jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Excavator Engine Noise: Diagnosis and Reduction Tips
- Excavator Engine Noise: Diagnosis and Reduction Tips
- Why excavator engine noise matters
- Common sources of excavator engine noise
- Typical noise levels and regulatory context
- Quick diagnostic checklist for operators
- Detailed diagnostic techniques
- Valvetrain and timing-related noise
- Fuel system noise: injectors and pumps
- Turbocharger and exhaust noise
- Accessory drive, belts, and fans
- Engine mounts and structure-borne noise
- Hydraulic system and drivetrain noise interference
- Cost-effective noise reduction measures
- Upgrades and retrofits that deliver strong results
- Maintenance best practices to prevent noise recurrence
- When to repair vs replace components
- Cost vs effectiveness: comparison of common options
- Practical case example
- How Weihuparts supports quieter excavator engines
- Operator and site best practices to minimize noise impact
- FAQ
- Q: How quickly should I act if I detect new engine noise?
- Q: Can poor fuel or contaminated diesel cause engine noise?
- Q: Will replacing the muffler affect engine performance?
- Q: How do I know if noise is engine-origin or hydraulic?
- Q: Are aftermarket parts safe for noise control?
- Q: What personal protection should operators use?
- Q: Can soundproofing the cab solve all operator noise issues?
- Q: Where can I get support or parts for noise-related repairs?
Excavator Engine Noise: Diagnosis and Reduction Tips
Why excavator engine noise matters
Excavator engine noise affects operator safety, jobsite communication, regulatory compliance, and equipment perception. Excessive noise can indicate underlying faults that lead to downtime and higher repair costs. Addressing excavator engine noise proactively improves machine life, lowers occupational hearing risks, and supports on-time project delivery.
Common sources of excavator engine noise
Understanding where noise originates is the first diagnostic step. Typical sources include combustion (misfires, detonation), valvetrain clatter, fuel injector knock, turbocharger whine, exhaust leaks, loose or worn engine mounts, accessory belts and pulleys, cooling fan and fan clutch, and nearby hydraulic pumps or gearboxes that transmit structure-borne noise into the chassis.
Typical noise levels and regulatory context
Diesel-powered excavators at the engine compartment commonly register between roughly 85–105 dB(A) depending on size and load; inside operator cabs, well-insulated cabins are often 75–95 dB(A). Many jurisdictions follow exposure guidelines: the EU action value is 80 dB(A) (limit 87 dB(A)), and occupational guidance such as OSHA identifies 85–90 dB(A) as thresholds for hearing protection and exposure limits. Knowing these ranges helps prioritize repairs when noise exceeds safe levels.
Quick diagnostic checklist for operators
Start with a quick, consistent checklist during daily inspections: listen to the engine at idle and under load, note whether noise varies with RPM or load, visually inspect for loose components and exhaust leaks, check fluid levels and filter conditions, and verify that mounts and belts are tensioned. Record observations (time, engine hours, RPM) to help technicians reproduce and diagnose the issue.
Detailed diagnostic techniques
When a quick check doesn’t locate the issue, use targeted diagnostic methods: use a mechanic's stethoscope or chassis ear to pinpoint noise sources; perform a borescope inspection for cylinder/head issues; conduct compression and leak-down tests to detect worn rings or valves; monitor fuel rail pressure and injector pulse with diagnostic tools; inspect turbocharger shafts for play; and use vibration analysis tools to identify structure-borne resonances.
Valvetrain and timing-related noise
Rattling or ticking that tracks engine RPM often originates from the valvetrain (tappets, rockers, camshaft) or incorrect valve lash. Diesel engines with mechanical or hydraulic lifters can develop noise from wear or improper adjustment. Check valve clearances at cold start per manufacturer specs and inspect for cam lobe wear or broken spring components. Correcting timing or replacing worn valvetrain parts usually reduces this kind of noise significantly.
Fuel system noise: injectors and pumps
Tapping or metallic knock that intensifies with load can signal injector issues or high-pressure fuel pump wear. Common causes include worn injector tips, loose injector clamps, incorrect injector timing, or air in the fuel system. Use fuel pressure gauges and injector diagnostic tools to measure spray pattern and pressures. Replacing or servicing injectors and maintaining clean fuel filters often resolves fuel-related noise.
Turbocharger and exhaust noise
Whines, whistles, or sudden changes under boost are commonly turbo-related—worn bearings, shaft play, or inlet/exhaust leaks. Exhaust leaks at the manifold or gasket produce sharp, pulsating sounds and reduce backpressure regulation. Visually inspect the turbo housing, check for oil leaks, and pressure-test the intake/exhaust plumbing. Repairing leaks, replacing worn turbos, or installing correctly sized mufflers are typical solutions.
Accessory drive, belts, and fans
Screeching, chirping, or oscillating noises often come from accessory drives—alternator, air compressor, water pump, tensioners, or belt slippage. Belt glazing, worn pulleys, and loose tensioners introduce characteristic noises that change with RPM. Tighten to manufacturer torque, replace worn belts and pulleys, and verify bearing smoothness to eliminate these issues.
Engine mounts and structure-borne noise
Worn or failed engine mounts transfer more vibration into the frame and cab, amplifying perceived noise. Inspect mounts for cracks, oil saturation (which degrades rubber), and looseness. Replacing mounts or adding isolation pads where appropriate reduces vibration transmission and lowers cabin noise without altering engine performance.
Hydraulic system and drivetrain noise interference
Not all noise that seems like an excavator engine issue is engine-origin. Hydraulic pumps, swing motors, undercarriage gearboxes, and track components can generate noise that radiates through the frame. To isolate, run the engine at idle with hydraulics unloaded, then selectively engage hydraulics to see if noise levels change. If noise increases with hydraulic load independent of RPM, focus diagnostics on the hydraulic circuit.
Cost-effective noise reduction measures
Before expensive retrofits, implement cost-effective fixes: regular oil and filter changes, clean fuel and air filters, correct valve lash and belt tension, replace worn mufflers or silencers, repair exhaust leaks, and restore engine mounts. These maintenance actions often yield substantial noise reduction at low cost and improve fuel efficiency and longevity.
Upgrades and retrofits that deliver strong results
For persistent problems or to achieve quieter operation beyond maintenance, consider upgrades: high-performance mufflers and silencers, acoustic engine enclosures, upgraded engine mounts with better isolation, variable-speed or viscous fan clutches, turbocharger replacement with modern low-noise designs, and improved cab soundproofing. These are higher cost but can significantly reduce operator exposure and improve comfort.
Maintenance best practices to prevent noise recurrence
Follow manufacturer-recommended service intervals for oil, filters, valve adjustments, and belt replacement. Implement a vibration-monitoring routine and keep a log of noise-related complaints mapped to service actions. Use OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts—poor-quality parts can reintroduce noise. Regular preventive maintenance is the most cost-efficient noise-control strategy over the equipment lifecycle.
When to repair vs replace components
Deciding between repair and replacement depends on severity, cost, and downtime. Minor valve adjustments, belt replacements, and mount renewals are usually repairs. Turbocharger bearing failure, severely worn injectors, or cracked exhaust manifolds often warrant replacement. Consider remaining service life, parts availability, and safety—when repairs will not restore reliability, replacement is preferable.
Cost vs effectiveness: comparison of common options
Use the table below to compare typical noise-control measures by relative cost and expected effectiveness. Cost and effectiveness are relative and depend on machine size and condition.
| Measure | Relative Cost | Typical Effectiveness | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Routine maintenance (oil, filters, belts) | Low | High | Often reduces noise and prevents faults |
| Replace muffler / exhaust repair | Medium | High | Directly reduces exhaust noise and backpressure issues |
| Engine mount replacement / isolation pads | Medium | Medium–High | Reduces transmitted vibration and cabin noise |
| Acoustic engine enclosure / cab soundproofing | High | High | Effective for operator noise reduction; high retrofit cost |
| Turbocharger rebuild / replacement | Medium–High | High | Eliminates turbo whine and oil leak-related noises |
| Hydraulic pump/service | Medium | Medium–High | Reduces hydraulic-origin noises that couple to structure |
| ECU tuning / engine derating | Medium | Medium | Can reduce noise by lowering RPM or smoothing torque curves but may affect power |
Practical case example
An excavator reported a high-pitched whine that increased with load. A diagnosis sequence isolated the noise to the turbocharger: borescope inspection showed oil trace near the turbine, and shaft play was measurable. Replacing the turbocharger and repairing an adjacent oil feed line eliminated the whine and improved fuel consumption. The cost of replacement was balanced against avoided downtime and restored performance.
How Weihuparts supports quieter excavator engines
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive selection of excavator parts to help diagnose and reduce excavator engine noise—replacement mounts, mufflers, turbochargers, injectors, filters, and high-quality consumables. Our R&D-backed components meet industry standards for durability and fit, helping technicians restore quiet, reliable operation quickly and cost-effectively. For operators seeking parts that fit maintenance schedules or retrofit projects, Weihuparts can advise on compatible, high-performance options to reduce noise and extend service life.
Operator and site best practices to minimize noise impact
Beyond mechanical fixes, adopt site practices: schedule noisy work during daytime windows, use barriers or temporary acoustic screens where feasible, maintain vehicle isolation zones, rotate operators to limit exposure, and enforce hearing protection when levels exceed recommended limits. Combining engineering controls with administrative measures gives the best outcomes for safety and compliance.
FAQ
Q: How quickly should I act if I detect new engine noise?
A: Investigate immediately. Early diagnosis often avoids larger repairs. Start with the quick checklist—visual checks, fluid levels, look for leaks—and record symptoms so a technician can reproduce them.
Q: Can poor fuel or contaminated diesel cause engine noise?
A: Yes. Contaminants and incorrect fuel quality can cause injector damage, incomplete combustion, and knocking. Regular fuel filter changes and fuel quality control reduce related noise risks.
Q: Will replacing the muffler affect engine performance?
A: Replacing a damaged muffler usually improves performance by restoring proper backpressure characteristics. Ensure replacement parts meet OEM specifications to avoid adverse effects on engine breathing.
Q: How do I know if noise is engine-origin or hydraulic?
A: Isolate systems—run the engine at idle with hydraulics unloaded, then apply hydraulic functions. If noise changes with hydraulic load but not with engine RPM, focus on hydraulic components. Use a stethoscope or vibration analyzer to pinpoint sources.
Q: Are aftermarket parts safe for noise control?
A: High-quality aftermarket parts that meet OEM specs can be effective and cost-efficient. Source parts from reputable suppliers—like Weihuparts—to ensure fit, durability, and predictable noise-control performance.
Q: What personal protection should operators use?
A: Use hearing protection when noise exceeds recommended exposure thresholds (generally above 85 dB(A)). Protecting hearing is essential even if mechanical noise sources are being addressed.
Q: Can soundproofing the cab solve all operator noise issues?
A: Cab soundproofing significantly improves operator comfort but does not fix mechanical faults. Combine cab insulation with mechanical repairs for the best long-term results.
Q: Where can I get support or parts for noise-related repairs?
A: Weihuparts supplies a wide range of excavator spare parts—engine mounts, mufflers, turbos, injectors, filters, and more—and can advise on replacements and compatible upgrades to reduce excavator engine noise while maintaining reliability.
For diagnostic support, parts selection, or quotes on retrofits, contact Weihuparts' technical team to match solutions to your model and operational needs.

How suppliers ensure authenticity of engine assemblies

Material and Seal Quality in Heavy Duty Hydraulic Pumps
Common Excavator Engine Problems and Solutions

Choosing the Right Mounting and Interface for 336D Pumps
FAQ
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.
Are your parts compatible with all excavator brands?
Weihuparts strives to offer parts compatible with a wide range of excavator brands and models. However, we recommend checking the product specifications or consulting with our team to ensure compatibility with your specific excavator.
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
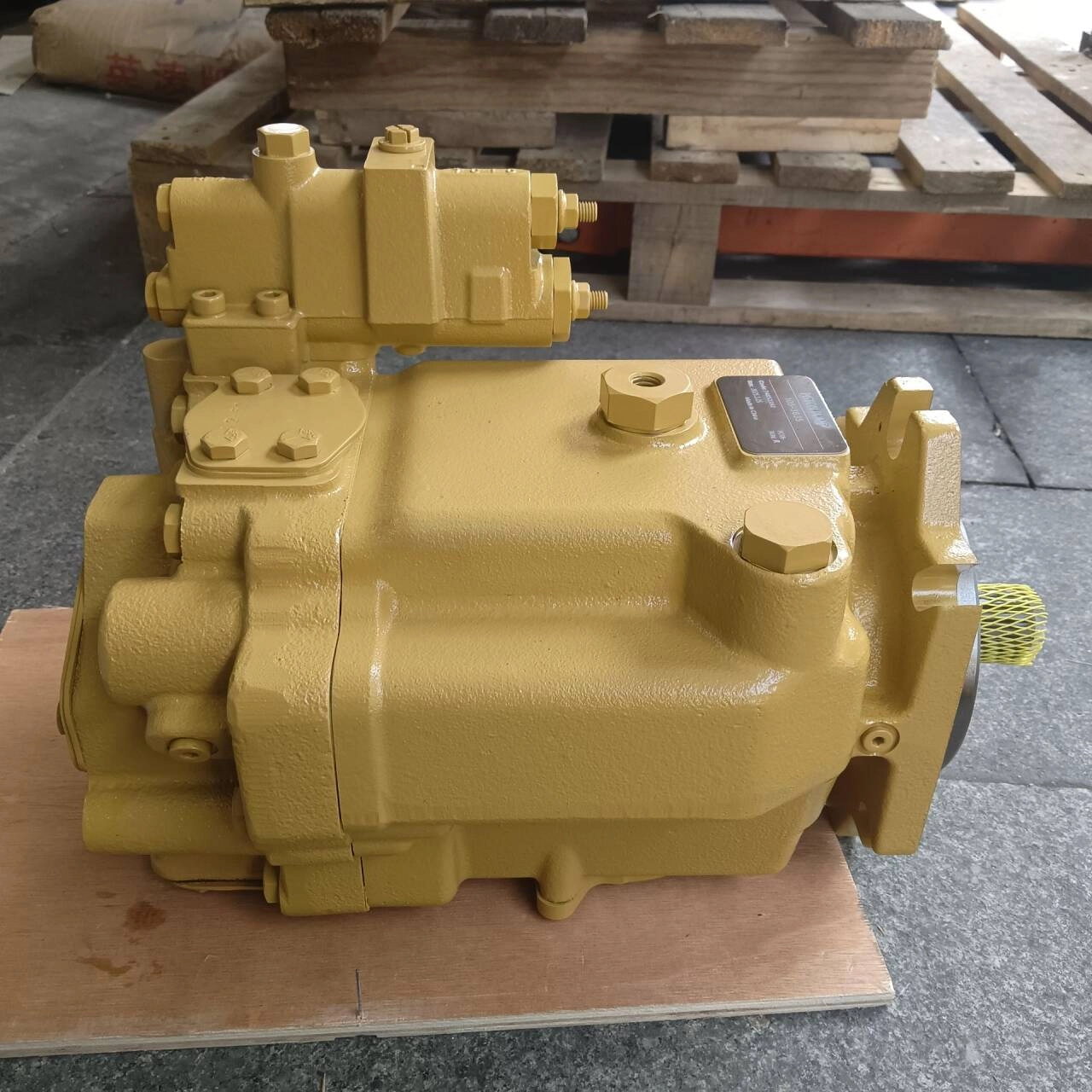

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
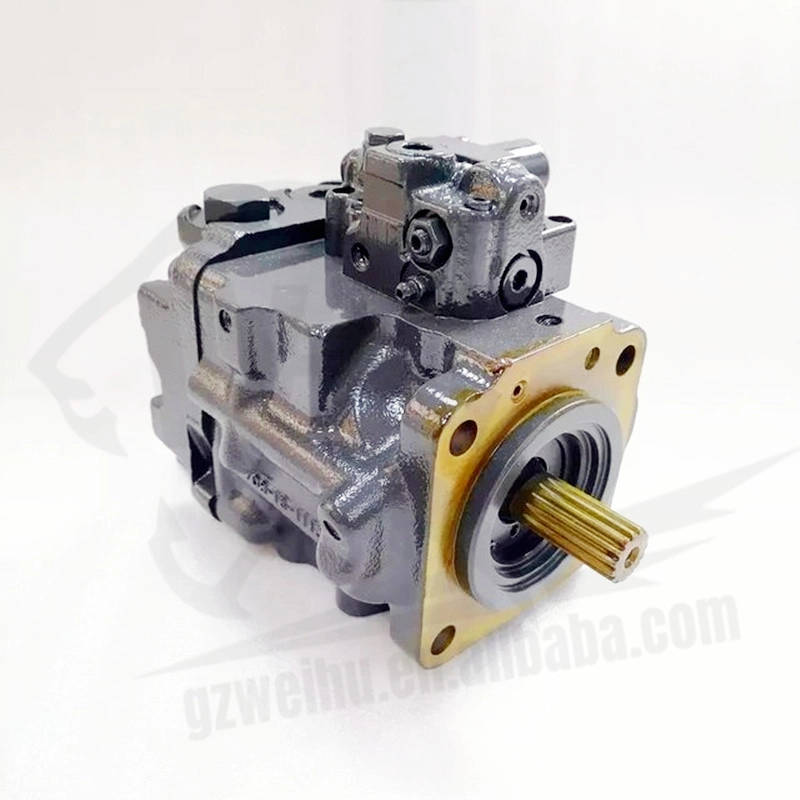

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
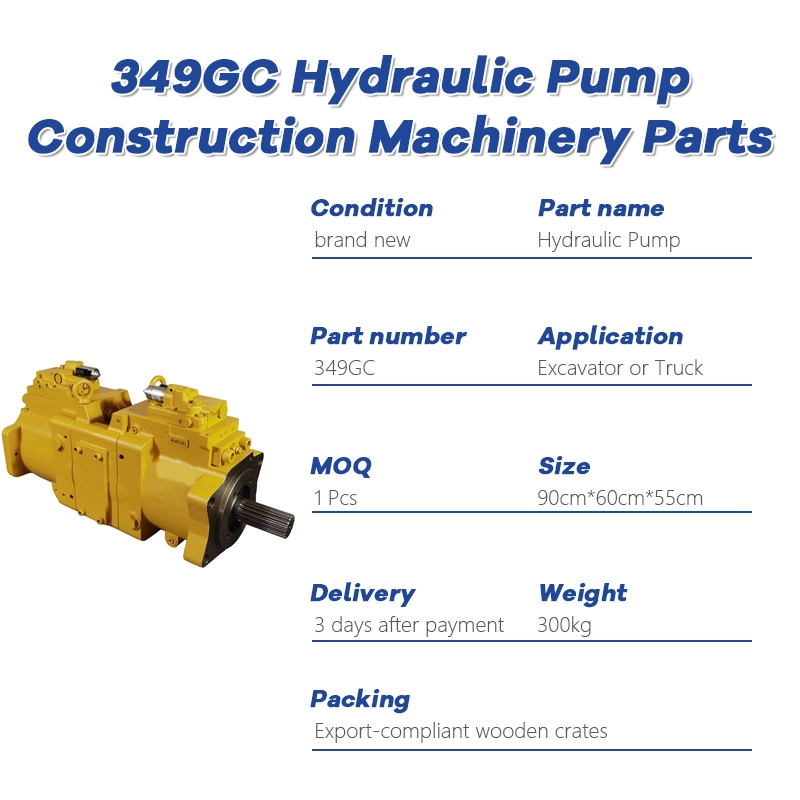
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

