jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Hydraulic Oil Tips to Extend Pump Life in Excavators
- Introduction: Why Hydraulic Oil Matters for Excavator Pump Life
- Understand How Hydraulic Oil Affects Pump Wear
- How pumps fail when hydraulic oil is wrong
- Types of pumps and sensitivity
- Choose the Right Hydraulic Oil
- Match viscosity to OEM recommendations
- Prefer high-quality anti-wear hydraulic fluids
- Maintain Cleanliness and Proper Filtration
- Set and monitor ISO 4406 cleanliness targets
- Use the right filters and understand beta ratios
- Seal, fill, and handle fluids properly
- Monitor Fluid Health Regularly
- What to test and how often
- Water tolerance targets
- Operating Practices That Reduce Pump Stress
- Manage temperature
- Avoid cavitation and air ingestion
- Warm-up and cooldown procedures
- Maintenance Schedules and Intervals
- Quick Comparisons: Cleanliness Targets by Pump Type
- Practical Implementation Checklist
- Conclusion: Small Actions, Big Impact on Pump Life
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction: Why Hydraulic Oil Matters for Excavator Pump Life
When operators search for Hydraulic Oil Tips to Extend Pump Life in Excavators, they want practical, actionable guidance that reduces downtime, lowers repair costs, and keeps systems performing reliably. Excavator hydraulic pumps (axial piston, gear, and vane) are expensive components; fluid-related issues such as contamination, incorrect viscosity, water, and overheating cause the majority of premature failures. This article explains simple, proven hydraulic oil practices—selection, cleanliness, monitoring, filtration, and operating habits—that significantly extend pump life and protect your investment.
Understand How Hydraulic Oil Affects Pump Wear
How pumps fail when hydraulic oil is wrong
Pumps suffer from abrasive wear (solid particles), corrosive wear (water + acids), and fatigue from poor lubrication or cavitation. High-pressure axial piston pumps are especially sensitive to contamination and viscosity deviations because tight clearances and high shear stresses amplify damage.
Types of pumps and sensitivity
- Axial piston pumps: high sensitivity — need the cleanest oil and stable viscosity.
- Vane pumps: moderate sensitivity — benefit from anti-wear additives and good filtration.
- Gear pumps: most tolerant but still harmed by abrasives and water.
Choose the Right Hydraulic Oil
Match viscosity to OEM recommendations
Select an oil with the ISO VG and viscosity grade recommended by the equipment OEM. Operating viscosity should remain within ±20% of the recommended value at operating temperature. Oils that are too thin increase metal-to-metal contact; oils that are too thick increase internal stress and temperature.
Prefer high-quality anti-wear hydraulic fluids
Use hydraulic oils with anti-wear additives (e.g., ZDDP or modern ashless alternatives) suited for your pump type. Consider synthetic esters or high-quality Group II/III base oils for better thermal stability and oxidation resistance where temperatures and loads are severe.
Maintain Cleanliness and Proper Filtration
Set and monitor ISO 4406 cleanliness targets
Cleanliness is one of the most important controllable factors. For high-pressure axial piston pumps target ISO 4406 cleanliness of 16/14/11 or better; for vane pumps 18/16/13; for gear pumps 19/17/14. Maintaining these targets reduces abrasive wear and failure risk.
Use the right filters and understand beta ratios
Select filters sized to remove particles that cause wear. Look for filters with published beta ratios (e.g., beta2000 > 200 at the target micron). Typical best practice: system return line filters at 3–10 µm absolute for sensitive pumps, and pressure filters upstream of control valves where required. Use breathers and tank filtration to prevent ingression of contaminants when tanks are refilled or vented.
Seal, fill, and handle fluids properly
Use sealed containers, clean funnels, and dedicated pumps when topping off. Ensure good seals on hoses and connections to prevent air and dust ingress. Even brief exposure while refilling can drastically increase particle counts.
Monitor Fluid Health Regularly
What to test and how often
Implement routine oil analysis (laboratory or onsite particle counting) to track: particle counts (ISO 4406), water content (ppm), viscosity at 40°C and 100°C, total acid number (TAN)/oxidation, and elemental wear metals (Fe, Cu, Sn, Pb). For active machines a common cadence is: particle counts and water checks every 250 hours, full oil analysis every 500–1,000 hours — adjust frequency based on severity of duty.
Water tolerance targets
Free water is dangerous. Aim for <200 ppm water in typical hydraulic systems; for the most sensitive pumps keep water <100 ppm. Use breathers, desiccant breathers, and water-separating filters or offline centrifuges if water ingress is persistent.
Operating Practices That Reduce Pump Stress
Manage temperature
Keep operating temperatures within OEM limits—most hydraulic oils perform well between 40–80°C. Elevated temperatures accelerate oxidation and varnish formation; use coolers, proper fan control, and maintain adequate fluid volume to dissipate heat. Avoid repeated thermal cycling that promotes oxidation.
Avoid cavitation and air ingestion
Cavitation causes pitting and rapid pump wear. Maintain proper inlet conditions: ensure adequate suction head, short suction lines, appropriate hose diameters, and avoid excessive pump inlet restriction. Check for failed seals or loose fittings that allow air entry.
Warm-up and cooldown procedures
Warm systems gently at low loads to achieve operating viscosity before heavy work. After long runs under high load, allow a brief cool-down cycle if possible to reduce thermal shock and oxidation stress.
Maintenance Schedules and Intervals
Maintenance intervals depend on duty cycle and contamination control. Typical industry guidance (adjust to OEM):
| Item | Typical Interval | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Particle count and water check | Every 250 hours | On severe duty, increase frequency |
| Full oil analysis (viscosity, TAN, wear metals) | Every 500–1,000 hours | Use results to set oil change timing |
| Filter element change (return/pressure) | Every 250–1,000 hours | Change earlier if delta-P rises or contamination spikes |
| Hydraulic oil replacement | 2,000–4,000 hours (typical) | Follow OEM and oil analysis; severe duty shortens life |
Quick Comparisons: Cleanliness Targets by Pump Type
| Pump Type | Recommended ISO 4406 Target | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Axial piston | 16/14/11 or better | High pressure and tight clearances — very sensitive to particles |
| Vane | 18/16/13 | Moderate sensitivity; benefits from anti-wear additives and filtration |
| Gear | 19/17/14 | More tolerant but still harmed by abrasives and water |
Practical Implementation Checklist
- Confirm OEM-recommended oil viscosity and change intervals.
- Set cleanliness targets by pump type and verify with particle counters.
- Use high-quality anti-wear hydraulic fluids and change filters on a schedule.
- Install desiccant breathers, proper tank filtration, and consider offline filtration for busy fleets.
- Sample oil regularly and act on lab trends (rising particles, water, TAN, or wear metals).
- Train operators on warm-up/cooldown, avoiding shock loads, and proper topping-off techniques.
Conclusion: Small Actions, Big Impact on Pump Life
Extending excavator pump life comes down to controlling the lubricant environment: choose the correct hydraulic oil, keep it clean, monitor its condition, manage temperature and air/water ingress, and follow disciplined maintenance. These steps reduce abrasive wear, corrosion, and fatigue failures—saving repair costs and downtime. Weihuparts supports global customers with quality excavator components and technical guidance so your fleet runs longer and more reliably. If you need replacement filters, pump components, or guidance on part selection for contamination control, Weihuparts can help source the right parts and advise on best practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How often should I change hydraulic oil in an excavator?A: Oil change intervals vary by duty and oil condition. Typical industry ranges are 2,000–4,000 operating hours; use oil analysis to determine the optimal interval for your machine. Severe duty may require more frequent changes.
Q: What ISO 4406 cleanliness code should I target?A: For high-pressure axial piston pumps target around 16/14/11 or cleaner. For vane pumps aim for ~18/16/13 and gear pumps ~19/17/14. Adjust based on OEM and operating severity.
Q: How much water in hydraulic oil is acceptable?A: Aim for <200 ppm in general; for sensitive pumps target <100 ppm. Free water must be eliminated immediately to avoid corrosion and loss of lubrication.
Q: Can I use synthetic oil to extend pump life?A: High-quality synthetic or ester-based hydraulic fluids often offer better oxidation resistance and thermal stability, which helps extend life under high temperatures. Always confirm compatibility with seals and OEM specs.
Q: What filtration micron rating should I use?A: Sensitive systems often require return-line filters in the 3–10 µm absolute range and pressure filters where required. Use filters with good beta ratios and follow manufacturer recommendations.
Q: Will topping off with any hydraulic oil cause problems?A: Yes. Mixing incompatible oils (different base stocks or additive chemistries) can degrade performance. Always top off with the same oil grade and preferably the same brand/type recommended by the OEM.
Sources:
- ISO 4406: Cleanliness code for fluid contamination (international standard)
- Industry best practices from major hydraulic fluid suppliers (Shell, Mobil) and lubricant advisory groups
- Technical guidance from pump OEMs (axial piston, vane, gear pump manuals and maintenance recommendations)
- Noria Corporation: Oil analysis and contamination control best practices
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic equipment maintenance literature and fleet maintenance case studies
Excavator Hydraulic Pump Maintenance Checklist: A Practical Guide

Choosing an Original Hitachi Engine Supplier: ZAX870-5G Guide

Fuel Efficiency Metrics: Selecting the Best Diesel Engine

Warranty and service considerations for engine assemblies
FAQ
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.
Are your parts compatible with all excavator brands?
Weihuparts strives to offer parts compatible with a wide range of excavator brands and models. However, we recommend checking the product specifications or consulting with our team to ensure compatibility with your specific excavator.
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.
Do you provide warranties on your products?
Yes, we stand by the quality of our products. Most parts come with a warranty that covers manufacturing defects. Please refer to the specific warranty information provided with your purchase or contact our customer service team for details.
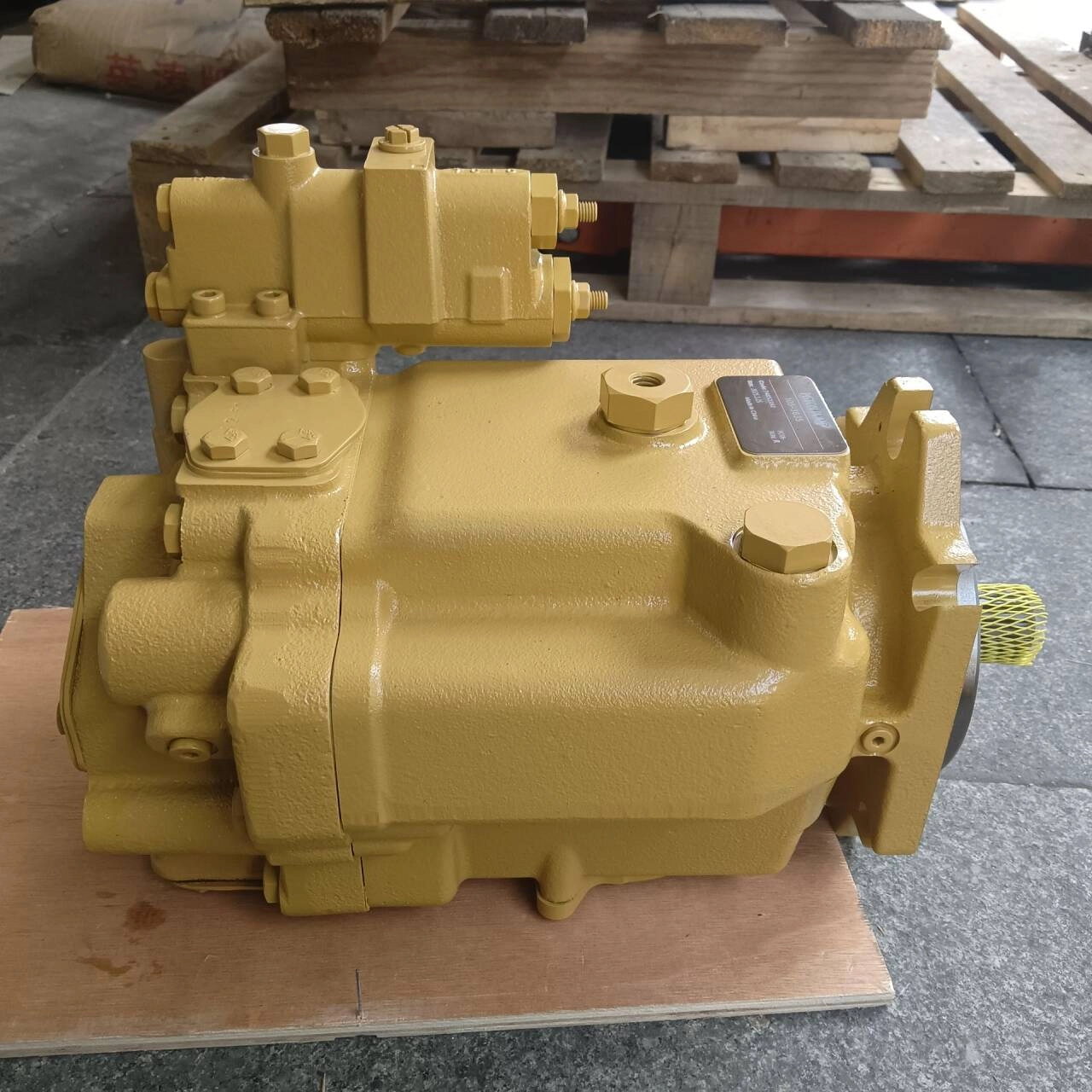

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
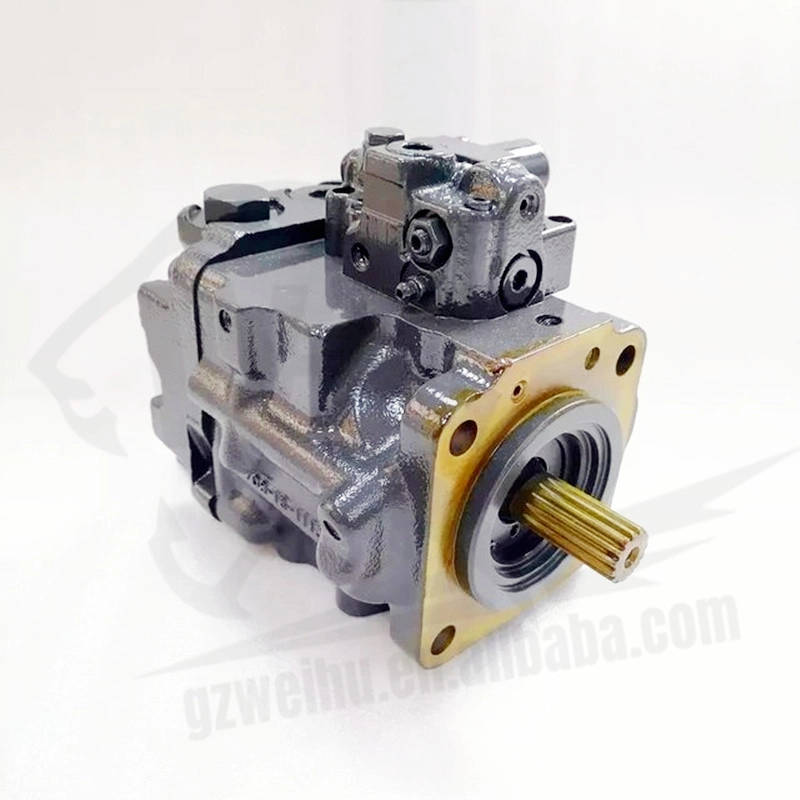

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
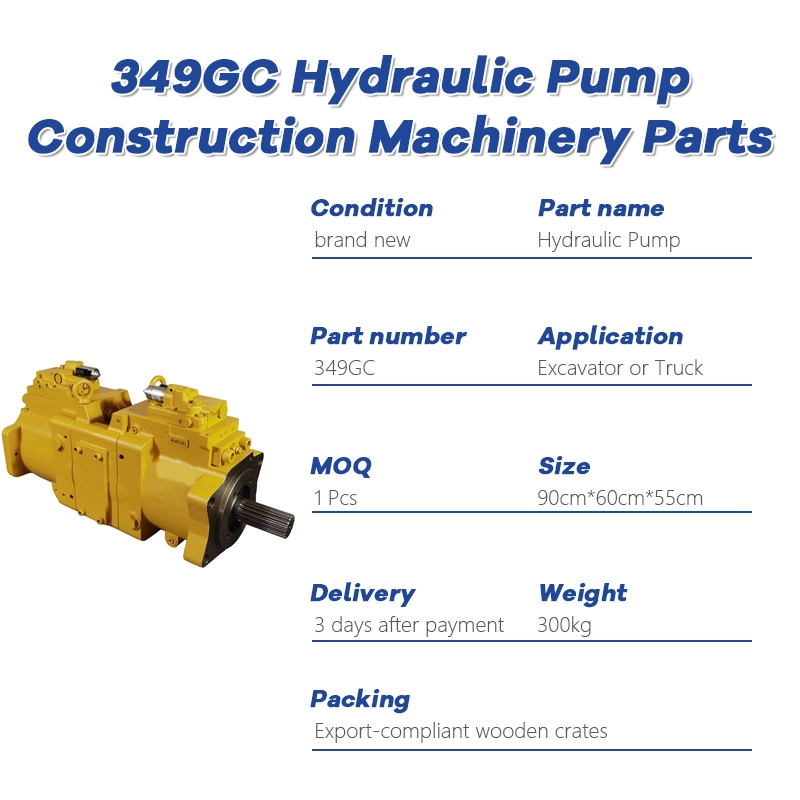
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-

