jackhuang5919@gmail.com
Common Excavator Engine Problems and Solutions
- Introduction: Why Timely Excavator Engine Care Matters
- How to Use This Guide: Practical Troubleshooting Steps
- Common Problem: Engine Won't Start or Hard Starting
- Symptoms
- Typical Causes
- Solutions
- Common Problem: Overheating
- Symptoms
- Typical Causes
- Solutions
- Common Problem: Loss of Power or Poor Performance
- Symptoms
- Typical Causes
- Solutions
- Common Problem: Excessive Smoke (Black, White, or Blue)
- Identifying Smoke Types
- Causes and Actions
- Common Problem: Oil Leaks and Low Oil Pressure
- Symptoms
- Typical Causes
- Solutions
- Common Problem: Fuel System Failures (Injectors, Pumps, Filters)
- Symptoms
- Causes and Solutions
- Common Problem: Turbocharger Failures
- Symptoms
- Causes and Solutions
- Maintenance Best Practices: Proactive Steps to Avoid Engine Problems
- Recommended Service Intervals (Typical Ranges)
- Troubleshooting Checklist: Step-by-Step
- When to Replace Parts vs Repair
- Parts and Supply Considerations for Repairs
- Safety and Environmental Best Practices
- Why Choose Weihuparts for Excavator Engine Parts
- Signs It's Time to Call a Professional Technician
- FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Excavator Engine Problems
- Q1: What causes sudden loss of engine power on an excavator?
- Q2: How often should I change excavator engine oil?
- Q3: Why is my excavator emitting blue smoke?
- Q4: Can I run an excavator with a small coolant leak?
- Q5: Are aftermarket parts reliable for engine repairs?
- Q6: What basic tools help onsite troubleshooting?
- Final Recommendations and Next Steps
- Contact Weihuparts for Parts and Technical Support
Introduction: Why Timely Excavator Engine Care Matters
Excavator engine health drives machine uptime, operational safety, and project profitability. Addressing common excavator engine issues quickly reduces costly downtime, extends component life, and improves fuel efficiency. This guide helps owners, fleet managers, and technicians identify symptoms, diagnose causes, and apply effective solutions while emphasizing preventive maintenance.
How to Use This Guide: Practical Troubleshooting Steps
Start with symptoms, follow the targeted diagnostic checks below, and apply the recommended fixes. If a repair requires replacement parts, choosing quality excavator parts designed for performance and durability is critical. Weihuparts supplies a wide range of components to support repairs and preventive service.
Common Problem: Engine Won't Start or Hard Starting
Symptoms
Cranking without starting, slow cranking, or intermittent start success.
Typical Causes
Weak/old battery, corroded battery terminals, poor starter motor, clogged fuel filters, air in fuel lines, or faulty glow/plugs in diesel preheat systems.
Solutions
1) Check battery voltage (12.6V+ for healthy 12V systems or per OEM battery spec). 2) Clean/secure terminals and test cold cranking amps (CCA). 3) Inspect starter and solenoid; load-test or replace if faulty. 4) Replace clogged fuel filters and bleed air from fuel system. 5) Verify glow plug operation on cold starts. 6) If wiring or ECU codes are present, read fault codes with a diagnostic tool.
Common Problem: Overheating
Symptoms
High coolant temperature gauge, steam or boiling coolant, reduced power, or automatic engine derate.
Typical Causes
Low coolant level, blocked radiator, failed water pump, thermostat stuck closed, collapsed coolant hose, dirty charge-air cooler, or high ambient load conditions.
Solutions
1) Safely check coolant level and top with OEM-recommended coolant mix. 2) Inspect radiator and coolers for debris; clean fins and remove buildup. 3) Test thermostat and water pump; replace failed units. 4) Verify fan clutch/fan drive operation (hydraulic or viscous). 5) Check for coolant leaks (hoses, clamps, head gasket). 6) Under sustained heavy load, reduce duty cycle and restore cooling systems before returning to full operation.
Common Problem: Loss of Power or Poor Performance
Symptoms
Low engine RPM under load, slow boom or bucket movement, frequent engine derates, or limp mode.
Typical Causes
Clogged air filter, restricted exhaust, fuel system faults (injectors, filters), turbocharger faults, or electronic sensor issues (MAP, MAF, or fuel pressure sensors).
Solutions
1) Inspect and replace air filters; many sites require daily visual checks and element changes every 500–1,000 hours depending on conditions. 2) Inspect exhaust for restrictions; check soot trap/DOC/DPF where fitted and follow regeneration procedures. 3) Service fuel system: replace fuel filters and test injectors. 4) Test turbocharger for boost pressure and shaft play; rebuild or replace if failed. 5) Read engine fault codes and address sensor failures promptly.
Common Problem: Excessive Smoke (Black, White, or Blue)
Identifying Smoke Types
Black smoke indicates rich combustion/fuel delivery issues. White smoke may signal unburned fuel (cold start or injector leak) or coolant ingress. Blue smoke points to oil burning due to worn rings, valve guides, or turbo seals.
Causes and Actions
1) Black smoke: Check air intake, turbo, and fuel system calibration. Replace dirty air elements and verify fuel pressure. 2) White smoke: Inspect injector sealing, check for coolant in combustion (head gasket) and warranty/repair as necessary. 3) Blue smoke: Perform compression test, inspect piston rings and valve guides, and check turbocharger seals. Use correct oil viscosity and maintain crankcase ventilation.
Common Problem: Oil Leaks and Low Oil Pressure
Symptoms
Visible oil on engine surfaces, dropping oil level, low oil pressure light or gauge reading.
Typical Causes
Worn seals/gaskets, loose drain plugs/filters, cracked oil cooler lines, failed oil pump, or degraded oil quality.
Solutions
1) Find leak source—use UV dye or clean-and-run to trace. 2) Replace gaskets, seals, and worn hoses. 3) Replace oil filter and perform oil change with OEM-spec oil. 4) If low oil pressure persists, test pump and bearings; repair or rebuild as needed. 5) Follow scheduled oil analysis for large fleets to catch wear early.
Common Problem: Fuel System Failures (Injectors, Pumps, Filters)
Symptoms
Misfires, rough idle, loss of power, smoke, and fuel smell.
Causes and Solutions
1) Replace fuel filters at recommended intervals—many OEMs suggest 250 hours as a common starting point, shorter in contaminated environments. 2) Test and clean or replace injectors; use ultrasonic cleaning for moderate deposits. 3) Inspect high-pressure fuel pump for leaks, pressure loss, or internal wear and replace if necessary. 4) Use clean fuel and maintain water separators to prevent microbial growth and contamination.
Common Problem: Turbocharger Failures
Symptoms
Loss of boost, loud whine or grinding, excessive smoke, or oil consumption.
Causes and Solutions
1) Contaminated air or oil feeds cause bearing wear—ensure air filters are intact and oil change intervals are maintained. 2) Inspect turbo shaft for play and damage. 3) Replace failed turbochargers with correctly specified units and follow proper oil priming procedures. 4) Address root cause (air leaks, oil contamination) before installing a new turbo to avoid repeat failure.
Maintenance Best Practices: Proactive Steps to Avoid Engine Problems
Regular inspection and service reduce most common failures. Key items: daily visual checks, scheduled oil/filter changes, air filter servicing, coolant system checks, fuel system maintenance, and routine diagnostic scans. Train operators to report changes in sound, performance, or exhaust.
Recommended Service Intervals (Typical Ranges)
Below is a practical comparison of common maintenance items and typical service intervals. Always follow the equipment OEM manual for exact schedules.
| Component | Typical Inspection Interval | Typical Replacement/Service Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Engine oil & oil filter | Every 50–250 hours (visual/level) | Every 250–500 hours (depends on oil type & load) |
| Fuel filters / water separators | Every 50–250 hours (inspect) | Every 250 hours (or sooner if contaminated) |
| Air cleaner elements | Daily visual; every 50–200 hours (inspect) | 500–1,000 hours for primary element; service more in dusty sites |
| Coolant & cooling system | Every 100–250 hours (check level & hoses) | Coolant replacement typically every 2,000–4,000 hours per OEM |
| Battery | Monthly (visual & connections) | 2–5 years depending on environment and usage |
Troubleshooting Checklist: Step-by-Step
1) Record exact symptom and context (load, temperature, recent service). 2) Check fluids (oil, coolant, fuel). 3) Inspect filters and intakes visually. 4) Scan engine ECU for error codes. 5) Test battery and starter if starting issues. 6) Check for leaks or loose/clogged lines. 7) Replace consumables (filters, fluids) before deeper component swap where reasonable. 8) If problem persists, escalate to component-level testing (compression, fuel pressure, turbo boost).
When to Replace Parts vs Repair
Replace consumables (filters, hoses, belts) on schedule. Repair vs replace decision for major components (injectors, turbo, water pump) should be based on: diagnostic test results, repair cost vs replacement cost, machine downtime criticality, part warranty, and availability. Using quality aftermarket excavator parts from reputable suppliers such as Weihuparts can balance cost with reliability.
Parts and Supply Considerations for Repairs
Select parts that meet OEM specifications—filters, gaskets, sensors, injectors, and turbochargers. Keep critical spares on hand for high-use fleets to minimize downtime. Weihuparts emphasizes R&D and quality control to provide durable parts, timely delivery, and technical support for correct fitment.
Safety and Environmental Best Practices
Always perform maintenance with the engine cool, battery isolated, and in a safe work area. Dispose of used oil, coolant, and filters through approved recycling channels. Use OEM or approved replacement fluids to avoid corrosion or catalytic damage.
Why Choose Weihuparts for Excavator Engine Parts
Weihuparts serves global customers with an extensive catalog of excavator parts. The company focuses on quality, cost-effectiveness, and on-time delivery. Backed by a technical team that emphasizes R&D, Weihuparts can help source correct parts—filters, gaskets, injectors, turbochargers, sensors—for both routine service and major repairs. Partnering with a reliable supplier reduces the risk of incorrect parts and helps keep your excavator engine running smoothly.
Signs It's Time to Call a Professional Technician
If troubleshooting lists (filters, fluids, simple repairs) do not restore performance, or if you observe severe symptoms—metallic debris in oil, persistent low compression, major coolant loss, or catastrophic turbo damage—engage a certified technician. Complex diagnostics often require specialized tools, calibration, and experience to avoid repeat failures.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Excavator Engine Problems
Q1: What causes sudden loss of engine power on an excavator?
A1: Sudden loss of power commonly results from clogged air or fuel filters, turbocharger failure, fuel supply interruptions, or engine derate due to fault codes. Start with filters and fault codes, then inspect turbo and fuel system.
Q2: How often should I change excavator engine oil?
A2: Typical intervals range from 250 to 500 hours depending on duty cycle, oil type, and OEM guidelines. Inspect oil frequently and follow manufacturer recommendations for your model.
Q3: Why is my excavator emitting blue smoke?
A3: Blue smoke indicates oil burning—often caused by worn piston rings, valve seals, or turbocharger oil seal problems. Perform a compression test and inspect the turbo before deciding on repairs.
Q4: Can I run an excavator with a small coolant leak?
A4: Running with any coolant leak risks overheating and engine damage. Make temporary repairs if immediate downtime is impossible, but schedule a permanent fix promptly.
Q5: Are aftermarket parts reliable for engine repairs?
A5: High-quality aftermarket parts that meet OEM specifications can be reliable and cost-effective. Choose suppliers with solid R&D, quality control, and clear fitment information—like Weihuparts—to ensure compatibility and performance.
Q6: What basic tools help onsite troubleshooting?
A6: A good multimeter, fuel pressure gauge, compression gauge, diagnostic code reader, boost gauge, and basic hand tools are essential for common excavator engine troubleshooting.
Final Recommendations and Next Steps
Regular inspections, timely replacement of consumables, and immediate attention to unusual symptoms are the best defenses against costly excavator engine failures. Keep a log of maintenance, invest in a few spare parts for critical failures, and partner with a trusted supplier for quality excavator parts and technical support.
Contact Weihuparts for Parts and Technical Support
For quality replacement parts and technical assistance tailored to excavator engines, visit Weihuparts or contact our team. We provide parts, troubleshooting guidance, and support to keep your fleet productive and compliant with OEM standards.

Hydraulic Pump Part Numbers and Identification Tips

Compatibility Guide: Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Fitment

Comparing OEM engine assemblies vs aftermarket options
Diesel vs Gas Excavator Engines: Pros and Cons
FAQ
What is your shipping policy?
We offer a variety of shipping options to meet your needs. Orders are typically processed within [insert processing time] days, and delivery times may vary based on your location. We will provide you with tracking information once your order has shipped.
Do you provide installation services for your parts?
While we do not offer installation services directly, we can recommend qualified professionals or resources to assist you with the installation of our parts. Our customer support team can provide guidance on finding local service providers.
Do you offer bulk purchasing options?
Yes, we offer competitive pricing for bulk orders. If you are interested in purchasing large quantities of parts, please contact our sales team to discuss your requirements and receive a customized quote.
Do you provide warranties on your products?
Yes, we stand by the quality of our products. Most parts come with a warranty that covers manufacturing defects. Please refer to the specific warranty information provided with your purchase or contact our customer service team for details.
How do I know which parts I need for my excavator?
If you are unsure which parts are needed, our knowledgeable customer support team can assist you. You can provide us with your excavator model and any relevant details, and we will help you identify the correct parts.

336D Excavator Hydraulic Pump | Heavy Duty CAT Replacement
This CAT 336D hydraulic pump is built for power, durability, and optimal performance. It is designed to fit Caterpillar 336D excavators and is available in both OEM and high-quality aftermarket versions. Whether you're replacing a damaged pump or upgrading your hydraulic system, this part ensures long-lasting and reliable operation in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 336D excavators
-
✔️ Available in OEM or premium aftermarket
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty operations
-
✔️ Smooth and efficient hydraulic flow
-
✔️ Rigorously tested for quality and durability
-
✔️ Global shipping and responsive support
-
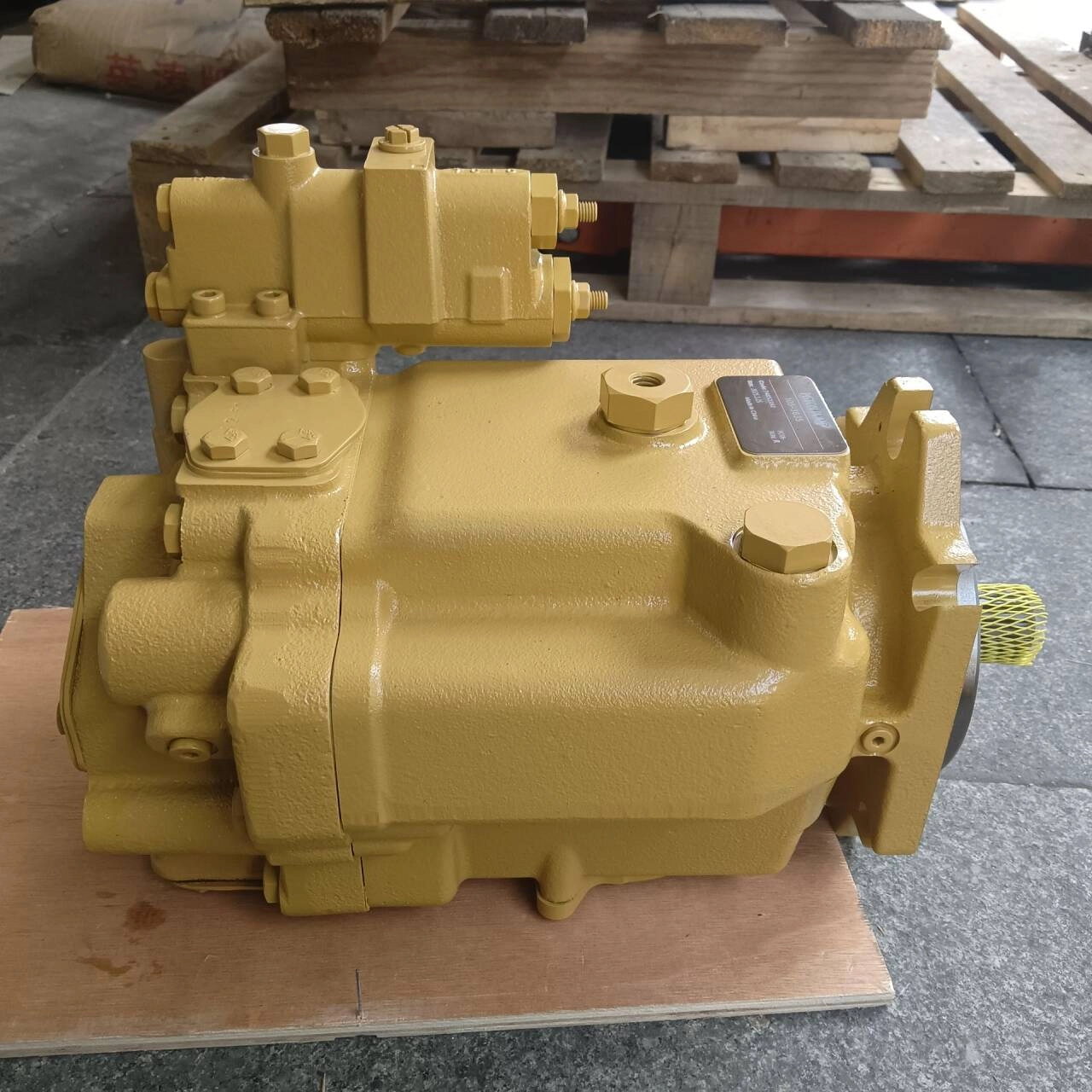

CAT 980H Hydraulic Pump | Heavy-Duty Loader Replacement Part
The CAT 980H and 980G hydraulic pumps are engineered to provide optimal hydraulic power and durability for Caterpillar loaders. Built with premium materials and precision manufacturing, these pumps are ideal for OEM replacements and high-quality aftermarket upgrades. They ensure smooth hydraulic operation and reliable performance in demanding construction environments.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 980H and 980G loaders
-
✔️ Available in OEM and aftermarket versions
-
✔️ High-pressure, heavy-duty hydraulic performance
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for durability and efficiency
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and excellent customer support
- 🛒 Order your CAT 980H & 980G Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk orders, technical support, or custom requests.
📦 Fast worldwide shipping | OEM & aftermarket options available -
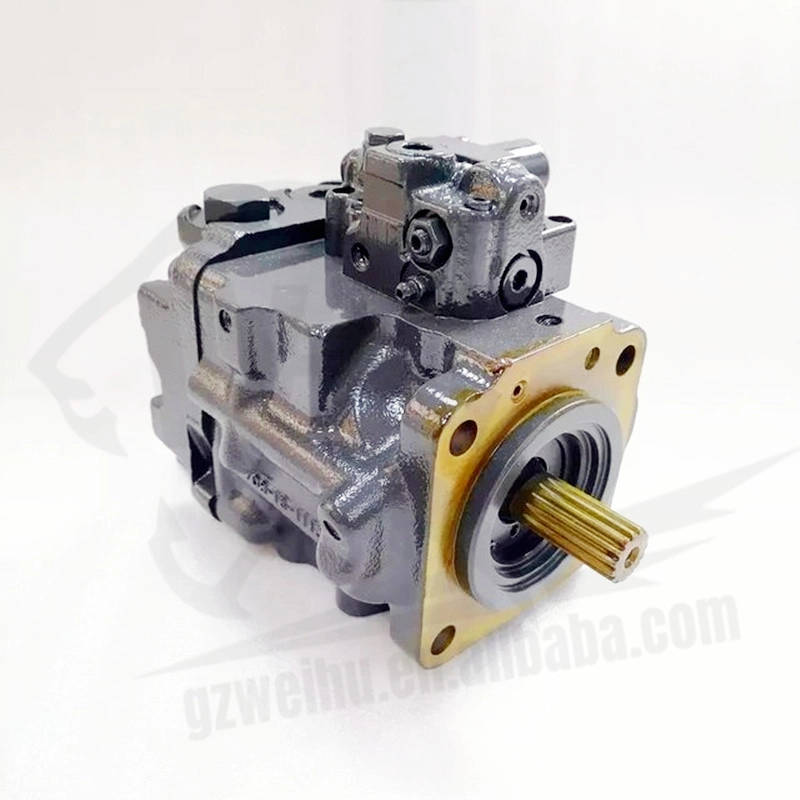

Doosan DX65 Excavator Hydraulic Pump | High-Performance Main Pump
The DX65 hydraulic pump is designed for Doosan DX65 mini excavators, delivering reliable and consistent hydraulic power for smooth machine operation. Whether you're replacing a worn pump or upgrading for enhanced performance, our OEM and aftermarket DX65 pumps offer durability, compatibility, and affordability. Each pump is manufactured using high-quality materials and precision engineering, ensuring long service life and reduced downtime.
-
✔️ 100% fit for Doosan DX65 excavators
-
✔️ Axial piston pump – compact and powerful
-
✔️ OEM & high-quality aftermarket versions available
-
✔️ Tested for pressure, performance & fluid consistency
-
✔️ Precision-sealed with robust alloy components
-
✔️ Global shipping with safe wooden packaging
- 🚜 Order Your Doosan DX65 Hydraulic Pump Today – Performance You Can Trust
📞 Contact Us for stock availability, bulk pricing, or compatibility check
🌍 Fast Global Shipping | OEM & Aftermarket | Secure Payment Options -
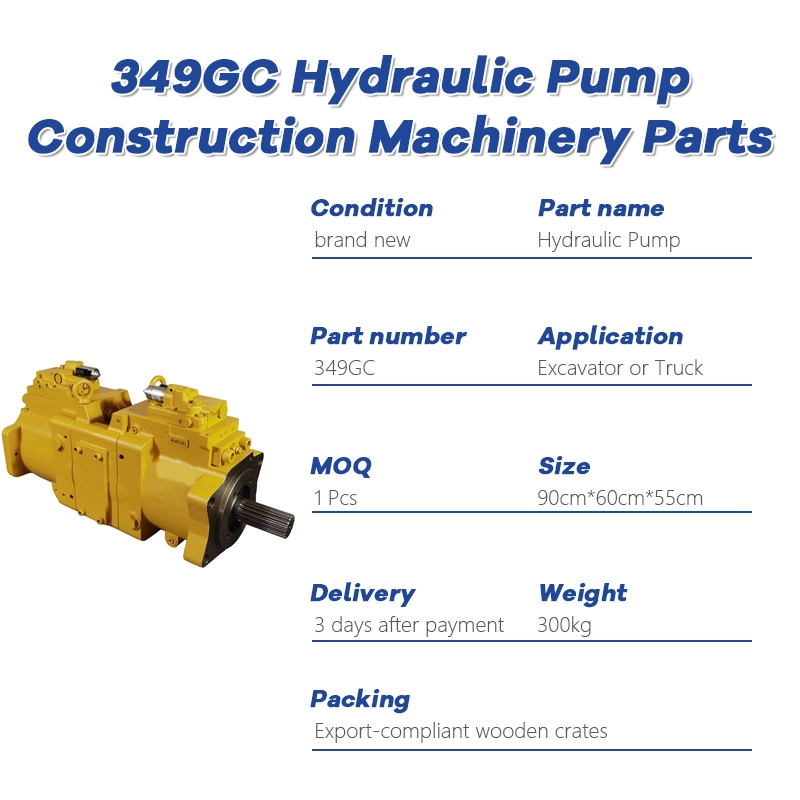
Hydraulic Pump for CAT 349GC | Reliable Performance, Fast Shipping
The CAT 349GC hydraulic pump is engineered to deliver efficient and reliable hydraulic power for Caterpillar 349GC excavators. Manufactured using premium materials and precision engineering, this pump is suitable for OEM replacement or high-quality aftermarket upgrades. It ensures smooth hydraulic flow, durability, and optimal performance even in the most demanding working conditions.
-
✔️ Direct fit for CAT 349GC excavators
-
✔️ OEM and aftermarket options available
-
✔️ High-pressure performance for heavy-duty applications
-
✔️ Manufactured with high-strength alloys and quality seals
-
✔️ Tested for reliability and longevity
-
✔️ Fast global shipping and responsive customer support
- 🚜 Order your CAT 349GC Hydraulic Pump now!
📞 Contact us for bulk pricing, customization, and technical support.
📦 Worldwide shipping available. OEM & aftermarket options.

