jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Diesel vs Gas Excavator Engines: Pros and Cons
- Diesel vs Gas Excavator Engines: Pros and Cons
- Why engine choice matters for your excavator engine
- Common applications for diesel and gas excavator engines
- Performance: torque, power delivery, and duty cycles
- Diesel performance characteristics
- Gas performance characteristics
- Fuel efficiency and operating cost
- Diesel: lower fuel consumption under load
- Gas: lower initial cost but higher fuel cost in many scenarios
- Maintenance, parts availability and lifecycle
- Diesel maintenance needs and parts
- Gas maintenance profile
- Emissions, regulations, and site requirements
- Diesel emissions technology and compliance
- Gas engines and emissions considerations
- Noise, vibration, and operator comfort
- Diesel NVH characteristics
- Gas: quieter operation for compact machines
- Applications and suitability by machine class
- Where diesel excels
- Where gas makes sense
- Cost comparison table: diesel vs gas excavator engines
- Parts, support, and supply chain considerations
- Sourcing reliable parts for your excavator engine
- How Weihuparts supports engine reliability
- Economic and environmental trade-offs
- Total cost of ownership (TCO)
- Environmental strategy and site requirements
- Making the right choice for your fleet
- Checklist to select the right excavator engine
- About Weihuparts and engine-part expertise
- Weihuparts: quality, R&D, and global support
- FAQ — common questions about excavator engine choice
- Q1: Are diesel excavator engines always better than gas?
- Q2: Do modern diesel engines require special parts?
- Q3: How does fuel choice affect resale value?
- Q4: Can I convert a diesel excavator to gas or vice versa?
- Q5: Where can I source reliable parts for my excavator engine?
- Q6: Are there electric alternatives to diesel and gas excavator engines?
Diesel vs Gas Excavator Engines: Pros and Cons
Choosing the right excavator engine affects fuel costs, uptime, maintenance schedules, emissions compliance, and overall project performance. This guide compares diesel and gasoline (petrol) excavator engines across the factors that matter most to fleet managers, contractors, and rental companies. We use the term excavator engine throughout to focus on how engine choice impacts machine behavior and lifecycle costs.
Why engine choice matters for your excavator engine
An excavator engine is the heart of the machine. It drives hydraulic pumps, generates torque for digging and lifting, and determines the environmental footprint of your equipment. Engine choice influences operational efficiency, maintenance intervals, parts availability, resale value, and compliance with emissions regulations such as Tier 4 (North America) and Stage V (EU).
Common applications for diesel and gas excavator engines
Diesel engines dominate medium- and large-class excavators used in heavy construction, mining, and infrastructure due to their torque and durability. Gasoline engines are more often found in compact or lightweight equipment where low upfront cost, lower weight, or reduced vibration is a priority. Understanding intended application is the first step to selecting the right excavator engine.
Performance: torque, power delivery, and duty cycles
Diesel performance characteristics
Diesel excavator engines produce high torque at low RPM. This characteristic is ideal for heavy digging, lifting, and continuous high-load operations. Diesel engines are designed for long duty cycles and tend to maintain performance under heavy, sustained loads—an important consideration for larger excavators and high-production sites.
Gas performance characteristics
Gas engines deliver power at higher RPMs and generally have quicker throttle response. For light-duty or intermittent tasks—landscaping, small trenching, and tasks where noise and vibration are concerns—gas-powered compact excavators can be appropriate. However, gasoline engines typically offer lower torque for a given displacement compared with diesel.
Fuel efficiency and operating cost
Diesel: lower fuel consumption under load
Diesel fuel has a higher energy density and diesel engines convert that energy into work efficiently, especially under heavy loads. For excavator applications with frequent heavy cycles, diesel engines usually provide better fuel economy per hour of heavy operation, which lowers operating cost over the machine's lifetime despite higher initial engine cost.
Gas: lower initial cost but higher fuel cost in many scenarios
Gasoline engines typically cost less to produce and buy, so the initial equipment cost for a gas-powered compact excavator can be lower. However, fuel burn per heavy-working hour is usually higher, and gasoline prices per energy unit are often comparable or higher than diesel, making long-term fuel costs potentially higher for heavy-usage applications.
Maintenance, parts availability and lifecycle
Diesel maintenance needs and parts
Diesel excavator engines require robust maintenance to protect fuel systems and emissions control equipment: fuel filters, high-pressure fuel injectors, fuel pumps, and sometimes turbochargers. Modern diesels also have diesel particulate filters (DPFs) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems that use DEF/AdBlue to reduce NOx—these items require attention and proper parts sourcing. For most fleets, diesel engines have longer service life when maintained properly.
Gas maintenance profile
Gas engines have simpler emissions controls in many cases and use spark plugs and ignition systems instead of high-pressure injectors and glow plugs. That can translate into simpler routine maintenance for small machines. However, replacements and wear parts for either engine type should be sourced from reputable suppliers to maintain reliability.
Emissions, regulations, and site requirements
Diesel emissions technology and compliance
Modern diesel excavator engines incorporate technologies to meet strict emissions standards (Tier 4/Stage V). These systems include DPFs, SCR with DEF, and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR). While effective at reducing particulate matter and NOx, these components add complexity and require periodic service. For projects with strict site emissions limits, a compliant diesel is often necessary for heavy equipment.
Gas engines and emissions considerations
Gasoline engines generally produce lower NOx and particulate emissions for small-displacement machines but can produce higher CO emissions. For indoor work or in areas with noise and vibration restrictions, small gas-powered excavators or alternative power sources (electric/hybrid) may be preferable. Always verify local emissions and site requirements before selecting equipment.
Noise, vibration, and operator comfort
Diesel NVH characteristics
Diesel engines typically generate more noise and vibration due to higher compression ratios and combustion characteristics. Manufacturers mitigate this with improved mounting, sound insulation, and modern engine design, but diesel machines can still be less comfortable than gas-powered equivalents in small classes.
Gas: quieter operation for compact machines
Gasoline engines can be quieter and smoother, improving operator comfort in compact excavators and tight jobsite environments. This can be an advantage for urban or residential projects where noise limits or operator fatigue are concerns.
Applications and suitability by machine class
Where diesel excels
Diesel is the standard for medium and large excavators used in continuous heavy work—road construction, deep excavations, mining, and large foundations. For fleets that prioritize uptime, fuel efficiency under load, and high torque, diesel remains the industry choice.
Where gas makes sense
Gas-powered excavators are most commonly used in compact classes or specialty machines where upfront cost, weight, or noise matters more than continuous heavy digging. For light construction, rental machines for DIY users, or situations with easier access to gasoline, a gas machine can be cost-effective.
Cost comparison table: diesel vs gas excavator engines
| Attribute | Diesel Excavator Engine | Gas Excavator Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Typical application | Medium to large excavators, heavy-duty continuous work | Compact/light excavators, intermittent/light-duty tasks |
| Torque delivery | High torque at low RPM (better for digging) | Lower torque, higher RPM power band |
| Fuel efficiency | Generally more efficient under heavy loads | Less efficient in heavy-duty cycles |
| Upfront cost | Higher (engine and emissions systems) | Lower (simpler engine design) |
| Maintenance complexity | Higher (FR filters, DPF, SCR, injectors) | Lower (ignition, simpler fuel systems) |
| Emissions systems | Advanced (DPF, SCR, EGR) to meet Tier 4/Stage V | Simpler, but verify local limits |
| Noise and vibration | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Resale value | Often higher for medium/large classes | Lower for heavy-duty markets, competitive for compacts |
Parts, support, and supply chain considerations
Sourcing reliable parts for your excavator engine
Whether you run diesel or gas machines, parts availability and quality directly affect uptime. Engines and emissions systems require genuine or OEM-equivalent components—filters, injectors, sensors, gaskets, and control modules. Use trusted suppliers who understand excavator applications and can support parts for modern emissions systems.
How Weihuparts supports engine reliability
Weihuparts serves as a reliable partner for global clients in the excavator spare parts sector. We provide a comprehensive selection of components for both diesel and gas excavator engines—filters, injectors, fuel pumps, gaskets, turbochargers, sensors, and emissions-related parts. With a focus on quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery, Weihuparts helps fleets reduce downtime by ensuring parts are available when needed.
Economic and environmental trade-offs
Total cost of ownership (TCO)
When comparing diesel and gas excavator engines, consider total cost of ownership, not just purchase price. TCO includes fuel consumption, maintenance, parts, regulatory compliance, downtime, and resale value. For heavy usage, diesel machines usually offer a lower TCO despite a higher initial investment. For intermittent, low-load tasks, gas machines can be more economical.
Environmental strategy and site requirements
Many fleets are shifting to cleaner technologies—Tier 4/Stage V diesel engines, hybrid drivetrains, and fully electric compact excavators—based on project needs and emissions goals. Where site emissions are tightly regulated, electric alternatives or newer diesel technologies with effective after-treatment systems may be required.
Making the right choice for your fleet
Checklist to select the right excavator engine
- Define typical duty cycle: heavy continuous work vs. intermittent light tasks.
- Assess site regulations: noise limits, emissions requirements, and fuel availability.
- Calculate total cost of ownership for expected life of the machine.
- Consider operator comfort and site constraints (urban, indoor, residential).
- Plan parts supply: ensure access to quality spare parts and technical support.
Use this checklist to weigh the trade-offs and choose the engine that best matches operational priorities.
About Weihuparts and engine-part expertise
Weihuparts: quality, R&D, and global support
Weihuparts emphasizes innovative R&D to advance the design and performance of excavator parts. With a dedicated team of engineers and technicians, Weihuparts develops durable, efficient components that meet industry standards. For customers, this means consistent parts quality, technical guidance, and timely delivery to keep machines running smoothly.
FAQ — common questions about excavator engine choice
Q1: Are diesel excavator engines always better than gas?
A: Not always. Diesel is better for medium-to-heavy continuous-duty applications due to torque and fuel efficiency under load. Gasoline can be better for compact machines where cost, weight, and noise matter more.
Q2: Do modern diesel engines require special parts?
A: Yes. Modern diesels often require DPF, SCR, sensors, and DEF systems. Regular maintenance and genuine or high-quality OEM-equivalent parts are important to maintain compliance and reliability.
Q3: How does fuel choice affect resale value?
A: Diesel excavators typically retain higher resale value in medium and large classes because they suit a wider range of heavy applications. For compact classes, resale value depends on condition, hours, and market demand.
Q4: Can I convert a diesel excavator to gas or vice versa?
A: Conversions are complex and generally not recommended. Engines are integrated with hydraulics, control systems, and emissions equipment. If you need a different fuel type, consider acquiring a machine designed for that fuel or a hybrid/electric alternative.
Q5: Where can I source reliable parts for my excavator engine?
A: Work with reputable suppliers experienced in excavator parts. Weihuparts supplies a wide range of engine components—filters, injectors, fuel pumps, gaskets, turbochargers, and emissions parts—backed by R&D and technical support to minimize downtime.
Q6: Are there electric alternatives to diesel and gas excavator engines?
A: Yes. Electric and hybrid excavators are increasingly available, especially in compact classes and for urban work where emissions and noise are restricted. Evaluate battery range, charging infrastructure, and duty cycle before switching.
If you need help selecting parts or understanding which excavator engine suits your projects, contact Weihuparts for expert advice and a reliable supply of high-quality components designed for real-world excavator applications.
The B2B Buyer’s Guide to electric hydraulic pump
Hydraulic Pump Noise Diagnosis and Fixes for 2026

Maintenance schedules for ZAX870-5G 6WG1 engine assemblies

Benefits of OEM vs Aftermarket Hydraulic Pumps for DX65
FAQ
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
How can I place an order?
You can place an order through our user-friendly online platform or by contacting our sales team directly. Simply browse our catalog, select the parts you need, and follow the checkout process to complete your order.
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.
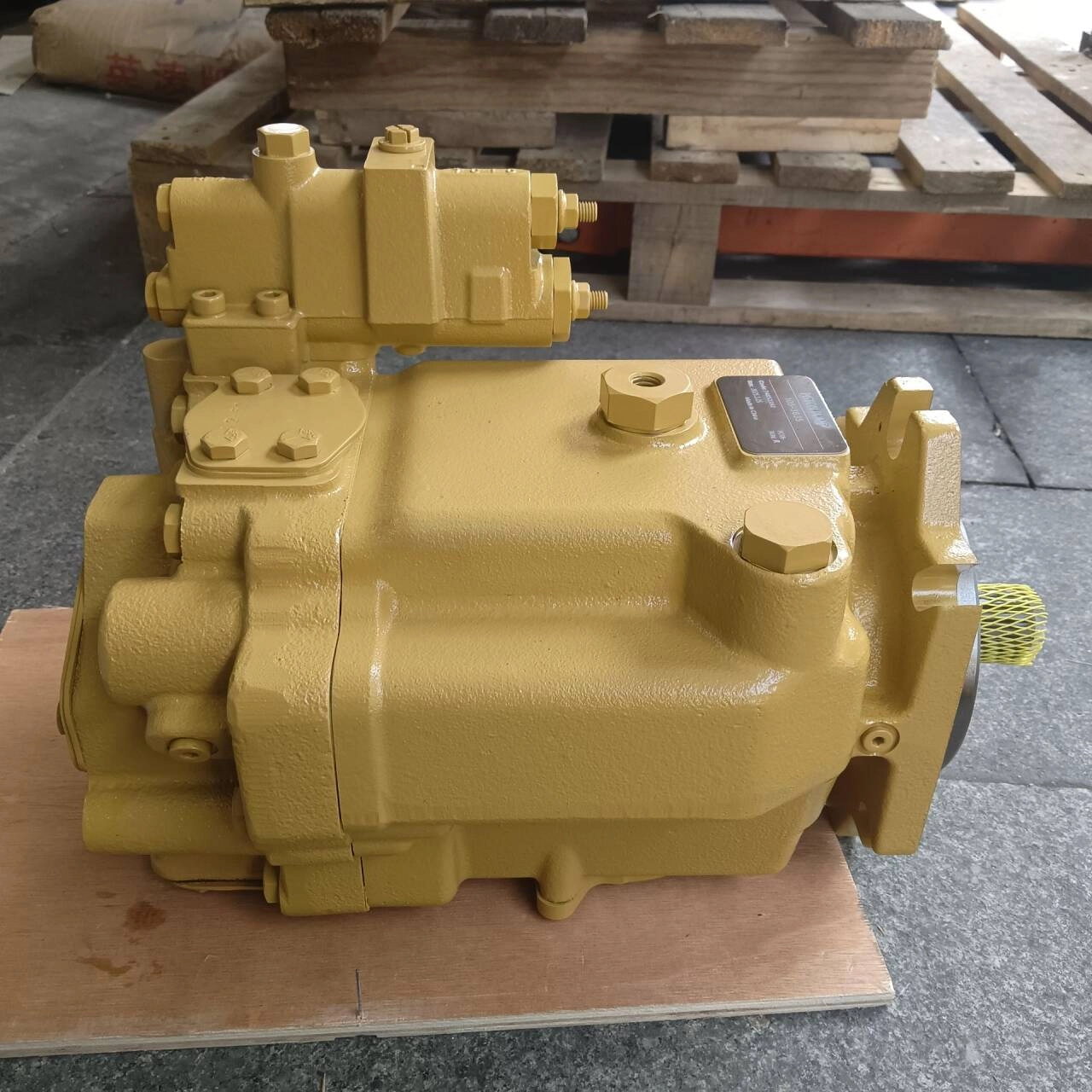

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
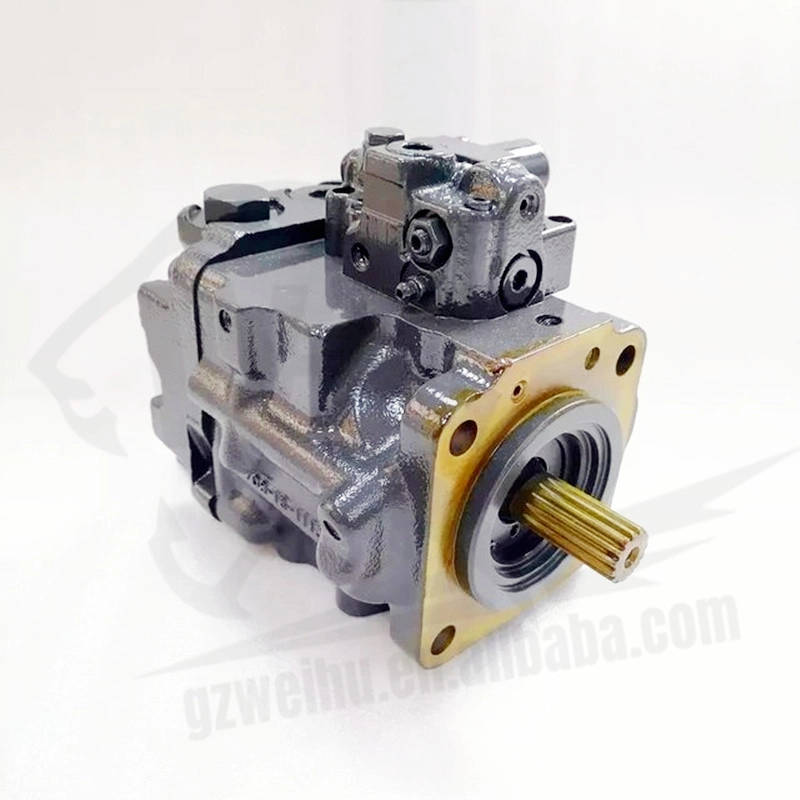

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
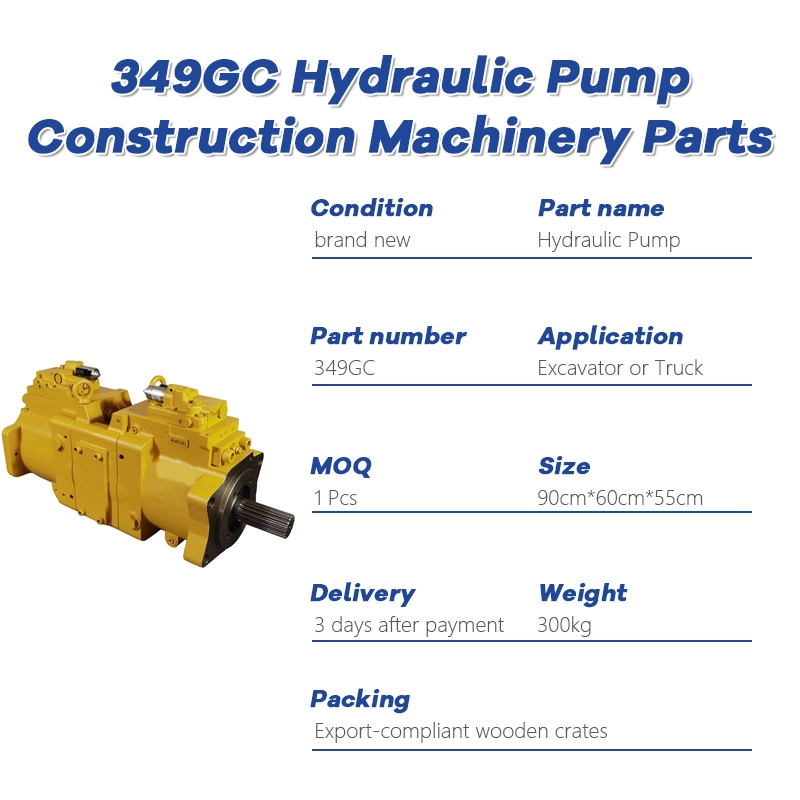
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-

