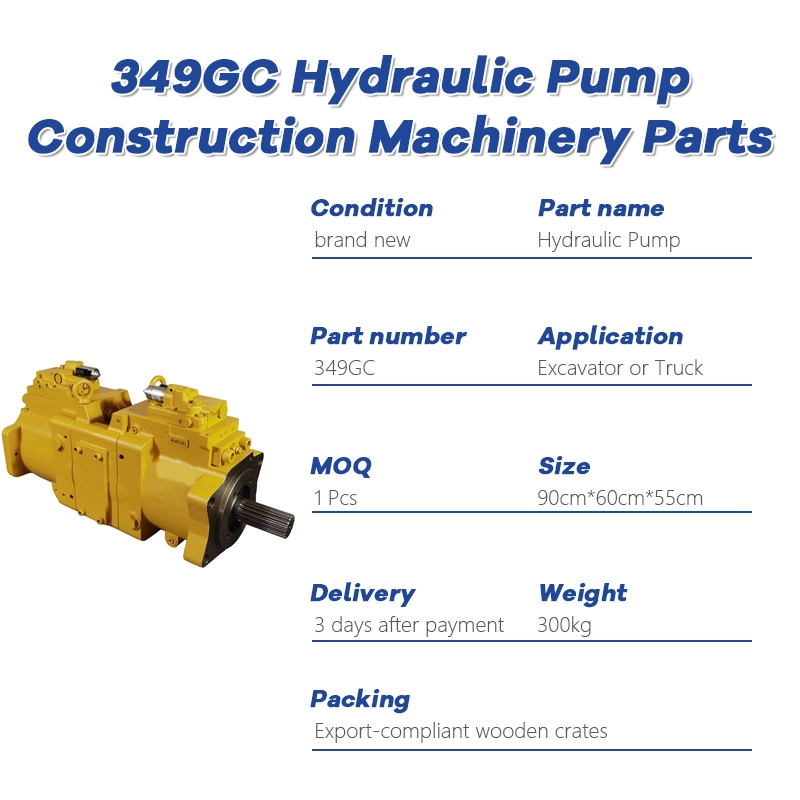
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

