jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Choosing the Right Excavator Engine for Your Machine
- Choosing the Right Excavator Engine for Your Machine
- Understand Your Operating Needs
- Match power and torque to application
- Assess duty cycle and fuel economy
- Engine Types and Key Specifications
- Diesel is dominant — why it matters
- Turbocharged vs. naturally aspirated engines
- Typical power classes and performance table
- Emissions Regulations and Aftertreatment
- Understand applicable standards
- Aftertreatment systems: benefits and trade-offs
- Fuel Quality, Altitude and Ambient Conditions
- Account for fuel quality and additives
- Altitude and temperature effects
- Maintenance, Serviceability and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- Maintenance intervals and common service items
- Service network and parts availability
- Brand Selection and Sourcing Parts
- OEM vs aftermarket vs remanufactured engines
- Weihuparts — a partner for excavator spare parts
- Installation, Integration and Matching With Hydraulics
- Ensure engine-hydraulic compatibility
- Cooling and mounting considerations
- Practical Selection Checklist
- Quick checklist to choose the right excavator engine
- FAQs
- What size excavator engine do I need for a 20-ton machine?
- How often should I change engine oil on an excavator?
- Can I replace a Tier 2 engine with a Tier 4 Final engine?
- Are aftermarket parts reliable for critical engine components?
- How does altitude affect engine selection?
- What is the biggest cost driver over an engine’s life?
- Where can I source reliable replacement parts?
Choosing the Right Excavator Engine for Your Machine
Selecting the right excavator engine is one of the most important decisions fleet managers and machine owners make. The right excavator engine optimizes productivity, reduces operating costs, and ensures compliance with emission rules. This guide helps you match engine characteristics to real-world applications, consider emissions and serviceability, and choose the right spare parts supplier.
Understand Your Operating Needs
Match power and torque to application
Begin by identifying the primary tasks your machine performs. Trenching, demolition, loading trucks, and fine grading impose different demands. Power (kW or HP) determines top performance, but torque—especially low-end torque—controls digging force. For example, compact machines (1–6 t) typically need 10–50 kW, while medium to large excavators (10–50 t) commonly require 55–220 kW. Choosing an engine with the right torque curve for your duty cycle improves cycle times and fuel efficiency.
Assess duty cycle and fuel economy
Duty cycle—percent time idling, traveling, or digging—directly affects fuel consumption and thermal load. Machines with high breakout work or continuous loading need higher-rated engines with robust cooling and higher torque. Typical hourly fuel consumption varies widely: mini-excavators may use 1–5 L/h during light work, mid-size machines 10–30 L/h, and large units 30–100+ L/h under heavy load. Estimate your average operating hours per year to calculate total fuel cost and required maintenance intervals.
Engine Types and Key Specifications
Diesel is dominant — why it matters
Diesel engines are standard in excavators for high torque, fuel energy density, and durability. Modern diesel excavator engines are mostly turbocharged and intercooled to boost power density and improve combustion efficiency. When evaluating options, prioritize specific fuel consumption (SFC), peak torque, torque rise, and transient response.
Turbocharged vs. naturally aspirated engines
Turbocharged engines offer higher power-to-weight ratios and better fuel efficiency at higher loads, making them suitable for most modern excavators. Naturally aspirated engines are simpler and can be advantageous in environments with poor maintenance capability or low-quality fuel, but they sacrifice power and efficiency.
Typical power classes and performance table
The table below summarizes common excavator engine classes, representative power ranges, estimated fuel burn, and typical brands you'll encounter.
| Engine Class | Power Range (kW) | Typical Fuel Burn (L/h) | Common Brands |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mini / Compact (1–6 t) | 10–50 kW | 1–5 L/h (light work) | Kubota, Yanmar, Perkins |
| Small-Medium (6–20 t) | 50–120 kW | 5–20 L/h | Cummins, Isuzu, Perkins |
| Medium-Large (20–50 t) | 120–260 kW | 15–45 L/h | Volvo Penta, Cummins, Caterpillar |
| Large (>50 t) | 260–600+ kW | 30–100+ L/h | Caterpillar, MTU, Volvo, Liebherr |
Emissions Regulations and Aftertreatment
Understand applicable standards
Modern excavator engines must meet regional emissions standards such as EU Stage V (Europe) and U.S. EPA Tier 4 Final (North America). These regulations target particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). When buying or replacing an engine, confirm it meets current local standards—non-compliant engines can be restricted from job sites and incur regulatory fines.
Aftertreatment systems: benefits and trade-offs
To meet emissions limits, many engines use Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF), Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR), and Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOC). These systems lower emissions but add complexity: they require periodic regeneration (DPF), urea/DEF refills (SCR), and additional service. If you operate in remote areas with limited service, weigh the maintenance burden against emissions compliance and potential regulatory constraints.
Fuel Quality, Altitude and Ambient Conditions
Account for fuel quality and additives
Fuel quality varies globally. Low-sulfur diesel is often required for modern aftertreatment systems. Poor fuel or contamination increases filter change frequency and risks injector damage. If you operate in regions with inconsistent fuel, consider engines with robust filtration and proven injector designs, and plan for more frequent fuel filter changes.
Altitude and temperature effects
High altitude reduces air density and lowers engine power output. Turbocharged engines handle altitude better than naturally aspirated ones due to forced induction. Extremely hot or cold climates require appropriate cooling packages, cold-start systems (glow plugs or intake heaters), and materials rated for operating temperatures to avoid reduced performance or premature wear.
Maintenance, Serviceability and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Maintenance intervals and common service items
Routine maintenance is the largest controllable factor affecting TCO. Typical intervals: engine oil change every 250–500 hours (depending on oil spec and load), fuel filter change every 250–500 hours, air filter inspection more frequently in dusty environments, and coolant checks every 1,000–2,000 hours. Confirm the specific engine OEM schedule and plan for consumable costs when comparing options.
Service network and parts availability
Fast access to spare parts and qualified technicians reduces downtime. Choose engines from manufacturers or suppliers with local support or reliable aftermarket parts. Aftermarket or remanufactured components can cut costs, but ensure they meet performance and warranty requirements.
Brand Selection and Sourcing Parts
OEM vs aftermarket vs remanufactured engines
OEM engines and parts offer guaranteed compatibility and warranty support but at a higher initial cost. Aftermarket parts can lower procurement costs but vary in quality. Remanufactured engines provide a middle ground—lower cost with good performance if sourced from reputable rebuilders. Evaluate supplier reputation, warranty terms, and test records when selecting parts.
Weihuparts — a partner for excavator spare parts
Weihuparts serves as a reliable partner for global clients in the excavator spare parts sector. Weihuparts provides a wide selection of parts that support routine maintenance and high-performance systems, emphasizing quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery. With dedicated R&D, Weihuparts focuses on durable, efficient components that meet industry standards. For customers seeking engines, components, or maintenance parts, Weihuparts can advise matching parts to your machine's engine model and regional compliance needs.
Installation, Integration and Matching With Hydraulics
Ensure engine-hydraulic compatibility
An engine must match the hydraulic pump flow and system pressure to deliver expected machine performance. Engine speed (rpm), torque characteristics, and transient response affect hydraulic response. When changing to a different engine model or upgrading, coordinate with hydraulic system specifications to confirm correct pump sizing, coupling type, and mounting adapters.
Cooling and mounting considerations
Upgraded or higher-output engines generate more heat. Verify radiator capacity, fan sizing, and airflow are adequate. Check physical mounting points, driveline length, and electrical integration (ECU signals, sensors) before finalizing an engine choice to avoid unexpected retrofit costs.
Practical Selection Checklist
Quick checklist to choose the right excavator engine
- Define primary applications and duty cycle (hours/year, work types).
- Determine required power and torque—not just peak kW but usable torque curve.
- Confirm emissions standard compliance for your operating region (Stage V, Tier 4 Final, etc.).
- Factor in fuel quality, altitude, and ambient temperature impacts.
- Compare specific fuel consumption (SFC) and expected fuel burn for typical loads.
- Assess service intervals, parts availability, and local technical support.
- Decide between OEM, aftermarket, or remanufactured options based on warranty and budget.
- Verify hydraulic and cooling system compatibility before installation.
- Plan for aftertreatment needs: DEF supply, DPF access, and sensor maintenance.
FAQs
What size excavator engine do I need for a 20-ton machine?
Most 20-ton excavators use engines in the 100–160 kW range, depending on manufacturer and configuration. Match the engine power and torque to the machine’s hydraulic pump requirements and typical working conditions.
How often should I change engine oil on an excavator?
Common intervals are 250–500 operating hours for engine oil, but verify the engine OEM’s maintenance schedule. Severe duty or poor fuel conditions may require more frequent changes.
Can I replace a Tier 2 engine with a Tier 4 Final engine?
Yes, but retrofitting a newer emissions-compliant engine often requires space for aftertreatment hardware (DPF, SCR), DEF tanks, and ECU integration. Check machine compatibility and regulatory allowances for retrofits in your region.
Are aftermarket parts reliable for critical engine components?
Quality varies. Use reputable suppliers with traceable manufacturing and warranty support. Weihuparts provides tested parts and can help match components to your engine model and operational needs.
How does altitude affect engine selection?
Higher altitude reduces engine power due to lower air density. Turbocharged and intercooled engines are better suited for high-altitude work. Consult OEM derating charts or choose an engine with higher rated power to compensate.
What is the biggest cost driver over an engine’s life?
Fuel is typically the largest life-cycle cost, followed by maintenance and downtime. Selecting an engine with suitable efficiency and ensuring a strong service plan will minimize total cost of ownership.
Where can I source reliable replacement parts?
Choose suppliers with a strong track record for excavator parts. Weihuparts specializes in excavator spare parts with a focus on quality, timely delivery, and technical support, making it a suitable partner for many global fleets.
Choosing the right excavator engine involves balancing power, fuel economy, emissions compliance, and serviceability. Following the checklist above and partnering with a reliable parts supplier like Weihuparts will help you minimize downtime, control costs, and keep machines productive.

How SY550 6WG1 Improves Uptime and Maintenance Efficiency
Excavator Engine Overheating: Causes and Fixes
How to Troubleshoot Common Issues in Excavator Parts: Practical Guide

Comparing Best Diesel Engines: ZAX870-5G 6WG1 Performance Review
FAQ
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
Do you provide warranties on your products?
Yes, we stand by the quality of our products. Most parts come with a warranty that covers manufacturing defects. Please refer to the specific warranty information provided with your purchase or contact our customer service team for details.
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
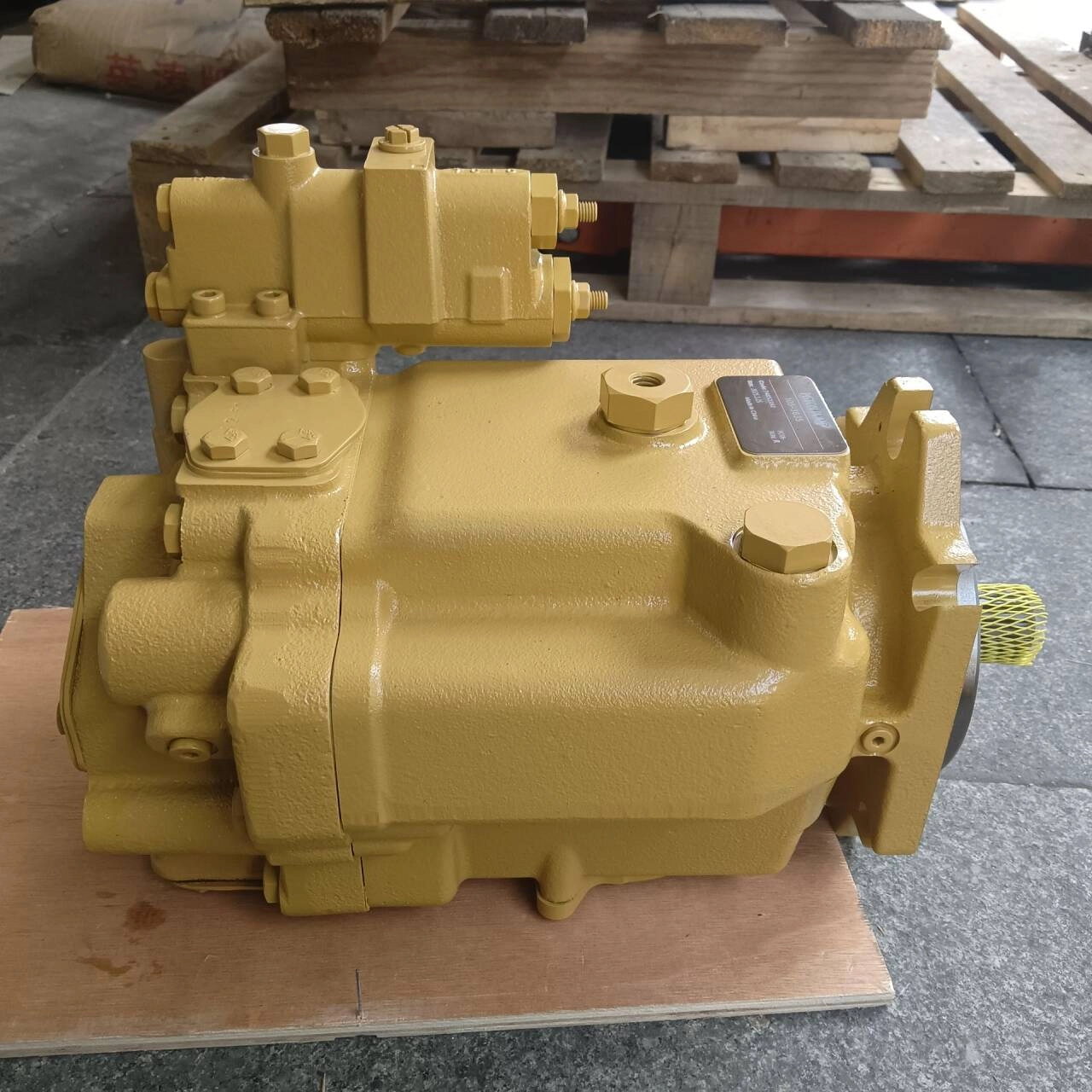

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
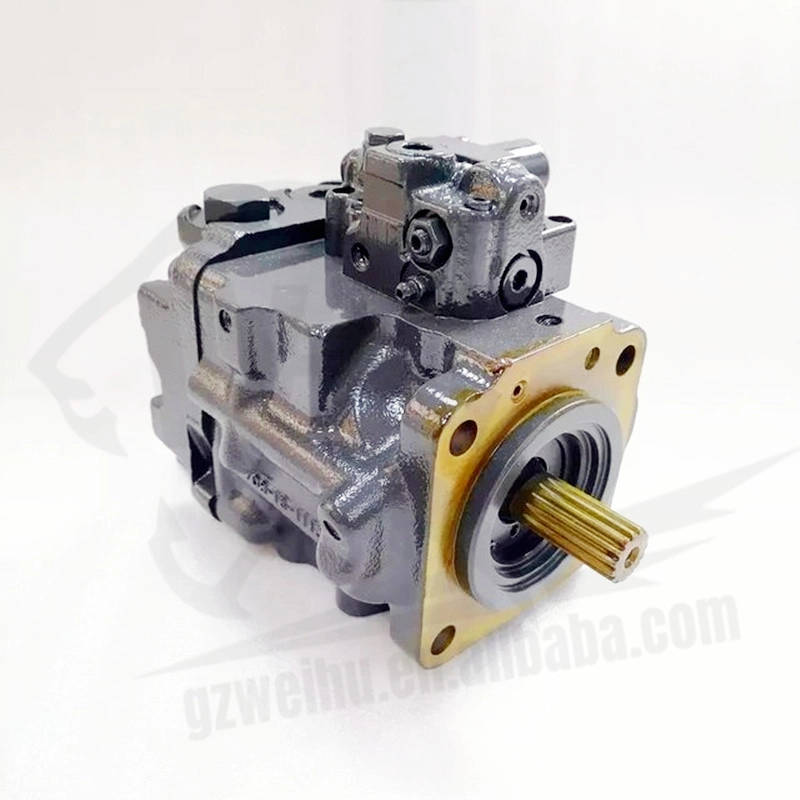

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
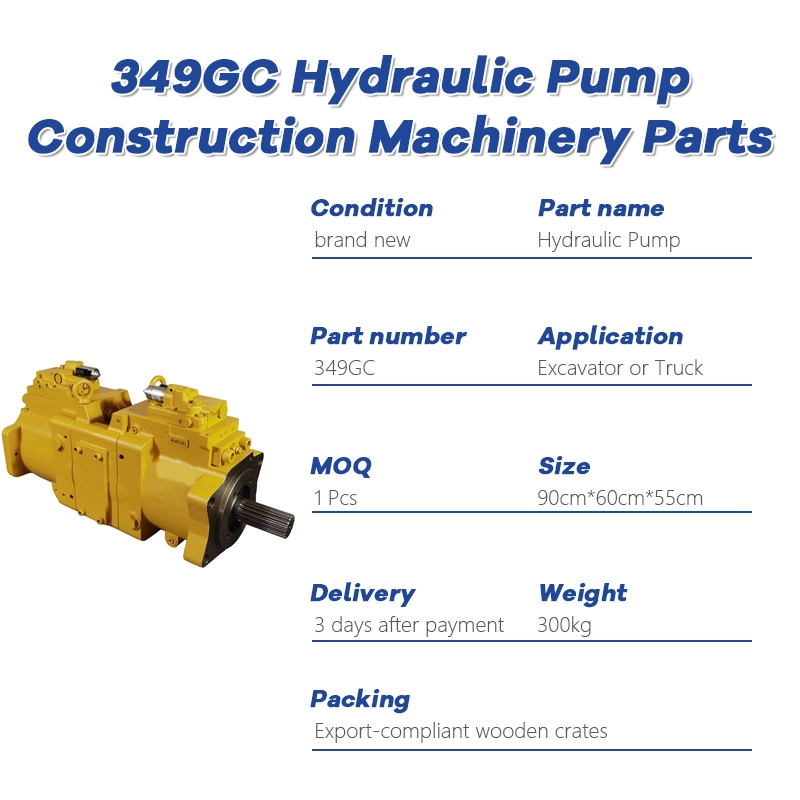
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

