jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Common Excavator Hydraulic Pump Problems and Fixes: Causes and Solutions
- Common Excavator Hydraulic Pump Problems and Fixes
- Introduction
- Common Symptoms and What They Mean
- Low Flow or Weak Boom/Arm Movement
- Pressure Loss and Inconsistent Pressure
- Overheating and High Fluid Temperatures
- Noisy Pump (Whine or Rattle)
- External Leaks and Seal Failure
- Root Causes: Why Pumps Fail
- Contamination and Fluid Degradation
- Suction Problems and Cavitation
- Mechanical Wear and Misalignment
- Thermal and Operating Stress
- Step-by-Step Diagnostics
- Visual and Operational Checks
- Pressure and Flow Testing
- Fluid Analysis and Contamination Check
- Practical Fixes and On-Site Repairs
- Immediate Remedies for Low Flow and Cavitation
- Addressing Contamination-Related Wear
- Fixing Leaks and Seal Replacements
- When to Rebuild vs Replace the Pump
- Maintenance Best Practices to Prevent Failures
- Scheduled Filter and Fluid Management
- Regular Inspection and Alignment
- Operator Training and Load Management
- Parts, Sourcing, and Why Weihuparts
- Choosing Quality Replacement Parts
- Inventory and Lead Times
- Quick Troubleshooting Table
- Symptoms, Likely Causes, and Practical Fixes
- Conclusion
- Keeping Pumps Performing and Downtime Low
- Frequently Asked Questions
Common Excavator Hydraulic Pump Problems and Fixes
Introduction
The hydraulic pump is the heart of any excavator. When it fails or underperforms, productivity drops and repair costs rise. This article on Common Excavator Hydraulic Pump Problems and Fixes explains the most frequent pump issues, how to diagnose them, practical fixes, and preventive maintenance tips. It is written to help equipment owners, service technicians, and fleet managers find fast, cost-effective solutions while considering replacement parts available from Weihuparts.
Common Symptoms and What They Mean
Low Flow or Weak Boom/Arm Movement
Low pump flow shows up as slow or weak actuator movement. Causes include internal wear, worn vanes or pistons, wrong fluid viscosity, clogged suction screens, or relief valve issues. Quick checks include fluid level and condition, suction hose collapse, and pressure readings at the pump outlet.
Pressure Loss and Inconsistent Pressure
Pressure loss may be steady or intermittent. Internal leakage (axial/radial clearance increase), relief valve misadjustment, or hose and fitting leaks are common causes. Use a calibrated pressure gauge to compare pump outlet pressure with manufacturer specifications.
Overheating and High Fluid Temperatures
Overheating shortens pump life and degrades hydraulic fluid. Causes include excessive flow through the cooling system, high ambient load, blocked oil cooler, incorrect fluid viscosity, or cavitation. Monitor operating temperature — sustained temperatures above 80°C (176°F) typically indicate trouble.
Noisy Pump (Whine or Rattle)
Noisy operation often signals cavitation (air in the system or suction restrictions), worn bearings, or misalignment. Cavitation sounds like gravel or a high-pitched whine. Stop and diagnose immediately because cavitation rapidly damages pump components.
External Leaks and Seal Failure
Visible hydraulic fluid leaks at pump seals and shaft couplings indicate seal wear, improper installation, or excessive shaft end play. Leaks reduce pressure, contaminate components, and present safety hazards. Replacing seals and addressing root causes is essential.
Root Causes: Why Pumps Fail
Contamination and Fluid Degradation
Contaminated fluid is the primary cause of hydraulic pump failure. Particulate contamination accelerates wear of pistons, gears, and valves. Water and varnish from degraded oil also reduce lubrication quality and lead to corrosion. Target hydraulic cleanliness levels based on system requirements; many heavy-equipment systems aim for ISO 4406 cleanliness codes around 18/16/13 or better.
Suction Problems and Cavitation
Cavitation results from vapor bubbles forming at the pump inlet then collapsing inside the pump. Causes include clogged suction filters, long suction lines, air leaks at fittings, low reservoir fluid level, and excessive viscosity. Cavitation produces pitting and rapid erosion on internal surfaces.
Mechanical Wear and Misalignment
Normal wear of vanes, pistons, cylinders, and bearings increases internal clearances and reduces pump efficiency. Misalignment between pump and engine or gearbox causes bearing load and premature failure. Proper mounting, coupling checks, and alignment are critical.
Thermal and Operating Stress
Operating a pump beyond recommended duty cycles or at improper temperatures accelerates material fatigue. Excessive relief valve settings, repeated shock loads, or overheating due to inadequate cooling will shorten pump life.
Step-by-Step Diagnostics
Visual and Operational Checks
Start with simple visual checks: fluid level, color and smell (burnt odor), visible leaks, loose fittings, and filter condition. Operate the machine to reproduce the symptom while observing gauges and listening for unusual noises.
Pressure and Flow Testing
Use a calibrated pressure gauge on the pump discharge and return lines. Compare measurements with OEM specifications. Low pressure with normal engine speed usually indicates internal pump wear or relief valve issues. Measure flow with inline flow meters if available to confirm pump output.
Fluid Analysis and Contamination Check
Send a hydraulic fluid sample for lab analysis (particle count, water content, viscosity, TAN/TBN). Particle counts and elemental analysis reveal wear metals and contamination sources. Fluid sampling every 250-500 operating hours is a common maintenance practice for fleets to catch issues early.
Practical Fixes and On-Site Repairs
Immediate Remedies for Low Flow and Cavitation
Check and replace clogged suction strainers and filters. Shorten suction lines if possible, ensure the reservoir fluid level is adequate, eliminate air leaks at fittings, and use the correct fluid viscosity at operating temperature. If cavitation damage has started, plan for pump overhaul or replacement.
Addressing Contamination-Related Wear
Implement a contamination-control plan: replace filters, flush or drain contaminated fluid, install breathers with desiccant or filtration, and add magnetic or high-efficiency return-line filters. For severe contamination, perform a full hydraulic system flush following OEM procedures.
Fixing Leaks and Seal Replacements
Replace worn seals and shaft bearings using quality parts. Inspect shaft couplings and mounting bolts for proper torque. Use Weihuparts replacement seals and components that meet or exceed OEM specifications to restore pump sealing and alignment.
When to Rebuild vs Replace the Pump
Rebuild when internal wear is moderate and replacement parts plus labor cost less than a new pump. Replace when cavitation pitting is extensive, bearing housings are damaged, or repair costs approach the price of a remanufactured/new pump. Weihuparts offers both replacement pumps and spare parts to support either option.
Maintenance Best Practices to Prevent Failures
Scheduled Filter and Fluid Management
Change return-line filters per OEM intervals and monitor differential pressure across filters. Implement scheduled fluid sampling and top-ups with approved hydraulic oil. Maintain breather and cooler cleanliness to reduce contamination and overheating risk.
Regular Inspection and Alignment
Inspect couplings, mounting bolts, and shaft alignment during routine maintenance windows. Check for unusual vibration or noise that may indicate bearing wear or misalignment. Tighten or replace components as necessary.
Operator Training and Load Management
Train operators to avoid continuous max-load cycles that overheat the system and to monitor dashboard indicators. Encourage staged operation and cool-down periods when working under heavy loads to extend pump life.
Parts, Sourcing, and Why Weihuparts
Choosing Quality Replacement Parts
Using high-quality replacement pump parts, seals, and filters reduces repeat failures. Weihuparts supplies a comprehensive selection of excavator spare parts designed for durability and compatibility with major excavator brands, backed by R&D and technical support.
Inventory and Lead Times
Maintain critical spare parts in inventory—seals, filters, relief valves, and common pump elements—so downtime is minimized. Weihuparts emphasizes timely delivery and cost-effective sourcing to help fleets stay productive.
Quick Troubleshooting Table
Symptoms, Likely Causes, and Practical Fixes
Use this table to match symptoms to actions for Common Excavator Hydraulic Pump Problems and Fixes.
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Recommended Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Low flow / Slow actuators | Worn pump internals, clogged suction, wrong viscosity | Check suction filter, fluid level, replace worn pump elements |
| Whining / gravel noise | Cavitation or air ingress | Inspect suction line, remove air leaks, ensure correct fluid |
| High temp / Overheating | Clogged cooler, high load, low airflow | Clean cooler, reduce duty cycle, verify fluid viscosity |
| External leaks | Seal failure, loose fittings | Replace seals, tighten fittings, check shaft play |
Conclusion
Keeping Pumps Performing and Downtime Low
Common Excavator Hydraulic Pump Problems and Fixes are usually preventable with good fluid cleanliness, correct installation, regular inspections, and prompt response to symptoms like noise or low flow. When repairs are needed, choose quality parts and follow systematic diagnostics. Weihuparts offers durable spare parts, technical guidance, and timely delivery to help keep excavators productive and reduce total cost of ownership.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly does cavitation damage a hydraulic pump?Cavitation can cause measurable erosion within a few hours under severe conditions, and significant damage within days. Stop operation on the first sign of cavitation and inspect the pump.
What hydraulic fluid viscosity should I use?Always follow the excavator OEM recommendations. Viscosity should match operating temperature ranges; using too-thin or too-thick fluid can cause cavitation or poor lubrication.
How often should I sample hydraulic fluid?Sampling every 250 to 500 operating hours is common for high-usage fleets. Increase frequency for older machines or harsh environments.
Can small leaks be left until scheduled maintenance?No. Even small leaks introduce contamination and reduce system efficiency. Repair leaks promptly to avoid larger failures.
When is a pump rebuild more economical than replacement?Rebuild when internal wear is moderate and OEM or high-quality replacement parts are available at a lower total cost than a new pump. If cavitation or structural damage is extensive, replacement is typically better.
Does Weihuparts supply complete pump assemblies?Yes. Weihuparts supplies pump components, remanufactured assemblies, and full replacement pumps to support repairs and quick returns to service.

Compatibility and Fitment: ZAX870-5G for Excavator Models
The B2B Buyer’s Guide to electric hydraulic pump

Warranty, Support and Service Options for Diesel Engine Purchases
Where to Buy excavator engine in China
FAQ
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
What types of excavator parts do you offer?
Weihuparts provides a comprehensive range of excavator parts, including but not limited to buckets, hydraulic components, undercarriage parts, and engine components. Our goal is to be your one-stop solution for all excavator needs.
Can I return or exchange parts if I change my mind?
Yes, we accept returns and exchanges within [insert return period, e.g., 30 days] of purchase. The items must be unused and in their original packaging. Please contact our customer service team to initiate a return or exchange.
How can I place an order?
You can place an order through our user-friendly online platform or by contacting our sales team directly. Simply browse our catalog, select the parts you need, and follow the checkout process to complete your order.
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
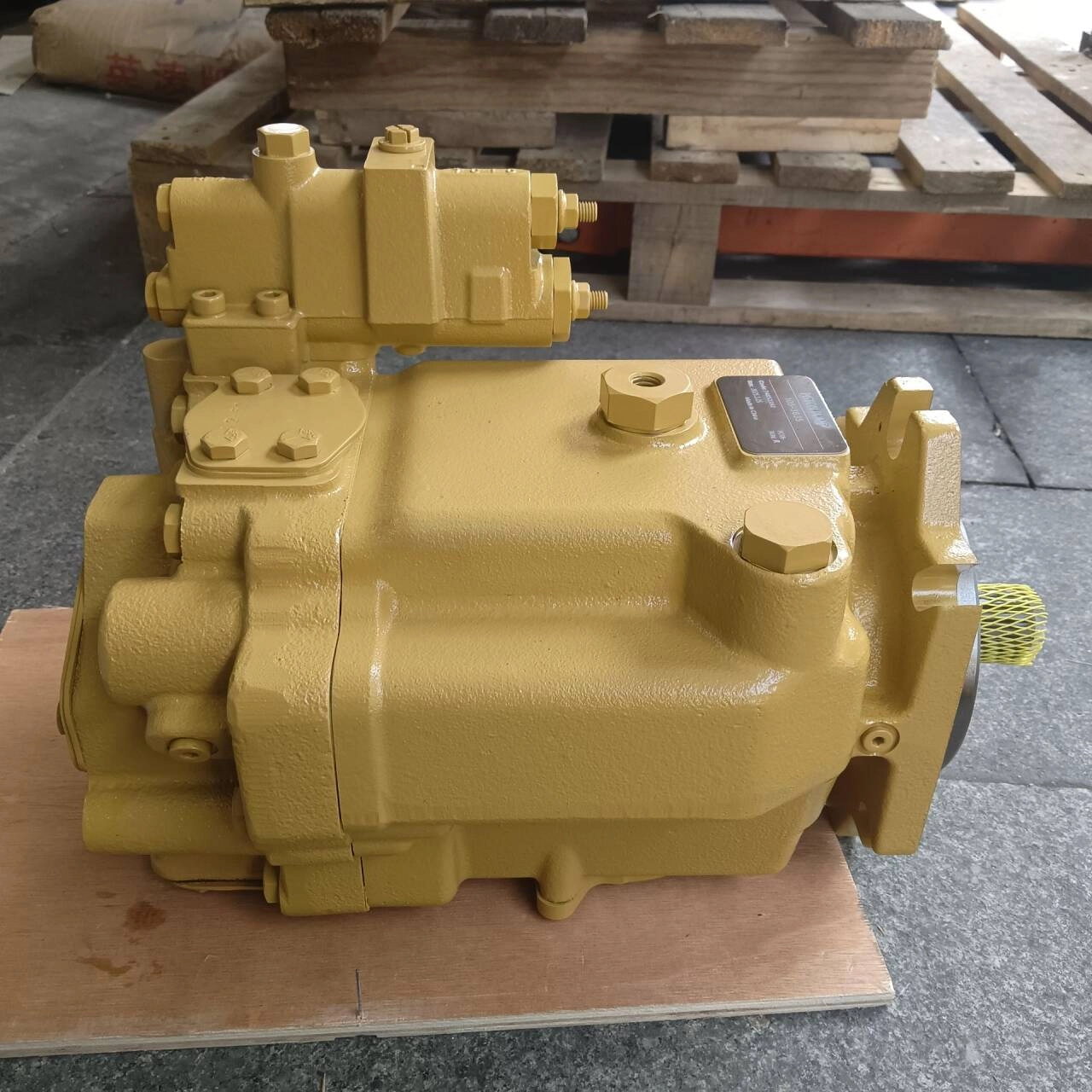

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
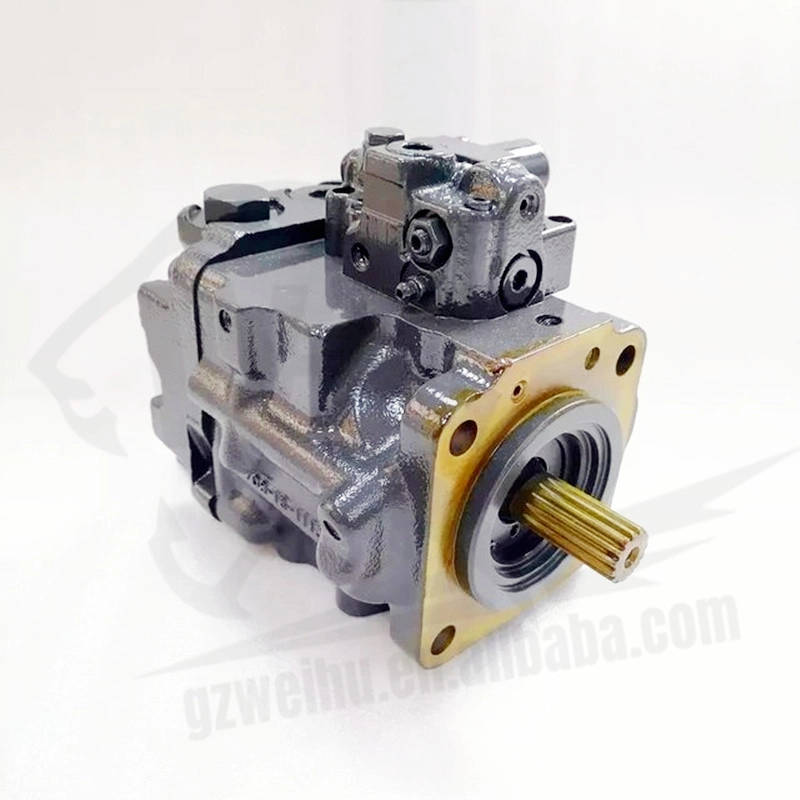

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
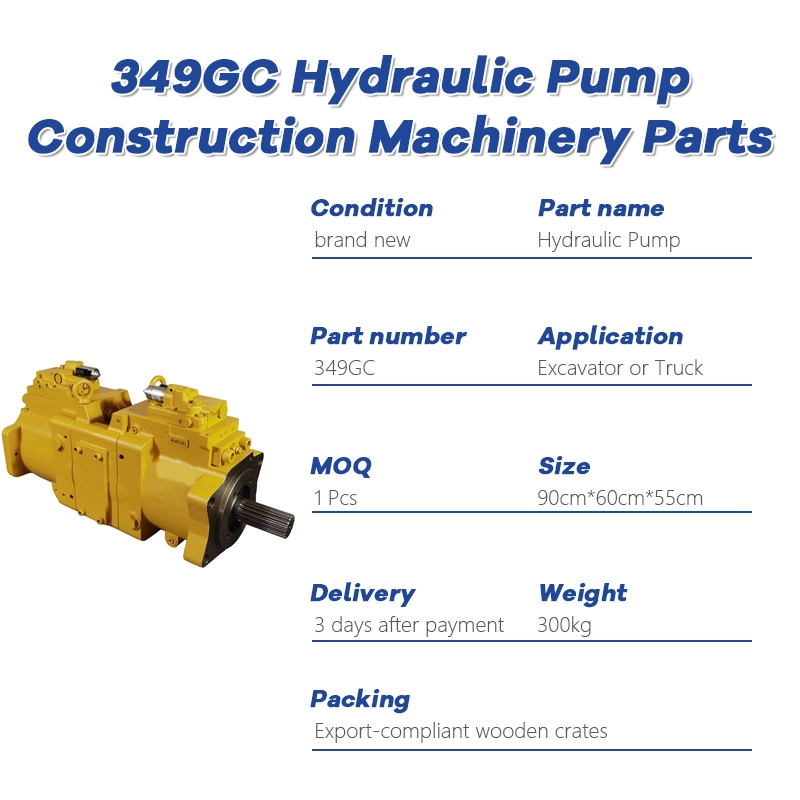
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

